Comparison of Effects Exerted by 4% Articaine Buccal Infiltration and 2% Lidocaine Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block on Pain Perception and Behavioral Feedback of Children during Pulp Treatment of Mandibular Second Primary Molars
- PMID: 33603905
- PMCID: PMC7879360
- DOI: 10.26574/maedica.2020.15.4.477
Comparison of Effects Exerted by 4% Articaine Buccal Infiltration and 2% Lidocaine Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block on Pain Perception and Behavioral Feedback of Children during Pulp Treatment of Mandibular Second Primary Molars
Abstract
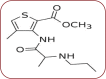
Background: One of the most impressive factors discouraging many people from seeking dental treatment is the fear of experiencing pain during dental procedures. Thus, the use of an effective method for pain control is vital in this regard. Articaine, which has an additional ester and thiophene groups that increase its biosolubility and permeability compared to older anesthetic agents, can be more effective on inducing anesthesia during dental treatment. Given the inconsistent currently available information on this concept, the present study was designed to compare the efficacy of articaine with that of lidocaine on pain control during pulp treatment of deciduous molar. Methods and materials: In this cross-sectional study, 38 patients who needed pulpotomy in both mandibular second molar of primary teeth were randomly divided into two groups, using the Randlist software. In the first meeting, infiltration with articaine 4% (epinephrine 1/100 000) was performed for all patients in group 1 on the left side of the mandible. At the next appointment, inferior alveolar nerve block was done with lidocaine 2% on the right side of the mandible (epinephrine 1/80 000). Notably, for all patients in the second group, the first injection was performed on the right second primary molar with articaine 4% (epinephrine 1/100 000), and inferior alveolar nerve block was also done with lidocaine 2% on the left side of the mandible (epinephrine 1/80 000). Results:Of the 38 patients included in the current study, 10 (26.3%) subjects in the lidocaine group and nine (23.6%) in the articaine group complained of pain during their dental treatment procedures, but this difference was not statistically significant. Conclusion: According to the findings of this study, buccal infiltration of 4% articaine had a comparable anesthetic outcome to that of 2% lidocaine for inferior alveolar nerve block in pulp treatment of the second primary mandibular molars.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparing anesthetic efficacy of articaine versus lidocaine as a supplemental buccal infiltration of the mandibular first molar after an inferior alveolar nerve block.J Am Dent Assoc. 2008 Sep;139(9):1228-35. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2008.0338. J Am Dent Assoc. 2008. PMID: 18762633 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of Buccal Infiltration with Articaine and Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block with Lignocaine for Pulp Therapy in Mandibular Primary Molars.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2016;40(4):301-5. doi: 10.17796/1053-4628-40.4.301. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2016. PMID: 27471808 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of anaesthetic efficacy of 4% articaine buccal infiltration versus 2% lidocaine inferior alveolar nerve block for pulpotomy in mandibular primary second molars.J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2021 Jul-Sep;39(3):299-302. doi: 10.4103/jisppd.jisppd_21_21. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2021. PMID: 34810348 Clinical Trial.
-
Can 4% Articaine Buccal Infiltration Replace Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block (IANB) with 2% Xylocaine for Pulp Therapy in Primary Mandibular Molars? A Systematic Review.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021 May-Jun;14(3):420-425. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1974. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2021. PMID: 34720518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can single buccal infiltration with 4% articaine induce sufficient analgesia for the extraction of primary molars in children: a systematic literature review.J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020 Aug;20(4):179-186. doi: 10.17245/jdapm.2020.20.4.179. Epub 2020 Aug 27. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2020. PMID: 32934983 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Intraosseous Local Anesthesia (QuickSleeper 5) During Pulpotomy and Stainless Steel Crown Placement on Mandibular Primary Molars: A Crossover Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Children (Basel). 2025 Feb 27;12(3):294. doi: 10.3390/children12030294. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150577 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Local Anesthesia in Pediatric Dentistry: A Survey of Specialists' Current Practices in Children and Attitudes in Relation to Articaine.Int J Dent. 2024 Feb 12;2024:2468502. doi: 10.1155/2024/2468502. eCollection 2024. Int J Dent. 2024. PMID: 38375437 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of two behavioural management techniques during inferior alveolar nerve block administration in pre-school children: a randomised clinical trial.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2023 Feb;24(1):85-93. doi: 10.1007/s40368-022-00758-y. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2023. PMID: 36260279 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Malamed SF. Handbook of local anesthesia.6th ed., St. Louis, USA, Mosby Co. 2013;228:282–283.
-
- Zafarmand AAH, Aghaeipour N, Amiri Tehrani N. Effectiveness of mandibular infiltration compared with mandibular block technique in second primary molar pulpotomy. J Dent School Shahid Beheshti Uni. 2004;3:470–477.
-
- Malamed SF, Gangnon S, Leblanc D. A comparison between Articaine HCl and Lidocaine HCl in pediatric dental patients. Am Acad Pediatr Dent. 2000;4:307–311. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources