The time of onset of intradialytic hypotension during a hemodialysis session associates with clinical parameters and mortality
- PMID: 33607178
- PMCID: PMC8165353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.01.018
The time of onset of intradialytic hypotension during a hemodialysis session associates with clinical parameters and mortality
Abstract
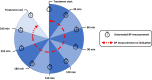
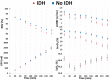
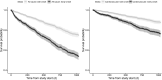
Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) is a common complication of hemodialysis, but there is no data about the time of onset during treatment. Here we describe the incidence of IDH throughout hemodialysis and associations of time of hypotension with clinical parameters and survival by analyzing data from 21 dialysis clinics in the United States to include 785682 treatments from 4348 patients. IDH was defined as a systolic blood pressure of 90 mmHg or under while IDH incidence was calculated in 30-minute intervals throughout the hemodialysis session. Associations of time of IDH with clinical and treatment parameters were explored using logistic regression and with survival using Cox-regression. Sensitivity analysis considered further IDH definitions. IDH occurred in 12% of sessions at a median time interval of 120-149 minutes. There was no notable change in IDH incidence across hemodialysis intervals (range: 2.6-3.2 episodes per 100 session-intervals). Relative blood volume and ultrafiltration volume did not notably associate with IDH in the first 90 minutes but did thereafter. Associations between central venous but not arterial oxygen saturation and IDH were present throughout hemodialysis. Patients prone to IDH early as compared to late in a session had worse survival. Sensitivity analyses suggested IDH definition affects time of onset but other analyses were comparable. Thus, our study highlights the incidence of IDH during the early part of hemodialysis which, when compared to later episodes, associates with clinical parameters and mortality.
Keywords: blood volume; hemodialysis; intradialytic hypotension; oximetry; survival.
Copyright © 2021 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Intradialytic hypotension: is timing everything?Kidney Int. 2021 Jun;99(6):1269-1272. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.03.012. Kidney Int. 2021. PMID: 34023027
References
-
- McIntyre C.W. Haemodialysis-induced myocardial stunning in chronic kidney disease—a new aspect of cardiovascular disease. Blood Purif. 2010;29:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Shoji T., Tsubakihara Y., Fujii M. Hemodialysis associated hypotension as an independent risk factor for two-year mortality in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2004;66:1212–1220. - PubMed
-
- Zucchelli P., Santoro A. Dialysis-induced hypotension: a fresh look at pathophysiology. Blood Purif. 1993;11:85–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

