Left ventricular myocardial strain and tissue characterization by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in immune checkpoint inhibitor associated cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 33606757
- PMCID: PMC7895343
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246764
Left ventricular myocardial strain and tissue characterization by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in immune checkpoint inhibitor associated cardiotoxicity
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are highly effective in treating cancer; however, cardiotoxicity can occur, including myocarditis. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging is useful for evaluation of myocarditis, although it has not been well studied in ICI cardiotoxicity.
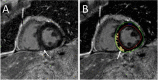
Methods: We identified patients referred for CMR evaluation of ICI cardiotoxicity from September 2015 through September 2019. We assessed structural and functional parameters, feature tracking (FT) left ventricular and atrial strain, T2- weighted ratios and quantitative late gadolinium enhancement (LGE). We also applied the Updated Lake Louise Criteria for diagnosis of myocarditis.
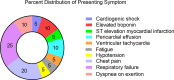
Results: Of the 20 patients referred, the median left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was 52.5% ± 19.1 and 50% had a normal LVEF (≥53%). FT strain analysis revealed an average abnormal global longitudinal strain (GLS) of -9.8%± 4.2%. In patients with a normal LVEF, the average GLS remained depressed at -12.3%± 2.4%. In all patients, GLS demonstrated a significant negative correlation with LVEF (rs = -0.64, p 0.002). Sixteen patients (80%) had presence of LGE (14 non-ischemic pattern and 2 ischemic). Percent LGE did not correlate with any CMR parameters and notably did not correlate with LVEF (rs = -0.29, p = 0.22) or GLS (rs = 0.10, p = 0.67), highlighting the value of tissue characterization beyond functional assessment. Nine patients (45%) met full Updated Lake Louise Criteria and 85% met at least one criterion, suggestive of myocarditis in the correct clinical context. Thirteen patients (65%) were treated for ICI-associated myocarditis and, of these, 54% (n = 7) had recovery of LVEF to normal. There was no correlation between LVEF (p = 0.47), GLS (0.89), or % LGE (0.15) and recovery of LVEF with treatment.
Conclusion: In patients with suspected ICI cardiotoxicity, CMR is an important diagnostic tool, even in the absence of overt left ventricular dysfunction, as abnormalities in left ventricular strain, T2 signal and LGE can identifying disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

