An interdisciplinary team-training protocol for robotic gynecologic surgery improves operating time and costs: analysis of a 4-year experience in a university hospital setting
- PMID: 33606159
- PMCID: PMC8863701
- DOI: 10.1007/s11701-021-01209-4
An interdisciplinary team-training protocol for robotic gynecologic surgery improves operating time and costs: analysis of a 4-year experience in a university hospital setting
Abstract
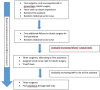
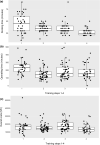
Main aim of this study is to assess the effect of a structured, interdisciplinary, surgical, team-training protocol in robotic gynecologic surgery, with the gradual integration of an advanced nurse practitioner. Data from all robotic surgical procedures were prospectively acquired. The surgical team consisted of one experienced surgeon and two surgical fellows and the scrub nurse team from three advance nurse practitioners, specialized in robotic surgery. The training was performed in a four-phase manner over 4 years and included theoretical training, hands-on training and team-communication skills enhancement. Scrub nurses increasingly adopted an active role during surgery. For a period of 4 years, 175 patients could be included in the analysis. All of them underwent a robotic gynecologic procedure. Mean docking time decreased from 45.3 to 27.3 min (p < 0.001), mean operating time from 235 to 179 min (p = 0.0071) and costs per case from 17,891 to 14,731 Swiss Francs (p = 0.035). There were no statistically significant changes in perioperative complications and conversions to laparotomy. An interdisciplinary long-term training protocol for high specialized robotic surgery within a "fixed" team with the gradually addition of an advanced study nurse improves the efficacy of the procedure in terms of time and costs. Although the surgery is performed quicker, the same performance and quality of surgical care could be reached.
Keywords: Advanced nurse practitioner; Gynecologic surgery; Robotic surgery; Surgical training.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources