Structure-function relationships in the feto-placental circulation from in silico interpretation of micro-CT vascular structures
- PMID: 33607145
- PMCID: PMC7613408
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2021.110630
Structure-function relationships in the feto-placental circulation from in silico interpretation of micro-CT vascular structures
Abstract
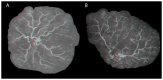
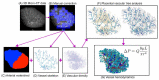
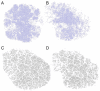
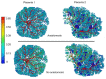
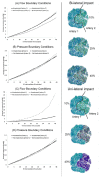
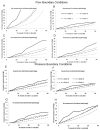
A well-functioning placenta is critical for healthy fetal development, as the placenta brings fetal blood in close contact with nutrient rich maternal blood, enabling exchange of nutrients and waste between mother and fetus. The feto-placental circulation forms a complex branching structure, providing blood to fetal capillaries, which must receive sufficient blood flow to ensure effective exchange, but at a low enough pressure to prevent damage to placental circulatory structures. The branching structure of the feto-placental circulation is known to be altered in complications such as fetal growth restriction, and the presence of regions of vascular dysfunction (such as hypovascularity or thrombosis) are proposed to elevate risk of placental pathology. Here we present a methodology to combine micro-computed tomography and computational model-based analysis of the branching structure of the feto-placental circulation in ex vivo placentae from normal term pregnancies. We analyse how vascular structure relates to function in this key organ of pregnancy; demonstrating that there is a 'resilience' to placental vascular structure-function relationships. We find that placentae with variable chorionic vascular structures, both with and without a Hyrtl's anastomosis between the umbilical arteries, and those with multiple regions of poorly vascularised tissue are able to function with a normal vascular resistance. Our models also predict that by progressively introducing local heterogeneity in placental vascular structure, large increases in feto-placental vascular resistances are induced. This suggests that localised heterogeneities in placental structure could potentially provide an indicator of increased risk of placental dysfunction.
Keywords: Computational model; Haemodynamics; Micro-CT; Placenta.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Bappoo N, Kelsey LJ, Parker L, et al. Viscosity and haemodynamics in a late gestation rat feto-placental arterial network. Biomech Model Mechan. 2017;16(4):1361–1372. - PubMed
-
- Burton GJ, Jauniaux E. Pathophysiology of placental-derived fetal growth restriction. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;218(2):S745–S761. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

