Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function by Microbial Metabolites
- PMID: 33610769
- PMCID: PMC8025057
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.02.007
Regulation of Intestinal Barrier Function by Microbial Metabolites
Abstract
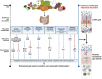
The human gastrointestinal tract (GI) harbors a diverse population of microbial life that continually shapes host pathophysiological responses. Despite readily available abundant metagenomic data, the functional dynamics of gut microbiota remain to be explored in various health and disease conditions. Microbiota generate a variety of metabolites from dietary products that influence host health and pathophysiological functions. Since gut microbial metabolites are produced in close proximity to gut epithelium, presumably they have significant impact on gut barrier function and immune responses. The goal of this review is to discuss recent advances on gut microbial metabolites in the regulation of intestinal barrier function. While the mechanisms of action of these metabolites are only beginning to emerge, they mainly point to a small group of shared pathways that control gut barrier functions. Amidst expanding technology and broadening knowledge, exploitation of beneficial microbiota and their metabolites to restore pathophysiological balance will likely prove to be an extremely useful remedial tool.
Keywords: Gut Barrier Function; Microbial Metabolites; Microbiota; Permeability; Tight Junction Proteins.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Li M., Wang B., Zhang M., Rantalainen M., Wang S., Zhou H., Zhang Y., Shen J., Pang X., Zhang M., Wei H., Chen Y., Lu H., Zuo J., Su M., Qiu Y., Jia W., Xiao C., Smith L.M., Yang S., Holmes E., Tang H., Zhao G., Nicholson J.K., Li L., Zhao L. Symbiotic gut microbes modulate human metabolic phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:2117–2122. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lynch S.V., Pedersen O. The human intestinal microbiome in health and disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2369–2379. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

