Individual, social, and environmental factors for infection risk among home healthcare patients: A multi-method study
- PMID: 33606903
- PMCID: PMC8084932
- DOI: 10.1111/hsc.13321
Individual, social, and environmental factors for infection risk among home healthcare patients: A multi-method study
Abstract
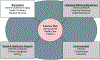
There has been limited research into the individual, social, and environmental factors for infection risk among patients in the home healthcare (HHC) setting, where the infection is a leading cause of hospitalisation. The aims of this study were to (1) explore nurse perceptions of individual, social, and environmental factors for infection risk among HHC patients; and (2) identify the frequency of environmental barriers to infection prevention and control in HHC. Data were collected in 2017-2018 and included qualitative interviews with HHC nurses (n = 50) and structured observations of nurse visits to patients' homes (n = 400). Thematic analyses of interviews with nurses suggested they perceived infection risk among patients as being influenced by knowledge of and attitudes towards infection prevention and engagement in hygiene practices, receipt of support from informal caregivers and nurse interventions aimed at cultivating infection control knowledge and practices, and the home environment. Statistical analyses of observation checklists revealed nurses encountered an average of 1.7 environmental barriers upon each home visit. Frequent environmental barriers observed during visits to HHC patients included clutter (39.5%), poor lighting (38.8%), dirtiness (28.5%), and pets (17.2%). Additional research is needed to clarify inter-relationships among these factors and identify strategies for addressing each as part of a comprehensive infection control program in HHC.
Keywords: home environment; home healthcare; infection; nursing; observation; qualitative.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report in relation to this study.
Figures
References
-
- Adams V, Song J, Shang J, McDonald M, Dowding D, Ojo M, & Russell D (2020). Infection prevention and control practices in the home environment: Examining enablers and barriers to adherence among home health care nurses. American Journal of Infection Control. 10.1016/j.ajic.2020.10.021 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). (2018). Home Health Agency (HHA) interpretive guidelines. August 31, 2018. https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Provider-Enrollment-and-Certification/Surve...
-
- Dowding D, Russell D, Trifilio M, McDonald MV, & Shang J (2020). Home care nurses’ identification of patients at risk of infection and their risk mitigation strategies: A qualitative interview study. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 107, 103617. 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2020.103617 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical