SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors with antiviral activity in a transgenic mouse model
- PMID: 33602867
- PMCID: PMC8099175
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abf1611
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors with antiviral activity in a transgenic mouse model
Abstract
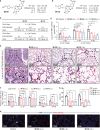
The COVID-19 pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) continually poses serious threats to global public health. The main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 plays a central role in viral replication. We designed and synthesized 32 new bicycloproline-containing Mpro inhibitors derived from either boceprevir or telaprevir, both of which are approved antivirals. All compounds inhibited SARS-CoV-2 Mpro activity in vitro, with 50% inhibitory concentration values ranging from 7.6 to 748.5 nM. The cocrystal structure of Mpro in complex with MI-23, one of the most potent compounds, revealed its interaction mode. Two compounds (MI-09 and MI-30) showed excellent antiviral activity in cell-based assays. In a transgenic mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 infection, oral or intraperitoneal treatment with MI-09 or MI-30 significantly reduced lung viral loads and lung lesions. Both also displayed good pharmacokinetic properties and safety in rats.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
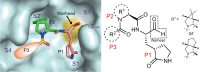
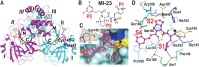

Comment in
-
Newly synthesized Mpro inhibitors as potential oral anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Mar 31;6(1):138. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00560-0. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 33790219 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Identification of proteasome and caspase inhibitors targeting SARS-CoV-2 Mpro.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Jun 1;6(1):214. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00639-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021. PMID: 34075025 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.-R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.-L., Chen H.-D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.-D., Liu M.-Q., Chen Y., Shen X.-R., Wang X., Zheng X.-S., Zhao K., Chen Q.-J., Deng F., Liu L.-L., Yan B., Zhan F.-X., Wang Y.-Y., Xiao G.-F., Shi Z.-L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579, 270–273 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu F., Zhao S., Yu B., Chen Y.-M., Wang W., Song Z.-G., Hu Y., Tao Z.-W., Tian J.-H., Pei Y.-Y., Yuan M.-L., Zhang Y.-L., Dai F.-H., Liu Y., Wang Q.-M., Zheng J.-J., Xu L., Holmes E. C., Zhang Y.-Z., A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 579, 265–269 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

