Effect of incubation temperature and substrate moisture on embryonic development, hatchling phenotypes and post-hatching growth in the Reeves' Turtle, Mauremys reevesii
- PMID: 33614259
- PMCID: PMC7883692
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.10553
Effect of incubation temperature and substrate moisture on embryonic development, hatchling phenotypes and post-hatching growth in the Reeves' Turtle, Mauremys reevesii
Abstract
Background: Reeves' Turtles (Mauremys reevesii) are economically important in aquaculture in China. Understanding the effects of incubation temperature and substrate moisture on embryos and hatchlings is of great significance for improving the artificial culture of M. reevesii. However, available studies have not yet determined the thermal and hydric optima for M. reevesii eggs, and the potential interaction between the two factors.
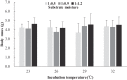
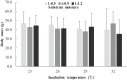
Methods: In this study, eggs of M. reevesii were incubated at five temperature levels (23, 26, 29, 32 and 35 °C, fluctuation range ± 0.5 °C). In each temperature level, there were three substrate moisture levels (1:0.5, 1:0.9 and 1:1.2, weight ratio of vermiculite to water). Thus, a total of 15 combinations of temperature and moisture were used to examine the effects of incubation temperature and substrate moisture on incubation duration, hatching success, hatchling phenotypes, post-hatching growth and hatchling survival.
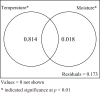
Results: Substrate moisture did not significantly affect most development parameters (except incubation duration and carapace width of hatchlings). Eggs incubated at low moisture level (1:0.5) had a longer incubation duration and produced hatchlings with smaller carapace widths than those incubated at medium (1:0.9) or high (1:1.2) moisture levels. Incubation temperature had a significant effect on incubation duration, hatching success, hatchling phenotypes and hatchling survival. Incubation duration decreased as incubation temperature increased. Eggs incubated at 23, 26 and 29 °C showed higher hatching success than those incubated at 32 and 35 °C. Hatchlings incubated at 32 °C were smaller in body size and mass than those incubated at 23, 26 and 29 °C. At 12 months of age, incubation temperature had no long-lasting effect on body mass, but hatchlings incubated at 23 and 35 °C had lower survival rates than those incubated at 26, 29 and 32 °C. For the development of embryos and hatchlings, the interaction between incubation temperature and substrate moisture was not significant.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that incubation temperature has a significant influence on the development of embryos and hatchlings of M. reevesii, while substrate moisture only significantly affects the incubation duration and carapace width of hatchlings. The combination of an incubation temperature of 29 ± 0.5 °C and a substrate moisture level of 1:1.2 represented optimal incubation conditions in this experiment. Such incubation conditions are helpful in obtaining higher hatching success, shorter incubation duration and higher survival rates for this aquaculture species.
Keywords: Hatchling phenotypes; Incubation temperature; Mauremys reevesii; Post-hatching growth; Substrate moisture.
© 2021 Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The effects of thermal and hydric environments on hatching success, embryonic use of energy and hatchling traits in a colubrid snake, Elaphe carinata.Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2001 Jun;129(2-3):461-71. doi: 10.1016/s1095-6433(01)00271-9. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11423316
-
Influence of incubation temperature on hatching success, energy expenditure for embryonic development, and size and morphology of hatchlings in the oriental garden lizard, Calotes versicolor (Agamidae).J Exp Zool. 2002 Jun 1;292(7):649-59. doi: 10.1002/jez.10101. J Exp Zool. 2002. PMID: 12115930
-
[Effects of incubation temperature and substrate humidity on embryonic development of Mauremys mutica].Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2010 Jan;21(1):215-20. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 20387446 Chinese.
-
Influence of incubation temperature on embryo development, hatchling morphology and early growth rate in red-footed tortoise (Chelonoidis carbonaria).Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2021 Sep;259:110999. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.110999. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34098130
-
A review of the effects of incubation conditions on hatchling phenotypes in non-squamate reptiles.J Comp Physiol B. 2022 Mar;192(2):207-233. doi: 10.1007/s00360-021-01415-4. Epub 2022 Feb 10. J Comp Physiol B. 2022. PMID: 35142902 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronology of embryonic and gonadal development in the Reeves' turtle, Mauremys reevesii.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 8;12(1):11619. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15515-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35804180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bobyn ML, Brooks RJ. Interclutch and interpopulation variation in the effects of incubation conditions on sex, survival and growth of hatchling turtles (Chelydra serpentina) Journal of Zoology. 1994;233(2):233–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7998.1994.tb08586.x. - DOI
-
- Brooks RJ, Bobyn ML, Galbraith DA, Layfield JA, Nancekivell EG. Maternal and environmental influences on growth and survival of embryonic and hatchling snapping turtles (Chelydra serpentina) Canadian Journal of Zoology. 1991;69(10):2667–2676. doi: 10.1139/z91-375. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

