Antimicrobial Peptides and Cell-Penetrating Peptides for Treating Intracellular Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 33614528
- PMCID: PMC7892433
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.612931
Antimicrobial Peptides and Cell-Penetrating Peptides for Treating Intracellular Bacterial Infections
Abstract
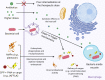
Bacterial infections caused by intracellular pathogens are difficult to control. Conventional antibiotic therapies are often ineffective, as high doses are needed to increase the number of antibiotics that will cross the host cell membrane to act on the intracellular bacterium. Moreover, higher doses of antibiotics may lead to elevated severe toxic effects against host cells. In this context, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) have shown great potential to treat such infections by acting directly on the intracellular pathogenic bacterium or performing the delivery of cargos with antibacterial activities. Therefore, in this mini-review, we cover the main AMPs and CPPs described to date, aiming at intracellular bacterial infection treatment. Moreover, we discuss some of the proposed mechanisms of action for these peptide classes and their conjugation with other antimicrobials.
Keywords: AMPs; CPPs; antimicrobial peptides; cell-penetrating peptides; intracellular bacteria.
Copyright © 2021 Buccini, Cardoso and Franco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delivery of Antibiotics by Cell-Penetrating Peptides to Kill Intracellular Pathogens.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2383:335-345. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1752-6_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34766300
-
Synergism between Host Defence Peptides and Antibiotics Against Bacterial Infections.Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(14):1238-1263. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200303122626. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32124698 Review.
-
Application of Antimicrobial Peptides of the Innate Immune System in Combination With Conventional Antibiotics-A Novel Way to Combat Antibiotic Resistance?Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Apr 30;9:128. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00128. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31114762 Free PMC article.
-
Modified horseshoe crab peptides target and kill bacteria inside host cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec 31;79(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04041-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34971427 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic-cell-penetrating peptide conjugates targeting challenging drug-resistant and intracellular pathogenic bacteria.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Nov;98(5):762-778. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13930. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 34315189 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances of Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Their Application as Vectors for Delivery of Peptide and Protein-Based Cargo Molecules.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 7;15(8):2093. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082093. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Antimicrobial Effects of Hybrid Peptides Synthesized Based on the Sequence of Ribosomal S1 Protein from Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 4;23(1):524. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010524. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35008951 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Delivery Systems for the Oral Administration of Antimicrobial Peptides: Promising Tools to Treat Infectious Diseases.Front Med Technol. 2022 Jan 25;3:778645. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2021.778645. eCollection 2021. Front Med Technol. 2022. PMID: 35146486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of Membrane Active Peptides Considering Multi-Objective Optimization for Biomedical Application.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Feb 2;12(2):180. doi: 10.3390/membranes12020180. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Antimicrobial Peptides: Antimicrobial, Anti-Inflammatory and Antibiofilm Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 22;22(21):11401. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111401. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768832 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abu-Humaidan A. H., Elvén M., Sonesson A., Garred P., Sørensen O. E. (2018). Persistent intracellular Staphylococcus aureus in keratinocytes lead to activation of the complement system with subsequent reduction in the intracellular bacterial load. Front. Immunol. 9 (396), 1–14. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00396 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai H., You Y., Yan H., Meng J., Xue X., Hou Z., et al. (2012). Antisense inhibition of gene expression and growth in gram-negative bacteria by cell-penetrating peptide conjugates of peptide nucleic acids targeted to rpoD gene. Biomaterials 33 (2), 659–667. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.09.075 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

