Protective Effects of Pelargonium graveolens Essential Oil on Methomyl-Induced Oxidative Stress and Spatial Working Memory Impairment in Association with Histopathological Changes in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats
- PMID: 33613881
- PMCID: PMC7878032
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.11.4.1402.1
Protective Effects of Pelargonium graveolens Essential Oil on Methomyl-Induced Oxidative Stress and Spatial Working Memory Impairment in Association with Histopathological Changes in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats
Abstract
Introduction: Methomyl (MET) is a carbamate insecticide, used in agriculture and public health to eliminate harmful insects. Besides its advantages in agriculture, it causes neurotoxic effects. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of MET on Spatial Working Memory (SWM), oxidative stress parameters, and histopathological changes in the hippocampus, as well as the possible protective role of Pelargonium graveolens Essential Oil (EO).
Methods: Male Wistar rats were randomized into four groups of six animals: group I as the control that received the vehicle; group II received EO (75 mg/kg b.w), group III received MET (2 mg/kg b.w); and group IV received both MET and EO. The rats were administered the respective doses orally by gavage for 28 days. SWM was assessed using Y-maze on the day before the first treatment and day 28 after the last dose. They were sacrificed by decapitation and their brains were taken for assessing oxidative stress parameters and histopathological analysis.
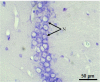
Results: MET treatment caused SWM deficits. Furthermore, drastic changes were observed in aspartate transaminase, alanine aminotransferase, and alkaline phosphatase activities. The level of malondialdehyde significantly increased, whereas antioxidant (glutathioneS-transferase and catalase) enzyme activities significantly decreased. The CA1 region of the hippocampus of rats exposed to MET revealed severe histological alterations. However, supplementation with EO improved SWM and partially restored the activities of antioxidant systems and prevented neuronal cell damage.
Conclusion: P. graveolens EO has the potential in mitigating most of the adverse effects in the hippocampus and prevents SWM impairment induced by MET toxicity.
Keywords: Hippocampus; Methomyl; Oxidative stress; Pelargonium graveolens; Spatial working memory.
Copyright© 2020 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Protective effects of vitamin C and selenium supplementation on methomyl-induced tissue oxidative stress in adult rats.Toxicol Ind Health. 2015 Jan;31(1):31-43. doi: 10.1177/0748233712468020. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Toxicol Ind Health. 2015. PMID: 23222694
-
Hypoglycemic and antioxidant effects of leaf essential oil of Pelargonium graveolens L'Hér. in alloxan induced diabetic rats.Lipids Health Dis. 2012 Jun 26;11:81. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-81. Lipids Health Dis. 2012. PMID: 22734822 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant properties of Pelargonium graveolens L'Her essential oil on the reproductive damage induced by deltamethrin in mice as compared to alpha-tocopherol.Lipids Health Dis. 2013 Mar 7;12:30. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-30. Lipids Health Dis. 2013. PMID: 23496944 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of Pelargonium graveolens (geranium) oil against cefotaxime-induced hepato-renal toxicity in rats.Front Toxicol. 2024 Dec 4;6:1489310. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2024.1489310. eCollection 2024. Front Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39698236 Free PMC article.
-
N-acetyl cysteine supplementation prevents impairment of spatial working memory functions in rats following exposure to hypobaric hypoxia.Physiol Behav. 2007 Nov 23;92(4):643-50. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.05.051. Epub 2007 May 24. Physiol Behav. 2007. PMID: 17602713
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Effect of White Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn. Petal Tea in Rats Poisoned with Mancozeb.Foods. 2023 May 28;12(11):2175. doi: 10.3390/foods12112175. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37297420 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatorenal protective effects of essential oils against chemical overexposure induced oxidative damage.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1580805. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1580805. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40308777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comparative UPLC-orbitrap-MS-based metabolite profiling of three Pelargonium species cultivated in Egypt.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 1;14(1):22765. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72153-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39353957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdollahi M., Ranjbar A., Shadnia S., Nikfar S., Rezaie A. (2004). Pesticides and oxidative stress. A review. Medical Science Monitor, 10(6), 141–7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15173684/ - PubMed
-
- Andersen H. R., Debes F., Wohlfahrt-Veje C., Murata K., Grandjean P. (2015). Occupational pesticide exposure in early pregnancy associated with sex-specific neurobehavioral deficits in the children at school age. Neurotoxicology and Teratology, 47, 1–9. [DOI:10.1016/j.ntt.2014.10.006] [PMID ] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ballard C. G., O’Brien J. T., Reichelt K., Perry E. K. (2002). Aromatherapy as a safe and effective treatment for the management of agitation in severe dementia: the results of a doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial with Melissa. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 63, 553–8. [DOI:10.4088/JCP.v63n0703] [PMID ] - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
