AI-based mobile application to fight antibiotic resistance
- PMID: 33608509
- PMCID: PMC7895972
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21187-3
AI-based mobile application to fight antibiotic resistance
Abstract
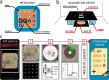
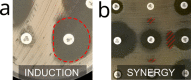
Antimicrobial resistance is a major global health threat and its development is promoted by antibiotic misuse. While disk diffusion antibiotic susceptibility testing (AST, also called antibiogram) is broadly used to test for antibiotic resistance in bacterial infections, it faces strong criticism because of inter-operator variability and the complexity of interpretative reading. Automatic reading systems address these issues, but are not always adapted or available to resource-limited settings. We present an artificial intelligence (AI)-based, offline smartphone application for antibiogram analysis. The application captures images with the phone's camera, and the user is guided throughout the analysis on the same device by a user-friendly graphical interface. An embedded expert system validates the coherence of the antibiogram data and provides interpreted results. The fully automatic measurement procedure of our application's reading system achieves an overall agreement of 90% on susceptibility categorization against a hospital-standard automatic system and 98% against manual measurement (gold standard), with reduced inter-operator variability. The application's performance showed that the automatic reading of antibiotic resistance testing is entirely feasible on a smartphone. Moreover our application is suited for resource-limited settings, and therefore has the potential to significantly increase patients' access to AST worldwide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- O’Neill, J. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a crisis for the health and wealth of nations. Review on Antimicrobial Resistancehttps://amr-review.org/Publications.html (2014).
-
- De Kraker ME, Davey PG, Grundmann H, BURDEN study group Mortality and hospital stay associated with resistant staphylococcus aureus and escherichia coli bacteremia: estimating the burden of antibiotic resistance in europe. PLoS Med. 2011;8:e1001104. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

