High-grade fetal adenocarcinoma of the lung with abnormal expression of alpha-fetoprotein in a female patient: Case report
- PMID: 33607799
- PMCID: PMC7899914
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024634
High-grade fetal adenocarcinoma of the lung with abnormal expression of alpha-fetoprotein in a female patient: Case report
Abstract
Introduction: Fetal adenocarcinoma of the lung (FLAC) is an extremely rare tumor. Due to its rarity, most of the knowledge about FLAC comes from case reports. FLAC is an invasive adenocarcinoma that is similar to the fetal lung in the pseudo-glandular stage (8-16 weeks of gestation). Owing to the differences in histopathology and clinical process, FLAC has been further divided into low-level (L-FLAC) and high-level (H-FLAC). H-FLAC is usually associated with other conventional types of lung adenocarcinoma. Lung adenocarcinoma that produces alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) is a rare type of lung cancer. Its characteristics have not been fully elucidated.
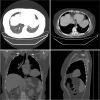
Patients concerns: We recently encountered this type of FLAC in a 51-year-old female patient. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest revealed a 74 × 51-mm sized tumor in the lingual segment of the superior lobe of the left lung. Among the tumor markers, serum AFP was elevated (816.2 ng/mL).
Primary diagnosis, interventions, and outcomes: The diagnosis of FLAC in this patient was confirmed by bronchoscopy with lung biopsy. Through a thoracoscope, left lung pneumonectomy, and mediastinal lymph node dissection were performed. The postoperative pathological results were consistent with the preoperative diagnosis of H-FLAC. Western blotting showed the difference in the AFP expression between the normal lung tissue and the cancerous lung tissue. Eventually, the diagnosis was AFP-producing H-FLAC. Using an immunohistochemical marker for AFP, cancer cells were shown to express AFP, specifically in their nuclei. After the operation, the patient underwent conventional chemotherapy. Her serum AFP gradually decreased over the course of 2 weeks.
Conclusion: Presently, specific tumor markers for the diagnosis of lung cancer have not been established. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of abnormal AFP expression in a patient with H-FLAC. It may provide a basis for the clinical diagnosis of H-FLAC, a rare tumor, and AFP may be considered as a specific tumor marker.
Copyright © 2021 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Patnayak R, Jena A, Rukmangadha N. Well-differentiated fetal adenocarcinoma of the lung in an adult male: report of an unusual tumor with a brief review of literature. J Cancer Res Ther 2014;10:419–21. - PubMed
-
- Esper A, Force S, Gal A. A 36-year-old woman with hemoptysis and a lung mass 3 months after delivery. Chest 2006;130:1620–3. - PubMed
-
- Ou SH, Kawaguchi T, Soo RA, et al. Rare subtypes of adenocarcinoma of the lung. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2011;11:1535–42. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Classification of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart. 4th ed.Geneva: WHO; 2011. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

