Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Mitochondrial Encephalopathy Due to FOXRED1 Mutations: Two Chinese Case Reports and a Review of the Literature
- PMID: 33613441
- PMCID: PMC7887287
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.633397
Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Mitochondrial Encephalopathy Due to FOXRED1 Mutations: Two Chinese Case Reports and a Review of the Literature
Abstract
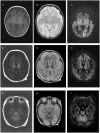
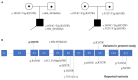
Background: As one of the assembly factors of complex I in the mitochondrial respiratory chain, FOXRED1 plays an important role in mitochondrial function. However, only a few patients with mitochondrial encephalopathy due to FOXRED1 defects have been reported. Methods: Two Chinese patients with mitochondrial encephalopathy due to mutations in FOXRED1 were identified through trio whole-exome sequencing. The clinical presentation, laboratory data, brain imaging findings, and genetic results were collected and reviewed. All previously reported cases with FOXRED1-related mitochondrial encephalopathy were collected using a PubMed search, and their data were reviewed. Results: Two patients presented with severe neurodevelopmental delay, epilepsy, high lactic acid levels, and remarkable diffuse brain atrophy and polycystic encephalomalacia during early infancy. Trio whole-exome sequencing revealed compound heterozygous variants in both patients: one case harbored a c.606_607delAG frameshift variant and a c.1054C>T (p.R352W) variant. At the same time, the other carried a novel c.352C>T (p.Q118X) variant and a reported c.1054C>T (p.R352W) variant. To date, nine patients have been reported with FOXRED1 defects, including our two cases. The most common presentations were neurodevelopment delay (100%), epilepsy (80%), poor feeding (30%), and vision loss (20%). Multisystem involvement comprised cardiovascular dysfunction (30%), abnormal liver function (20%), and hypoglycemia (10%). The neuroimaging results ranged from normal to severe cerebral atrophy and polycystic encephalomalacia in early infancy. Eleven pathogenic variants in FOXRED1 have been reported, comprising six missense variants, two non-sense variants, two frameshift variants, and one splice variant; among these the c.1054C>T (p.R352W) and c.612_615dupAGTG (p.A206SfsX15) variants are more common. Conclusion: FOXRED1-related mitochondrial disorders have high clinical and genetic heterogeneity. Our study expanded the clinical and genetic spectrum of FOXRED1 defects. Early infantile onset and progressive encephalopathy are the most common clinical presentations, while the variants c.1054C>T (p.R352W) and c.612_615dupAGTG (p.A206SfsX15) may be critical founder mutations.
Keywords: FOXRED1; complex I defect; cystic encephalomalacia; mitochondrial encephalopathy; neuroimage.
Copyright © 2021 Hu, Xu, Shen and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Congenital lactic acidosis, cerebral cysts and pulmonary hypertension in an infant with FOXRED1 related complex 1 deficiency.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019 Apr 30;19:100472. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2019.100472. eCollection 2019 Jun. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019. PMID: 31065540 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital lactic acidosis, cerebral cysts and pulmonary hypertension in an infant with FOXRED1 related complex I deficiency.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019 Jan 18;18:32-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2018.12.006. eCollection 2019 Mar. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019. PMID: 30723688 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Characterization of New Variants in FOXRED1 Gene Expands the Clinical Spectrum Associated with Mitochondrial Complex I Deficiency.J Clin Med. 2019 Aug 20;8(8):1262. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081262. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31434271 Free PMC article.
-
[Early onset epileptic encephalopathy caused by mitochondrial arginyl-tRNA synthetase gene deficiency: report of two cases and literature review].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Nov 2;58(11):893-899. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20200716-00729. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33120460 Review. Chinese.
-
[Molybdenum cofactor deficiency type B manifested as Leigh-like syndrome: a case report and literature review].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Feb 2;59(2):119-124. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20200911-00866. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33548958 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Expanding the genetic spectrum of mitochondrial diseases in Tunisia: novel variants revealed by whole-exome sequencing.Front Genet. 2024 Jan 12;14:1259826. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1259826. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38283147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fassone E, Duncan AJ, Taanman JW, Pagnamenta AT, Sadowski MI, Holand T, et al. . FOXRED1, encoding an FAD-dependent oxidoreductase complex-I-specific molecular chaperone, is mutated in infantile-onset mitochondrial encephalopathy. Hum Mol Genet. (2010) 19:4837–47. 10.1093/hmg/ddq414 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

