ECMO in COVID-19-prolonged therapy needed? A retrospective analysis of outcome and prognostic factors
- PMID: 33612020
- PMCID: PMC8369905
- DOI: 10.1177/0267659121995997
ECMO in COVID-19-prolonged therapy needed? A retrospective analysis of outcome and prognostic factors
Abstract
Background: The role of venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (VV ECMO) in patients with COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) still remains unclear. Our aim was to investigate the clinical course and outcome of those patients and to identify factors associated with the need for prolonged ECMO therapy.
Methods: A retrospective single-center study on patients with VV ECMO for COVID-19-associated ARDS was performed. Baseline characteristics, ventilatory and ECMO parameters, and laboratory and virological results were evaluated over time. Six months follow-up was assessed.
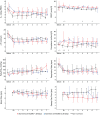
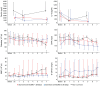
Results: Eleven of 16 patients (68.8%) survived to 6 months follow-up with four patients requiring short-term (<28 days) and seven requiring prolonged (⩾28 days) ECMO support. Lung compliance before ECMO was higher in the prolonged than in the short-term group (28.1 (28.8-32.1) ml/cmH2O vs 18.7 (17.7-25.0) ml/cmH2O, p = 0.030). Mechanical ventilation before ECMO was longer (19 (16-23) days vs 5 (5-9) days, p = 0.002) and SOFA score was higher (12.0 (10.5-17.0) vs 10.0 (9.0-10.0), p = 0.002) in non-survivors compared to survivors. Low viral load during the first days on ECMO tended to indicate worse outcomes. Seroconversion against SARS-CoV-2 occurred in all patients, but did not affect outcome.
Conclusions: VV ECMO support for COVID-19-induced ARDS is justified if initiated early and at an experienced ECMO center. Prolonged ECMO therapy might be required in those patients. Although no relevant predictive factors for the duration of ECMO support were found, the decision to stop therapy should not be made dependent of the length of ECMO treatment.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; ECMO; SARS-CoV-2; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; prolonged.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19, https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re... (2020, accessed 20 October 2020).
-
- World Health Organization. WHO coronavirus disease (COVID-19) dashboard, https://covid19.who.int/ (2020, accessed 02 December 2020).
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM.Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020; 323: 1239–1242. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

