Effects of Isoniazid on Tolerance and Sensitization to the Rewarding Properties of Morphine: A Conditioned Place Preference Procedure Investigation in Mice
- PMID: 33613886
- PMCID: PMC7878033
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.11.4.1940.1
Effects of Isoniazid on Tolerance and Sensitization to the Rewarding Properties of Morphine: A Conditioned Place Preference Procedure Investigation in Mice
Abstract
Introduction: The GABAergic system of the brain plays a key role in morphine tolerance and sensitization. As isoniazid is a modulator of the GABAergic system, the present study aims to understand whether isoniazid can influence the induction of tolerance and sensitization to the rewarding effects of morphine.
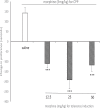
Methods: The rewarding effects of morphine and isoniazid were assessed using a Conditioned Place Preference (CPP) procedure in female mice. Tolerance to the rewarding effects of morphine was induced with high-dose morphine (25 mg/kg, SC), twice a day, for four days. Also, the sensitization was induced with an effective dose of morphine (5 mg/kg, SC), once a day, for three days. During the induction of tolerance or sensitization, the different groups of mice received saline or isoniazid (25, 50, and 75 mg/kg, IP) one hour before each morphine injection.
Results: Morphine (0.5-10 mg/kg, SC) produced a significant CPP, but isoniazid (25, 50, and 75 mg/kg, IP) did not induce place preference or place aversion in mice. Although an effective dose of morphine (5 mg/kg, SC) did not induce CPP in morphine tolerated mice, an ineffective dose (0.5 mg/kg, SC) could produce a significant CPP in morphine-sensitized animals. The administration of isoniazid before morphine (on the days of tolerance or sensitization induction) inhibited the development of tolerance or sensitization to the rewarding effect of morphine in the CPP paradigm.
Conclusion: Isoniazid can be a useful drug for the prevention of tolerance and sensitization to the rewarding effects of morphine.
Keywords: Conditioned place preference; Isoniazid; Morphine; Reward; Sensitization; Tolerance.
Copyright© 2020 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest There is no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Theophylline inhibits tolerance and sensitization induced by morphine: a conditioned place preference paradigm study in female mice.Behav Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;17(7):621-8. doi: 10.1097/01.fbp.0000236274.18042.54. Behav Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17021395
-
A cannabinoid receptor antagonist attenuates conditioned place preference but not behavioural sensitization to morphine.Brain Res. 2004 Nov 12;1026(2):244-53. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.08.027. Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15488486
-
Distal and proximal pre-exposure to ethanol in the place conditioning task: tolerance to aversive effect, sensitization to activating effect, but no change in rewarding effect.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2002 Apr;160(4):414-24. doi: 10.1007/s00213-001-0990-1. Epub 2002 Jan 31. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2002. PMID: 11919669
-
Sensitization to the conditioned rewarding effects of morphine and cocaine: differential effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonist U69593.Eur J Pharmacol. 1998 Mar 12;345(1):27-34. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(97)01614-2. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9593590
-
Drug-sensitive reward in crayfish: an invertebrate model system for the study of SEEKING, reward, addiction, and withdrawal.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011 Oct;35(9):1847-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2010.12.008. Epub 2010 Dec 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2011. PMID: 21182861 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High Morphine Use Disorder Susceptibility Is Predicted by Impaired Learning Ability in Mice.Brain Sci. 2022 Dec 1;12(12):1650. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12121650. Brain Sci. 2022. PMID: 36552110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asehinde S., Ajayi A., Bakre A., Omorogbe O., Adebesin A., Umukoro S. (2018). Effects of Jobelyn® on Isoniazid-Induced Seizures, Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Glutamate Decarboxylase Activity in Mice. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience, 9(6), 389–96. [DOI:10.32598/bcn.9.6.389] [PMID ] [PMCID ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azizi P., Haghparast A., Hassanpour-Ezatti M. (2009). Effects of CB1 receptor antagonist within the nucleus accumbens on the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in morphine-sensitized rats. Behavioural Brain Research, 197(1), 119–24. [DOI:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.08.009] [PMID ] - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
