MicroRNA-489-3p plays a significant role in congenital hypothyroidism through regulating neuronal cell apoptosis via targeting translationally controlled tumor protein 1
- PMID: 33603838
- PMCID: PMC7851619
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.9660
MicroRNA-489-3p plays a significant role in congenital hypothyroidism through regulating neuronal cell apoptosis via targeting translationally controlled tumor protein 1
Abstract
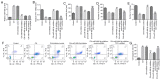
Accumulating reports have indicated that congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is an endocrine disorder caused by underdeveloped thyroid gland or thyroid dyshormonogenesis. It has been also reported that certain microRNAs (miRNAs) may exert protective effects against the development of CH. However, whether miR-489-3p regulates CH progression remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of miR-489-3p on CH and elucidate the underlying mechanisms. Therefore, Sprague Dawley rats were injected with propylthiouracil (50 mg/day) to establish a CH model. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) assay demonstrated that miR-489-3p was upregulated in the hippocampal tissues of CH rats. Furthermore, the TargetScan software was employed to predict the target gene of miR-489-3p, and a dual luciferase reporter assay revealed that translationally controlled tumor protein 1 (TPT1) was directly targeted by miR-489-3p. Additionally, RT-qPCR and western blot assays suggested that TPT1 was markedly downregulated in the hippocampal tissues of CH rats compared with control rats. In addition, inhibitor control, miR-489-3p inhibitor, control-shRNA or TPT1-shRNA were injected into CH rats. The results of the open-field and forced swimming tests revealed that miR-489-3p inhibitor notably improved the behavior of CH rats. Flow cytometry was applied to explore the effects of miR-489-3p inhibitor on neuronal cell apoptosis, and the findings indicated that miR-489-3p inhibitor attenuated CH-induced neuronal cell apoptosis, whereas these effects were reversed by treatment with miR-489-3p inhibitor and TPT1-shRNA. Finally, the function of miR-489-3p in neuronal cells was investigated in vitro. Neuronal cell viability, apoptosis and the expression of apoptosis-related proteins were determined using MTT assay, flow cytometry and western blot analysis, respectively. The results demonstrated that miR-489-3p inhibitor enhanced cell viability, suppressed apoptosis and upregulated Pim-3, phosphorylated (p)-Bad (Ser112) and Bcl-xL expression. Rescue experiments indicated that these effects were reversed following silencing of TPT1. Taken together, the findings of the present study demonstrated that miR-489-3p inhibitor could relieve CH-induced neurological damage through regulating TPT1 expression.
Keywords: congenital hypothyroidism; microRNA-489-3p; neuronal cells; translationally controlled tumor protein 1.
Copyright: © Liu et al.
Figures

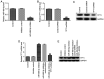

References
-
- Tiosano D, Pannain S, Vassart G, Parma J, Gershoni-Baruch R, Mandel H, Lotan R, Zaharan Y, Pery M, Weiss R, et al. The hypothyroidism in an inbred kindred with congenital thyroid hormone and glucocorticoid deficiency is due to a mutation producing a truncated thyrotropin receptor. Thyroid. 1999;9:887–894. doi: 10.1089/thy.1999.9.887. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
