Lifestyle and Comorbidities: Do We Take Enough Care of Preconception Health in Assisted Reproduction?
- PMID: 33603806
- PMCID: PMC7868650
- DOI: 10.18502/jfrh.v14i3.4667
Lifestyle and Comorbidities: Do We Take Enough Care of Preconception Health in Assisted Reproduction?
Abstract
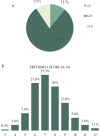
Objective: The preconception period is largely neglected, whereas it represents an opportunity to identify and modify clinical and behavioral risks, particularly in infertile women characterized by an unfavorable vascular burden. The present study was performed to strengthen previous findings and to increase the awareness of clinicians who should envision a broader preconception approach in infertile women, beyond their reproductive health. Materials and methods: In this cross-sectional study, we investigated 1003 Caucasian women, referred to the Internal Medicine Clinic at the Assisted Reproductive Technologies Center, Florence. Results: A high prevalence of dyslipidemia (57.4%), overweight/obesity (29.1%) and, smoking habit (26.6%) were found. We provided evidence of unhealthy lifestyle habits, represented by a closer adherence to the Mediterranean diet in the 9.5% only and by a sedentary behavior in 73%. A significant correlation between the Mediterranean Diet score and both anthropometric and metabolic parameters was found. We also observed a lower score adherence with both metabolic syndrome and diabetes (for both p=0.02), but not with hypertension. Conclusion: Before infertility treatment, the correction and the management of modifiable and non-modifiable cardiovascular risk factors are mandatory and represent the main goal for a safe pregnancy, and lifetime women's health.
Keywords: Assisted Reproduction; Cardiovascular Prevention; Lifestyle; Preconception Care; Pregnancy Planning; Women’s Health.
Copyright © 2020 Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Policy Brief. Preconception care: Maximizing the gains for maternal and child health. 2013. pp. 1–8.
-
- Karayiannis D, Kontogianni MD, Mendorou C, Mastrominas M, Yiannakouris N. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and IVF success rate among non-obese women attempting fertility. Hum Reprod. 2018;33:494–502. - PubMed
-
- Assaf-Balut C, García de la Torre N, Durán A, et al. A Mediterranean diet with additional extra virgin olive oil and pistachios reduces the incidence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM): A randomized controlled trial: The St. Carlos GDM prevention study. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0185873. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
