Functional Disconnection of the Angular Gyrus Related to Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 33613213
- PMCID: PMC7886792
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2021.621080
Functional Disconnection of the Angular Gyrus Related to Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
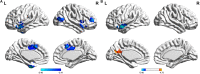
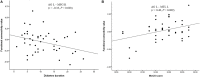
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is related to a variety of cognitive impairments that may even progress to dementia. Studies have found the angular gyrus (AG) is a cross-modal integration hub that is involved in a variety of cognitive processes. However, few studies have focused on the patterns of resting-state functional connections (rsFCs) of the AG in patients with T2DM. This study explored the functional connection (FC) between the AG and the whole brain and the relationship between the FC and clinical/cognitive variables in patients with T2DM. 44 patients with T2DM and 43 sex-, age-, and education-matched healthy controls underwent resting-state fMRI and received neuropsychological assessments. Compared with the control group, the T2DM group showed abnormal rsFCs between the AG and multiple brain regions. The FC between the left AG and the left medial temporal lobe in the T2DM group was positively correlated with scores on the Montreal Cognitive Assessment, after a Bonferroni correction (r = 0.40, P = 0.009). Collectively, patients with T2DM have abnormal FCs between the AG and extensive brain regions that may be related to various cognitive processes.
Keywords: angular gyrus; functional connectivity; neuroimaging; resting-state fMRI; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2021 Qi, Zhang, Gao, Tang, Wang, Su, Lei, Shao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baker L. D., Cross D. J., Minoshima S., Belongia D., Watson G. S., Craft S. (2011). Insulin resistance and Alzheimer-like reductions in regional cerebral glucose metabolism for cognitively normal adults with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes. Arch. Neurol. 68 51–57. 10.1001/archneurol.2010.225 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

