Nonselective cation permeation in an AMPA-type glutamate receptor
- PMID: 33602810
- PMCID: PMC7923540
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2012843118
Nonselective cation permeation in an AMPA-type glutamate receptor
Abstract
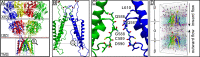
Fast excitatory synaptic transmission in the central nervous system relies on the AMPA-type glutamate receptor (AMPAR). This receptor incorporates a nonselective cation channel, which is opened by the binding of glutamate. Although the open pore structure has recently became available from cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM), the molecular mechanisms governing cation permeability in AMPA receptors are not understood. Here, we combined microsecond molecular dynamic (MD) simulations on a putative open-state structure of GluA2 with electrophysiology on cloned channels to elucidate ion permeation mechanisms. Na+, K+, and Cs+ permeated at physiological rates, consistent with a structure that represents a true open state. A single major ion binding site for Na+ and K+ in the pore represents the simplest selectivity filter (SF) structure for any tetrameric cation channel of known structure. The minimal SF comprised only Q586 and Q587, and other residues on the cytoplasmic side formed a water-filled cavity with a cone shape that lacked major interactions with ions. We observed that Cl- readily enters the upper pore, explaining anion permeation in the RNA-edited (Q586R) form of GluA2. A permissive architecture of the SF accommodated different alkali metals in distinct solvation states to allow rapid, nonselective cation permeation and copermeation by water. Simulations suggested Cs+ uses two equally populated ion binding sites in the filter, and we confirmed with electrophysiology of GluA2 that Cs+ is slightly more permeant than Na+, consistent with serial binding sites preferentially driving selectivity.
Keywords: electrophysiology; ion channel; molecular dynamics; neurotransmitter.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures





References
-
- Sommer B., Köhler M., Sprengel R., Seeburg P. H., RNA editing in brain controls a determinant of ion flow in glutamate-gated channels. Cell 67, 11–19 (1991). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

