Reduction in Nesfatin-1 Levels in the Cerebrospinal Fluid and Increased Nigrostriatal Degeneration Following Ventricular Administration of Anti-nesfatin-1 Antibody in Mice
- PMID: 33613183
- PMCID: PMC7890421
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2021.621173
Reduction in Nesfatin-1 Levels in the Cerebrospinal Fluid and Increased Nigrostriatal Degeneration Following Ventricular Administration of Anti-nesfatin-1 Antibody in Mice
Abstract
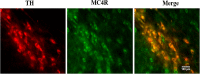
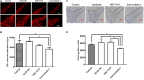
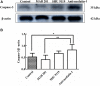
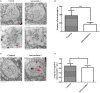
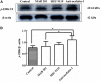
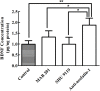
Nesfatin-1 is one of several brain-gut peptides that have a close relationship with the central dopaminergic system. Our previous studies have shown that nesfatin-1 is capable of protecting nigral dopaminergic neurons against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced neurotoxicity. A recent study also revealed a reduced blood level of nesfatin-1 in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). The current study was designed to investigate whether reduced nesfatin-1 in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) induces nigrostriatal system degeneration. An intra-cerebroventricular (ICV) injection technique was used to administer anti-nesfatin-1 antibody directly into the lateral ventricle of the brain. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) results showed that ICV injection of anti-nesfatin-1 antibody into the lateral ventricle of the brain once daily for 2 weeks caused a significant reduction in nesfatin-1 levels in the CSF (93.1%). Treatment with anti-nesfatin-1 antibody resulted in a substantial loss (23%) of TH-positive (TH+) dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc), as shown by immunofluorescence staining, a depletion in dopamine and its metabolites in the striatum detected by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and obvious nuclear shrinkage and mitochondrial lesions in dopaminergic neurons in the SNpc detected by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, the results from our Western blot and ELISA experiments demonstrated that anti-nesfatin-1 antibody injection induced an upregulation of caspase-3 activation, increased the expression of p-ERK, and elevated brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in the SNpc. Taken together, these observations suggest that reduced nesfatin-1 in the brain may induce nigrostriatal dopaminergic system degeneration; this effect may be mediated via mitochondrial dysfunction-related apoptosis. Our data support a role of nesfatin-1 in maintaining the normal physiological function of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; apoptosis; degeneration; dopaminergic neuron; mitochondrion; nesfatin-1; nigrostriatal system.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Li, Ma, Zheng and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

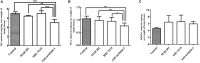
References
-
- Alieva A. K., Zyrin V. S., Rudenok M. M., Kolacheva A. A., Shulskaya M. V., Ugryumov M. V., et al. (2018). Whole-transcriptome analysis of mouse models with MPTP-induced early stages of Parkinson’s disease reveals stage-specific response of transcriptome and a possible role of myelin-linked genes in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 55 7229–7241. 10.1007/s12035-018-0907-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Angelone T., Filice E., Pasqua T., Amodio N., Galluccio M., Montesanti G., et al. (2013). Nesfatin-1 as a novel cardiac peptide: identification, functional characterization, and protection against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 70 495–509. 10.1007/s00018-012-1138-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anglade P., Vyas S., Javoy-Agid F., Herrero M. T., Michel P. P., Marquez J., et al. (1997). Apoptosis and autophagy in nigral neurons of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Histol. Histopathol. 12 25–31. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

