Echocardiographic parameters during prolonged targeted temperature Management in out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Survivors to predict neurological outcome - a post-hoc analysis of the TTH48 trial
- PMID: 33608045
- PMCID: PMC7893899
- DOI: 10.1186/s13049-021-00849-7
Echocardiographic parameters during prolonged targeted temperature Management in out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Survivors to predict neurological outcome - a post-hoc analysis of the TTH48 trial
Abstract
Background: Transthoracic echocardiographic (TTE) indices of myocardial function among survivors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) have been related to neurological outcome; however, results are inconsistent. We hypothesized that changes in average peak systolic mitral annular velocity (s') from 24 h (h) to 72 h following start of targeted temperature management (TTM) predict six-month neurological outcome in comatose OHCA survivors.
Methods: We investigated the association between peak systolic velocity of the mitral plane (s') and six-month neurological outcome in a population of 99 patients from a randomised controlled trial comparing TTM at 33 ± 1 °C for 24 h (h) (n = 47) vs. 48 h (n = 52) following OHCA (TTH48-trial). TTE was conducted at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after reaching target temperature. The primary outcome was 180 days neurological outcome assessed by Cerebral Performance Category score (CPC180) and the primary TTE outcome measure was s'. Secondary outcome measures were left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), global longitudinal strain (GLS), e', E/e' and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE).
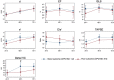
Results: Across all three scan time points s' was not associated with neurological outcome (ORs: 24 h: 1.0 (95%CI: 0.7-1.4, p = 0.98), 48 h: 1.13 (95%CI: 0.9-1.4, p = 0.34), 72 h: 1.04 (95%CI: 0.8-1.4, p = 0.76)). LVEF, GLS, E/e', and TAPSE recorded on serial TTEs following OHCA were neither associated with nor did they predict CPC180. Estimated median e' at 48 h following TTM was 5.74 cm/s (95%CI: 5.27-6.22) in patients with good outcome (CPC180 1-2) vs. 4.95 cm/s (95%CI: 4.37-5.54) in patients with poor outcome (CPC180 3-5) (p = 0.04).
Conclusions: s' assessed on serial TTEs in comatose survivors of OHCA treated with TTM was not associated with CPC180. Our findings suggest that serial TTEs in the early post-resuscitation phase during TTM do not aid the prognostication of neurological outcome following OHCA.
Trial registration: NCT02066753 . Registered 14 February 2014 - Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Cardiac arrest; Echocardiography; Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest; Prognostication; Targeted temperature management.
Conflict of interest statement
AMG declares to have received speaking fee from Novartis and Merck Sharp and Dome (MSD). All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nolan JP, Neumar RW, Adrie C, et al. Post-cardiac arrest syndrome: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, treatment, and prognostication: A scientific statement from the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation; the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee; the Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia; the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Perioperative, and Critical Care; the Council on Clinical Cardiology; the Council on Stroke (Part 1) Int Emerg Nurs. 2009;17:203–225. doi: 10.1016/j.ienj.2009.01.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

