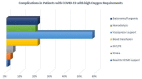
Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19 Disease and High Oxygen Requirements
- PMID: 33613798
- PMCID: PMC7869563
- DOI: 10.14740/jocmr4405
Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19 Disease and High Oxygen Requirements
Abstract
Background: Approximately 19% of people infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) progress to severe or critical stages of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with a mortality rate exceeding 50%. We aimed to examine the characteristics, mortality rates, intubation rate, and length of stay (LOS) of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 disease with high oxygen requirements (critically ill).
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis in a single center in Brooklyn, New York. Adult hospitalized patients with confirmed COVID-19 disease and high oxygen requirements were included. We performed multivariate logistic regression analyses for statistically significant variables to reduce any confounding.
Results: A total of 398 patients were identified between March 19th and April 25th, 2020 who met the inclusion criteria, of which 247 (62.1%) required intubation. The overall mortality rate in our study was 57.3% (n = 228). The mean hospital LOS was 19.1 ± 17.4 days. Patients who survived to hospital discharge had a longer mean LOS compared to those who died during hospitalization (25.4 ± 22.03 days versus10.7 ± 1.74 days). In the multivariate analysis, increased age, intubation and increased lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) were each independently associated with increased odds of mortality. Diarrhea was associated with decreased mortality (OR 0.4; CI 0.16, 0.99). Obesity and use of vasopressors were each independently associated with increased intubation.
Conclusions: In patients with COVID-19 disease and high oxygen requirements, advanced age, intubation, and higher LDH levels were associated with increased mortality, while diarrhea was associated with decreased mortality. Gender, diabetes, and hypertension did not have any association with mortality or length of hospital stay.
Keywords: COVID-19 disease; Critically ill; High oxygen requirement; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright 2021, Rojas-Marte et al.
Conflict of interest statement
None to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Epidemiology Working Group for Ncip Epidemic Response, Chinese Center for Disease Control Prevention. [The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China] Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(2):145–151. - PubMed
-
- Center JHCR. Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous