Asparagine couples mitochondrial respiration to ATF4 activity and tumor growth
- PMID: 33609439
- PMCID: PMC8102379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.02.001
Asparagine couples mitochondrial respiration to ATF4 activity and tumor growth
Abstract
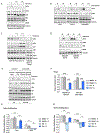
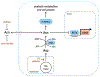
Mitochondrial respiration is critical for cell proliferation. In addition to producing ATP, respiration generates biosynthetic precursors, such as aspartate, an essential substrate for nucleotide synthesis. Here, we show that in addition to depleting intracellular aspartate, electron transport chain (ETC) inhibition depletes aspartate-derived asparagine, increases ATF4 levels, and impairs mTOR complex I (mTORC1) activity. Exogenous asparagine restores proliferation, ATF4 and mTORC1 activities, and mTORC1-dependent nucleotide synthesis in the context of ETC inhibition, suggesting that asparagine communicates active respiration to ATF4 and mTORC1. Finally, we show that combination of the ETC inhibitor metformin, which limits tumor asparagine synthesis, and either asparaginase or dietary asparagine restriction, which limit tumor asparagine consumption, effectively impairs tumor growth in multiple mouse models of cancer. Because environmental asparagine is sufficient to restore tumor growth in the context of respiration impairment, our findings suggest that asparagine synthesis is a fundamental purpose of tumor mitochondrial respiration, which can be harnessed for therapeutic benefit to cancer patients.
Keywords: asparaginase; asparagine; cancer metabolism; cancer treatment; dietary restriction; metformin; respiration.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests H.R.C. is a co-founder and Scientific Advisory Board member of Pelage Pharmaceuticals, a Scientific Advisory Board member of Faeth Therapeutics, and a member of the Cell Metabolism Advisory Board. This research was funded in part by Jazz Pharmaceuticals.
Figures





Comment in
-
Asparagine, a Key Metabolite in Cellular Response to Mitochondrial Dysfunction.Trends Cancer. 2021 Jun;7(6):479-481. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2021.04.001. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Trends Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33896762
References
-
- al-Jebawi AF, Lassman MN, and Abourizk NN (1998). Lactic acidosis with therapeutic metformin blood level in a low-risk diabetic patient. Diabetes Care 21, 1364–1365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

