Regulation of MRE11A by UBQLN4 leads to cisplatin resistance in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 33605536
- PMCID: PMC8024730
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.12929
Regulation of MRE11A by UBQLN4 leads to cisplatin resistance in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
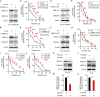
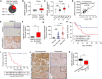
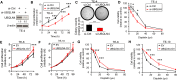
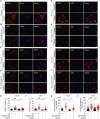
Resistance to standard cisplatin-based chemotherapies leads to worse survival outcomes for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Therefore, there is an urgent need to understand the aberrant mechanisms driving resistance in ESCC tumors. We hypothesized that ubiquilin-4 (UBQLN4), a protein that targets ubiquitinated proteins to the proteasome, regulates the expression of Meiotic Recombination 11 Homolog A (MRE11A), a critical component of the MRN complex and DNA damage repair pathways. Initially, immunohistochemistry analysis was conducted in specimens from patients with ESCC (n = 120). In endoscopic core ESCC biopsies taken from 61 patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) (5-fluorouracil and cisplatin), low MRE11A and high UBQLN4 protein levels were associated with reduced pathological response to NAC (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively). Multivariable analysis of surgically resected ESCC tissues from 59 patients revealed low MRE11A and high UBLQN4 expression as independent factors that can predict shorter overall survival [P = 0.01, hazard ratio (HR) = 5.11, 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.45-18.03; P = 0.02, HR = 3.74, 95% CI, 1.19-11.76, respectively]. Suppression of MRE11A expression was associated with cisplatin resistance in ESCC cell lines. Additionally, MRE11A was found to be ubiquitinated after cisplatin treatment. We observed an amplification of UBQLN4 gene copy numbers and an increase in UBQLN4 protein levels in ESCC tissues. Binding of UBQLN4 to ubiquitinated-MRE11A increased MRE11A degradation, thereby regulating MRE11A protein levels following DNA damage and promoting cisplatin resistance. In summary, MRE11A and UBQLN4 protein levels can serve as predictors for NAC response and as prognostic markers in ESCC patients.
Keywords: MRE11; chemoresistance; esophageal cancer; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; ubiquilin-4.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by FEBS Press and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HNRNPUL1 inhibits cisplatin sensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through regulating the formation of circMAN1A2.Exp Cell Res. 2021 Dec 1;409(1):112891. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112891. Epub 2021 Oct 22. Exp Cell Res. 2021. PMID: 34688610
-
Simple Cancer Stem Cell Markers Predict Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Resistance of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2021 Aug;41(8):4117-4126. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.15214. Anticancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34281882
-
GR, Sgk1, and NDRG1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: their correlation with therapeutic outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy.BMC Cancer. 2020 Feb 27;20(1):161. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-6652-7. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32106831 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Induces IL34 Signaling and Promotes Chemoresistance via Tumor-Associated Macrophage Polarization in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Jun;19(6):1085-1095. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0917. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33674443
-
Aberrant DNA Methylation in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and its Clinical Implications in Systemic Chemotherapy.Int J Med Sci. 2025 Feb 3;22(4):1002-1014. doi: 10.7150/ijms.109161. eCollection 2025. Int J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39991775 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Post-Translational Modification of MRE11: Its Implication in DDR and Diseases.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jul 28;12(8):1158. doi: 10.3390/genes12081158. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Multiomics Analysis Identified Ubiquilin 4 as a Promising Prognostic Biomarker of Immune-Related Therapy in Pan-Cancer.J Oncol. 2021 Sep 7;2021:7404927. doi: 10.1155/2021/7404927. eCollection 2021. J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34539785 Free PMC article.
-
Induced collagen type-I secretion by hepatocytes of the melanoma liver metastasis is associated with a reduction in tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70067. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70067. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39496484 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Amplification of UBQLN4 Is a Prognostic and Treatment Resistance Factor.Cells. 2022 Oct 21;11(20):3311. doi: 10.3390/cells11203311. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291176 Free PMC article.
-
UBQLN4 is activated by C/EBPβ and exerts oncogenic effects on colorectal cancer via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Dec 20;7(1):398. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00795-4. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34930912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA & Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68, 394–424. - PubMed
-
- Enzinger PC & Mayer RJ (2003) Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 349, 2241–2252. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J & Forman D (2015) Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut 64, 381–387. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

