Interleukin-20 exacerbates acute hepatitis and bacterial infection by downregulating IκBζ target genes in hepatocytes
- PMID: 33610678
- PMCID: PMC8323118
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.02.004
Interleukin-20 exacerbates acute hepatitis and bacterial infection by downregulating IκBζ target genes in hepatocytes
Abstract
Background & aims: Interleukin (IL)-20 and IL-22 belong to the IL-10 family. IL-10 is a well-documented anti-inflammatory cytokine while IL-22 is well known for epithelial protection and its antibacterial function, showing great therapeutic potential for organ damage; however, the function of IL-20 remains largely unknown.
Methods: Il20 knockout (Il20-/-) mice and wild-type littermates were generated and injected with Concanavalin A (ConA) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (K.P.) to induce acute hepatitis and bacterial infection, respectively.
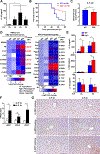
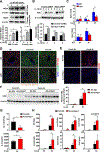
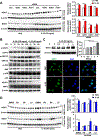
Results: Il20-/- mice were resistant to acute hepatitis and exhibited selectively elevated levels of the hepatoprotective cytokine IL-6. Such selective inhibition of IL-6 by IL-20 was due to IL-20 targeting hepatocytes that produce high levels of IL-6 but a limited number of other cytokines. Mechanistically, IL-20 upregulated NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) expression and subsequently promoted the protein degradation of transcription factor IκBζ, resulting in selective downregulation of the IκBζ-dependent gene Il6 as well several other IκBζ-dependent genes including lipocalin-2 (Lcn2). Given the important role of IL-6 and LCN2 in limiting bacterial infection, we examined the effect of IL-20 on bacterial infection and found Il20-/- mice were resistant to K.P. infection and exhibited elevated levels of hepatic IκBζ-dependent antibacterial genes. Moreover, IL-20 upregulated hepatic NQO1 by binding to IL-22R1/IL-20R2 and activating ERK/p38MAPK/NRF2 signaling pathways. Finally, the levels of hepatic IL1B, IL20, and IκBζ target genes were elevated, and correlated with each other, in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis.
Conclusions: IL-20 selectively inhibits hepatic IL-6 production rather than exerting IL-10-like broad anti-inflammatory properties. Unlike IL-22, IL-20 aggravates acute hepatitis and bacterial infection. Thus, anti-IL-20 therapy could be a promising option to control acute hepatitis and bacterial infection.
Lay summary: Several interleukin (IL)-20 family cytokines have been shown to play important roles in controllimg inflammatory responses, infection and tissue damage, but the role of IL-20 remains unclear. Herein, we elucidated the role of IL-20 in liver disease and bacterial infection. We show that IL-20 can aggravate hepatitis and bacterial infection; thus, targeting IL-20 holds promise for the treatment of patients with liver disease.
Keywords: IL-10; IL-22; Klebsiella pneumonia; NQO1; liver.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest No conflicts of interest exist for any of the authors. Please refer to the accompanying ICMJE disclosure forms for further details.
Figures





Comment in
-
Unscrambling a novel pathogenic role for interleukin-20 in acute hepatitis and bacterial infection: A double-edged sword?J Hepatol. 2021 Jul;75(1):22-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.03.011. Epub 2021 May 10. J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33985818 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rutz S, Wang X, Ouyang W. The IL-20 subfamily of cytokines--from host defence to tissue homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol 2014;14:783–795. - PubMed
-
- Sabat R, Ouyang W, Wolk K. Therapeutic opportunities of the IL-22-IL-22R1 system. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2014;13:21–38. - PubMed
-
- Blumberg H, Conklin D, Xu WF, Grossmann A, Brender T, Carollo S, et al. Interleukin 20: discovery, receptor identification, and role in epidermal function. Cell 2001;104:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Chiu YS, Wei CC, Lin YJ, Hsu YH, Chang MS. IL-20 and IL-20R1 antibodies protect against liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2014;60:1003–1014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

