Mechanisms of Effector-Mediated Immunity Revealed by the Accidental Human Pathogen Legionella pneumophila
- PMID: 33614523
- PMCID: PMC7886983
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.593823
Mechanisms of Effector-Mediated Immunity Revealed by the Accidental Human Pathogen Legionella pneumophila
Abstract
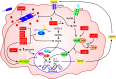
Many Gram-negative bacterial pathogens employ translocated virulence factors, termed effector proteins, to facilitate their parasitism of host cells and evade host anti-microbial defenses. However, eukaryotes have evolved to detect effector-mediated virulence strategies through a phenomenon termed effector-triggered immunity (ETI). Although ETI was discovered in plants, a growing body of literature demonstrates that metazoans also utilize effector-mediated immunity to detect and clear bacterial pathogens. This mini review is focused on mechanisms of effector-mediated immune responses by the accidental human pathogen Legionella pneumophila. We highlight recent advancements in the field and discuss the future prospects of harnessing effectors for the development of novel therapeutics, a critical need due to the prevalence and rapid spread of antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: Legionella pneumophila; effector-mediated immunity; effector-triggered immunity; innate immunity; macrophage.
Copyright © 2021 Ngwaga, Chauhan and Shames.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Innate Immunity to Intracellular Pathogens: Lessons Learned from Legionella pneumophila.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2012;79:43-71. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394318-7.00003-6. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22569517
-
Intrabacterial Regulation of a Cytotoxic Effector by Its Cognate Metaeffector Promotes Legionella pneumophila Virulence.mSphere. 2023 Feb 21;8(1):e0055222. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00552-22. Epub 2023 Jan 4. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 36598225 Free PMC article.
-
Using Genomic Deletion Mutants to Investigate Effector-Triggered Immunity During Legionella pneumophila Infection.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2523:23-41. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2449-4_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35759189
-
Legionella pneumophila, armed to the hilt: justifying the largest arsenal of effectors in the bacterial world.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016 Feb;29:74-80. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.11.002. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26709975 Review.
-
Legionella: virulence factors and host response.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2016 Jun;29(3):280-6. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000268. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26998861 Review.
Cited by
-
The unity of opposites: Strategic interplay between bacterial effectors to regulate cellular homeostasis.J Biol Chem. 2021 Dec;297(6):101340. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101340. Epub 2021 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34695417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and Laboratory Diagnosis of Legionella Pneumonia.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;13(2):280. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13020280. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36673091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Different Clinical Courses of Legionnaires' Disease in Newborns from the Same Maternity Hospital.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Aug 24;58(9):1150. doi: 10.3390/medicina58091150. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36143827 Free PMC article.
-
Eat or Be Eaten: Strategies Used by Legionella to Acquire Host-Derived Nutrients and Evade Lysosomal Degradation.Infect Immun. 2023 Apr 18;91(4):e0044122. doi: 10.1128/iai.00441-22. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Infect Immun. 2023. PMID: 36912646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effector-mediated subversion of proteasome activator (PA)28αβ enhances host defense against Legionella pneumophila under inflammatory and oxidative stress conditions.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Jun 22;19(6):e1011473. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011473. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37347796 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

