Uncovering the Pharmacological Mechanism of 2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2,5 -Diene-1,4-Dione Against Lung Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Evaluation
- PMID: 33613291
- PMCID: PMC7887632
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.617555
Uncovering the Pharmacological Mechanism of 2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2,5 -Diene-1,4-Dione Against Lung Cancer Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Evaluation
Abstract
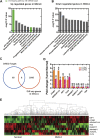
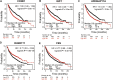
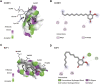
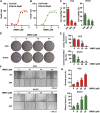
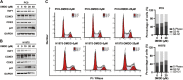
Background: 2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2, 5-Diene-1,4-Dione (DMDD) was purified from the roots of Averrhoa carambola L. Previous research demonstrated that DMDD is a small molecular compound with significant therapeutic potential for tumors. However, the potential targets and pharmacological mechanism of DMDD to treat lung cancer has not been reported. Methods: We employed network pharmacology and experimental evaluation to reveal the pharmacological mechanism of DMDD against lung cancer. Potential therapeutic targets of DMDD were screened by PharmMapper. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) lung cancer data sets were extracted and analyzed by GEPIA2. The mechanism of DMDD against lung cancer was determined by PPI, gene ontology (GO) and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. Survival analysis and molecular docking were employed to obtain the key targets of DMDD. Human lung cancer cell lines H1975 and PC9 were used to detect effects of DMDD treatment in vitro. The expression of key targets after DMDD treated was validated by Western Blot. Results: A total of 60 Homo sapiens potential therapeutic targets of DMDD and 3,545 DEGs in TCGA lung cancer datasets were identified. Gene ontology and pathway analysis revealed characteristic of the potential targets of DMDD and DEGs in lung cancer respectively. Cell cycle and pathways in cancer were overlapping with DMDD potential targets and lung cancer DEGs. Eight overlapping genes were found between DMDD potential therapeutic targets and lung cancer related DEGs. Survival analysis showed that high expression of DMDD potential targets CCNE1 and E2F1 was significantly related to poor patient survival in lung cancer. Molecular docking found that DMDD exhibited significant binding affinities within the active site of CCNE1 and E2F1. Further tests showed that DMDD inhibited the proliferation, migration and clone formation in lung cancer cell lines (H1975 and PC9) in a dose and time dependent manner. Mechanistically, DMDD treatment decreased the expression of CDK2, CCNE1, E2F1 proteins and induced cell cycle arrest at the G1/S phase in H1975 and PC9 cells. Conclusion: These results delineated that DMDD holds therapeutic potential that blocks tumorigenesis by cell cycle regulation in lung cancer, and may provide potential therapies for lung cancer.
Keywords: DMDD; TCGA; cell cycle arrest; lung cancer; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2021 Wang, Yang, Song, Fu, Wang, Du, Chen, Cao, Huang and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The antidiabetic compound 2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione, isolated from Averrhoa carambola L., demonstrates significant antitumor potential against human breast cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 15;6(27):24304-19. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4475. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26203774 Free PMC article.
-
2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione protects against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress, apoptosis and autophagy in SH-SY5Y cells.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 Jan 29;40(1):113. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01544-7. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 39878879
-
Anti-Breast Cancer Effect of 2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2,5-Diene-1,4-Dione in vivo and in vitro Through MAPK Signaling Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Jul 7;14:2667-2684. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S237699. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32764871 Free PMC article.
-
2-Dodecyl-6-Methoxycyclohexa-2, 5-Diene-1, 4-Dione isolated from Averrhoa carambola L. root inhibits high glucose-induced EMT in HK-2 cells through targeting the regulation of miR-21-5p/Smad7 signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Mar;172:116280. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116280. Epub 2024 Feb 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38368837
-
Exploring manzamine a: a promising anti-lung cancer agent from marine sponge Haliclona sp.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 25;16:1525210. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1525210. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40070571 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Innovating non-small cell lung cancer treatment with novel TM-GL/NPs nanoparticles for Glycitin delivery.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025 Feb 8;41(1):41. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09972-4. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39921782 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacological analysis of corosolic acid reveals P4HA2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 May 29;23(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04008-6. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37248456 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic cytomembrane-coated ZIF-8-loaded DMDD nanoparticle and sonodynamic co-therapy for cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Sep;10(18):971. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3646. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36267767 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of E2F1 gene expression in human cancer: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 5;23(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10865-8. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37277745 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of LRFN4 in prognosis and tumor microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 25;16:1540636. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1540636. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40070576 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Committee Z. B. E. (1999). Zhonghua Bencao. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press; 715.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

