Referral Patterns and Treatment Delays in Medulloblastoma: A Large Academic Proton Center Experience
- PMID: 33604411
- PMCID: PMC7886269
- DOI: 10.14338/IJPT-20-00038.1
Referral Patterns and Treatment Delays in Medulloblastoma: A Large Academic Proton Center Experience
Abstract
Purpose: Patient travel time can cause treatment delays when providers and families decide to seek proton therapy. We examined whether travel distance or referral pattern (domestic versus international) affects time to radiation therapy and subsequent disease outcomes in patients with medulloblastoma at a large academic proton center.
Patients and methods: Children with medulloblastoma treated at MD Anderson (MDA) with a protocol of proton beam therapy (PBT) between January 4, 2007, and June 25, 2014, were included in the analysis. The Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to study the association between time to start of radiation and distance. Classification- and regression-tree analyses were used to explore binary thresholds for continuous covariates (ie, distance). Failure-free survival was defined as the time interval between end of radiation and failure or death.
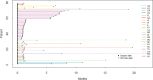
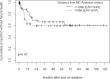
Results: 96 patients were included in the analysis: 17 were international (18%); 19 (20%) were from Houston, Texas; 21 were from other cities inside Texas (21%); and 39 (41%) were from other US states. The median time from surgery to start of radiation was not significantly different for international patients (median = 1.45 months) compared with US patients (median = 1.15 months; P = .13). However, time from surgery to start of radiation was significantly longer for patients residing > 1716 km (> 1066 miles) from MDA (median = 1.31 months) than for patients residing ≤ 1716 km (≤ 1066 miles) from MDA (median = 1.05 months; P = .01). This 1- to 2-week delay (median = 7.8 days) did not affect failure-free survival (hazard ratio = 1.34; P = .43).
Conclusion: We found that short delays in proton access can exist for patients traveling long distances to proton centers. However, in this study, treatment delays did not affect outcomes. This highlights the appropriateness of PBT in the face of travel coordination. Investment by proton centers in a rigorous intake process is justified to offer timely access to curative PBT.
Keywords: delay; distance; medulloblastoma; proton; travel.
©Copyright 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Steven J. Frank, MD, is an Associate Editor of the International Journal of Particle Therapy. Dr Frank discloses leadership and ownership interests in C4 Imaging and National Comprehensive Cancer Network Stock; honoraria from Boston Scientific, Hitachi, and Varian Medical Systems; research funding from Elekta, Hitachi, and Eli Lilly; a consulting or advisory role with Hitachi, Breakthrough Chronic Care, Varian Medical Systems; and patents developed at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, which have been licensed to C4 Imaging. Dr Frank also discloses travel, accommodations, and expenses provided by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network and Boston Scientific. The authors have no other conflicts to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Smoll NR, Drummond KJ. The incidence of medulloblastomas and primitive neurectodermal tumours in adults and children. J Clin Neurosci. 2012;19:1541–4. - PubMed
-
- Jones DT, Jäger N, Kool M, Zichner T, Hutter B, Sultan M, Cho YJ, Pugh TJ, Hovestadt V, Stütz AM, Rausch T, Warnatz HJ, Ryzhova M, Bender S, Sturm D, Pleier S, Cin H, Pfaff E, Sieber L, Wittmann A, Remke M, Witt M, Hutter S, Tzaridis T, Weischenfeldt J, Raeder B, Avci M, Amstislavskiy V, Zapatka M, Weber UD, Wang Q, Lasitschka B, Bartholomae CC, Schmidt M, von Kalle C, Ast V, Lawerenz C, Eils J, Kabbe R, Benes V, van Sluis P, Koster J, Volckmann R, Shih D, Betts MJ, Russell RB, Coco S, Tonini GP, Schüller U, Hans V, Graf N, Kim YJ, Monoranu C, Roggendorf W, Unterberg A, Herold-Mende C, Milde T, Kulozik AE, von Deimling A, Witt O, Maass E, Rössler E, Ebinger M, Schuhmann MU, Frühwald MC, Hasselblatt M, Jabado N, Rutkowski S, O von Bueren A, Williamson D, Clifford SC, McCabe MG, Collins VP, Wolf S, Wiemann S, Lehrach H, Brors B, Scheurlen A, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Northcott PA, Taylor MD, Meyerson M, Pomeroy SL, Yaspo ML, Korbel JO, Korshunov A, Eils R, Pfister SM, Lichter P. Dissecting the genomic complexity underlying medulloblastoma. Nature. 2012;488:100–5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- St Clair WH, Adams JA, Bues M, Fullerton BC, La Shell S, Kooy HM, Loeffler JS, Tarbell NJ. Advantage of protons compared to conventional X-ray or IMRT in the treatment of a pediatric patient with medulloblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004;58:727–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
