Dietary Intervention Impacts Immune Cell Functions and Dynamics by Inducing Metabolic Rewiring
- PMID: 33613560
- PMCID: PMC7890027
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.623989
Dietary Intervention Impacts Immune Cell Functions and Dynamics by Inducing Metabolic Rewiring
Abstract
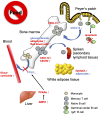
Accumulating evidence has shown that nutrient metabolism is closely associated with the differentiation and functions of various immune cells. Cellular metabolism, including aerobic glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and oxidative phosphorylation, plays a key role in germinal center (GC) reaction, B-cell trafficking, and T-cell-fate decision. Furthermore, a quiescent metabolic status consolidates T-cell-dependent immunological memory. Therefore, dietary interventions such as calorie restriction, time-restricted feeding, and fasting potentially manipulate immune cell functions. For instance, intermittent fasting prevents the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Meanwhile, the fasting response diminishes the lymphocyte pool in gut-associated lymphoid tissue to minimize energy expenditure, leading to the attenuation of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) response. The nutritional status also influences the dynamics of several immune cell subsets. Here, we describe the current understanding of the significance of immunometabolism in the differentiation and functionality of lymphocytes and macrophages. The underlying molecular mechanisms also are discussed. These experimental observations could offer new therapeutic strategies for immunological disorders like autoimmunity.
Keywords: AMPK; GCN2; calorie restriction; dietary intervention; fasting; mTOR; metabolic rewiring.
Copyright © 2021 Okawa, Nagai and Hase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

