SARS-CoV-2 genomic diversity and the implications for qRT-PCR diagnostics and transmission
- PMID: 33602693
- PMCID: PMC8015855
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.268961.120
SARS-CoV-2 genomic diversity and the implications for qRT-PCR diagnostics and transmission
Abstract
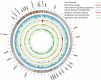
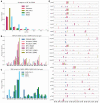
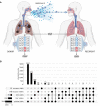
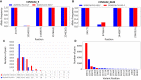
The COVID-19 pandemic has sparked an urgent need to uncover the underlying biology of this devastating disease. Though RNA viruses mutate more rapidly than DNA viruses, there are a relatively small number of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that differentiate the main SARS-CoV-2 lineages that have spread throughout the world. In this study, we investigated 129 RNA-seq data sets and 6928 consensus genomes to contrast the intra-host and inter-host diversity of SARS-CoV-2. Our analyses yielded three major observations. First, the mutational profile of SARS-CoV-2 highlights intra-host single nucleotide variant (iSNV) and SNP similarity, albeit with differences in C > U changes. Second, iSNV and SNP patterns in SARS-CoV-2 are more similar to MERS-CoV than SARS-CoV-1. Third, a significant fraction of insertions and deletions contribute to the genetic diversity of SARS-CoV-2. Altogether, our findings provide insight into SARS-CoV-2 genomic diversity, inform the design of detection tests, and highlight the potential of iSNVs for tracking the transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 Sapoval et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Update of
-
Hidden genomic diversity of SARS-CoV-2: implications for qRT-PCR diagnostics and transmission.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 2:2020.07.02.184481. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.02.184481. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Genome Res. 2021 Apr;31(4):635-644. doi: 10.1101/gr.268961.120. PMID: 32637955 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Butler D, Mozsary C, Meydan C, Foox J, Rosiene J, Shaiber A, Danko D, Afshinnekoo E, MacKay M, Sedlazeck FJ, et al. 2021. Shotgun transcriptome, spatial omics, and isothermal profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals unique host responses, viral diversification, and drug interactions. Nat Commun 12: 1660. 10.1038/s41467-021-21361-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
