The Economic Burden of Abortion and Its Complication Treatment Cares: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 33603795
- PMCID: PMC7865195
- DOI: 10.18502/jfrh.v14i2.4354
The Economic Burden of Abortion and Its Complication Treatment Cares: A Systematic Review
Abstract
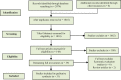
Objective: Abortion related procedures contribute to a significant economic burden because it resulted in prolonged hospital stays for patients. We aimed to gather available evidence on the economic burden of abortion and post-abortion complication treatment cares worldwide. Materials and methods: PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and Embase databases were searched through November 2019. Two researchers independently conducted the quality assessment and data extraction process. The latest web-based tool adjusted the estimates of costs expressed in one specific currency and price year into a specific target currency (the year 2016 $US). Results: Totally, 2082 records were retrieved and 32 studies were deemed eligible for qualitative synthesis. The mean total costs per patient with abortion or post-abortion care ranged from $23 to $564. The annual costs ranged from 189,000 $US to 134 million $US. Conclusion: Abortion and post-abortion care impose a substantial economic burden on society. Understanding the burdensome of abortion or pregnancy termination among policymakers provides vital information and enables informed decisions to be made to establish health care priorities and allocating scarce resources.
Keywords: Abortion; Cost of Illness; Economic Burden of Disease; Miscarriage; Review.
Copyright © Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Cahill N, Sonneveldt E, Stover J, Weinberger M, Williamson J, Wei C, et al. A Probabilistic Assessment of Trends in Modern Contraceptive Prevalence, Unmet Need for and Demand Satisfied with Modern methods in the Countries of the FP2020 initiative 2018
-
- Wulf D. Sharing responsibility: women society and abortion worldwide. New York: The Alan Guttmacher Institute; 1999.
-
- Vlassoff M, Shearer J, Walker D, Lucas H. Economic impact of unsafe abortion-related morbidity and mortality: evidence and estimation challenges. UK: Institute of Development Studies BrightonBN1 9RE; 2008.
-
- Calhoun BC. Book Review: Complications: Abortion’s Impact on Women. Linacre Q. 2018;85:178–9.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources