Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Analysis of the HD-ZIP Gene Family in Response to Salt Stress in Pepper
- PMID: 33604369
- PMCID: PMC7869415
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8105124
Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Analysis of the HD-ZIP Gene Family in Response to Salt Stress in Pepper
Abstract
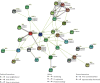
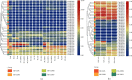
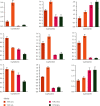
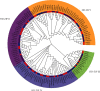
HD-ZIP is a unique type of transcription factor in plants, which are closely linked to the regulation of plant growth and development, the response to abiotic stress, and disease resistance. However, there is little known about the HD-ZIP gene family of pepper. In this study, 40 HD-ZIP family members were analyzed in the pepper genome. The analysis indicated that the introns number of Ca-HD-ZIP varied from 1 to 17; the number of amino acids was between 119 and 841; the theoretical isoelectric point was between 4.54 and 9.85; the molecular weight was between 14.04 and 92.56; most of them were unstable proteins. The phylogenetic tree divided CaHD-ZIP into 4 subfamilies; 40 CaHD-ZIP genes were located on different chromosomes, and all of them contained the motif 1; two pairs of CaHD-ZIP parallel genes of six paralogism genes were fragment duplications which occurred in 58.28~88.24 million years ago. There were multiple pressure-related action elements upstream of the start codon of the HD-Z-IP family. Protein interaction network proved to be coexpression phenomenon between ATML1 (CaH-DZ22, CaHDZ32) and At4g048909 (CaHDZ12, CaHDZ31), and three regions of them were highly homology. The expression level of CaHD-ZIP gene was different with tissues and developmental stages, which suggested that CaHD-ZIP may be involved in biological functions during pepper progress. In addition, Pepper HD-ZIP I and II genes played a major role in salt stress. CaHDZ03, CaHDZ 10, CaHDZ17, CaHDZ25, CaHDZ34, and CaHDZ35 were significantly induced in response to salt stress. Notably, the expression of CaHDZ07, CaHDZ17, CaHDZ26, and CaHDZ30, homologs of Arabidopsis AtHB12 and AtHB7 genes, was significantly upregulated by salt stresses. CaHDZ03 possesses two closely linked ABA action elements, and its expression level increased significantly at 4 h under salt stress. qRT-P-CR and transcription analysis showed that the expression of CaHDZ03 and CaHDZ10 was upregulated under short-term salt stress, but CaHDZ10 was downregulated with long-term salt stress, which provided a theoretical basis for research the function of Ca-HDZIP in response to abiotic stress.
Copyright © 2021 Zhongrong Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The roles of HD-ZIP proteins in plant abiotic stress tolerance.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 12;13:1027071. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1027071. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36311122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide characterization and their roles in abiotic stress responses of HD-Zip transcription factors in pepper.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jun 5;25(1):764. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06798-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40474057 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive characterization and RNA-Seq profiling of the HD-Zip transcription factor family in soybean (Glycine max) during dehydration and salt stress.BMC Genomics. 2014 Nov 3;15:950. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-950. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25362847 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of Eucalyptus grandis HD-Zip gene family in response to salt and temperature stress.BMC Plant Biol. 2020 Oct 1;20(1):451. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02677-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 33004006 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of HD-Zip II and III transcription factors in auxin-regulated plant development.J Exp Bot. 2015 Aug;66(16):5043-53. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv174. Epub 2015 Apr 23. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25911742 Review.
Cited by
-
The roles of HD-ZIP proteins in plant abiotic stress tolerance.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 12;13:1027071. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1027071. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36311122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and systematic analysis of the HD-Zip gene family and its roles in response to pH in Panax ginseng Meyer.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Jan 13;23(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04038-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 36639779 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Consequences of Functional and Regulatory Divergence of HD-Zip I Transcription Factors as a Source of Diversity in Protein Interaction Networks in Plants.J Mol Evol. 2023 Oct;91(5):581-597. doi: 10.1007/s00239-023-10121-4. Epub 2023 Jun 23. J Mol Evol. 2023. PMID: 37351602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of Homeodomain Leucine Zipper (HD-ZIP) Transcription Factor, Expression Analysis, and Protein Interaction of HD-ZIP IV in Oil Palm Somatic Embryogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 5;24(5):5000. doi: 10.3390/ijms24055000. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902431 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the HD-Zip I transcription factor family in Salvia miltiorrhiza and functional research of SmHD-Zip12 in tanshinone synthesis.PeerJ. 2023 Jun 27;11:e15510. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15510. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37397009 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

