Non-radioactive and sensitive tracking of neutrophils towards inflammation using antibody functionalized magnetic particle imaging tracers
- PMID: 33614400
- PMCID: PMC7893534
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.50721
Non-radioactive and sensitive tracking of neutrophils towards inflammation using antibody functionalized magnetic particle imaging tracers
Abstract
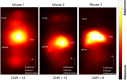
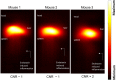
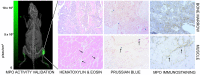
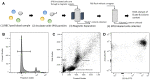
White blood cells (WBCs) are a key component of the mammalian immune system and play an essential role in surveillance, defense, and adaptation against foreign pathogens. Apart from their roles in the active combat of infection and the development of adaptive immunity, immune cells are also involved in tumor development and metastasis. Antibody-based therapeutics have been developed to regulate (i.e. selectively activate or inhibit immune function) and harness immune cells to fight malignancy. Alternatively, non-invasive tracking of WBC distribution can diagnose inflammation, infection, fevers of unknown origin (FUOs), and cancer. Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI) is a non-invasive, non-radioactive, and sensitive medical imaging technique that uses safe superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIOs) as tracers. MPI has previously been shown to track therapeutic stem cells for over 87 days with a ~200 cell detection limit. In the current work, we utilized antibody-conjugated SPIOs specific to neutrophils for in situ labeling, and non-invasive and radiation-free tracking of these inflammatory cells to sites of infection and inflammation in an in vivo murine model of lipopolysaccharide-induced myositis. MPI showed sensitive detection of inflammation with a contrast-to-noise ratio of ~8-13.
Keywords: antibody; inflammation; magnetic particle imaging; medical imaging; superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles; white blood cells.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: Professor Conolly is a co-founder of an MPI startup company, Magnetic Insight, and he holds stock in this company. Dr. Elaine Yu is an employee of Magnetic Insight. The authors declare no other competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Magnetic particle imaging for radiation-free, sensitive and high-contrast vascular imaging and cell tracking.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018 Aug;45:131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.04.014. Epub 2018 May 10. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29754007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A perspective on a rapid and radiation-free tracer imaging modality, magnetic particle imaging, with promise for clinical translation.Br J Radiol. 2018 Nov;91(1091):20180326. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180326. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Br J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29888968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Magnetic particle imaging (MPI) for NMR and MRI researchers.J Magn Reson. 2013 Apr;229:116-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2012.11.029. Epub 2012 Dec 27. J Magn Reson. 2013. PMID: 23305842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative "Hot Spot" Imaging of Transplanted Stem Cells using Superparamagnetic Tracers and Magnetic Particle Imaging (MPI).Tomography. 2015 Dec;1(2):91-97. doi: 10.18383/j.tom.2015.00172. Tomography. 2015. PMID: 26740972 Free PMC article.
-
Trimodal Cell Tracking In Vivo: Combining Iron- and Fluorine-Based Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Magnetic Particle Imaging to Monitor the Delivery of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and the Ensuing Inflammation.Tomography. 2019 Dec;5(4):367-376. doi: 10.18383/j.tom.2019.00020. Tomography. 2019. PMID: 31893235 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Applications of Magnetic Particle Imaging in Biomedicine: Advancements and Prospects.Front Physiol. 2022 Jul 1;13:898426. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.898426. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35846005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multidisciplinary approach to eosinophilia.Front Oncol. 2023 May 18;13:1193730. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1193730. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37274287 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elucidating Iron Metabolism through Molecular Imaging.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 22;46(4):2798-2818. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040175. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tomographic Magnetic Particle Imaging With a Single-Sided Field-Free Line Scanner.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2024 Dec;71(12):3470-3481. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2024.3427665. Epub 2024 Nov 21. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 39008388
-
ISMRM Clinical Focus Meeting 2023: "Imaging the Fire in the Brain".J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Apr;61(4):1580-1596. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29587. Epub 2024 Aug 28. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39193867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ludewig P, Gdaniec N, Sedlacik J, Forkert ND, Szwargulski P, Graeser M. et al. Magnetic particle imaging for real-time perfusion imaging in acute stroke. ACS Nano. 2017;11:10480–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

