Silver nanoparticles achieve cytotoxicity against breast cancer by regulating long-chain noncoding RNA XLOC_006390-mediated pathway
- PMID: 33613979
- PMCID: PMC7885187
- DOI: 10.1093/toxres/tfaa090
Silver nanoparticles achieve cytotoxicity against breast cancer by regulating long-chain noncoding RNA XLOC_006390-mediated pathway
Abstract
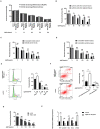
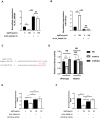
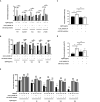
The specific cytotoxic effect of nanoparticles on tumor cells may be used in future antitumor clinical applications. Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have been reported to have potent cytotoxic effect, but the mechanism is unclear. Here, AgNPs were synthesized, and the particle average size was 63.1 ± 8.3 nm and showed a nearly circular shape, which were determined by transmission electron microscopy and field emission scanning electron microscopy. The selected area electron diffraction patterns showed that the nanoparticles were crystalline. The energy-dispersive X-ray spectrum proved that silver is the main component of nanoparticles. The AgNPs showed potent cytotoxicity in breast cancer cells, no matter whether they were tamoxifen sensitive or resistant. Next, we found that a long noncoding RNA, XLOC_006390, was decreased in AgNPs-treated breast cancer cells, coupled to inhibited cell proliferation, altered cell cycle and apoptotic phenotype. Downstream of AgNPs, XLOC_006390 was recognized to target miR-338-3p and modulate the SOX4 expression. This signaling pathway also mediates the AgNPs function of sensitizing tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells to tamoxifen. These results provide a new clue for the antitumor mechanism of AgNPs, and a new way for drug development by using AgNPs.
Keywords: breast cancer; cytotoxicity; lncRNA; microarray; silver nanoparticles.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ganoderma neo-japonicum Imazeki: a potential cytotoxic agent against breast cancer cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:4399-413. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S51881. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013. PMID: 24265551 Free PMC article.
-
Dual functions of silver nanoparticles in F9 teratocarcinoma stem cells, a suitable model for evaluating cytotoxicity- and differentiation-mediated cancer therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Oct 12;12:7529-7549. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S145147. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 29066898 Free PMC article.
-
Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia marschalliana Sprengel aerial part extract and assessment of their antioxidant, anticancer, and antibacterial properties.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Apr 29;11:1835-46. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S99882. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27199558 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis induction in lung and prostate cancer cells through silver nanoparticles synthesized from Pinus roxburghii bioactive fraction.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2020 Feb;25(1):23-37. doi: 10.1007/s00775-019-01729-3. Epub 2019 Oct 23. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 31641851
-
Ecofriendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Euphrasia officinalis leaf extract and its biomedical applications.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;46(6):1163-1170. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2017.1362417. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 28784039
Cited by
-
Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) as a Double-Edged Sword: Synthesis, Factors Affecting, Mechanisms of Toxicity and Anticancer Potentials-An Updated Review till March 2025.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1007/s12011-025-04688-w. Online ahead of print. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 40512370 Review.
-
Antitumor efficacy of silver nanoparticles reduced with β-D-glucose as neoadjuvant therapy to prevent tumor relapse in a mouse model of breast cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 25;14:1332439. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1332439. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38333224 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple RNA Profiling Reveal Epigenetic Toxicity Effects of Oxidative Stress by Graphene Oxide Silver Nanoparticles in-vitro.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 May 31;18:2855-2871. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S373161. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37283715 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinspired multifunctional silver nanoparticles by Smilax Chenensis and their enhanced biomedical and catalytic applications.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 2;14(1):29909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77071-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39622871 Free PMC article.
-
Silver Nanoparticles in 3D Printing: A New Frontier in Wound Healing.ACS Omega. 2024 Sep 16;9(40):41107-41129. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c04961. eCollection 2024 Oct 8. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39398164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Colović M, Todorović M, Colović N et al. Appearance of estrogen positive bilateral breast carcinoma with HER2 gene amplification in a patient with aplastic anemia. Pol J Pathol 2014;65:66–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

