Antimicrobial Peptides and Cell-Penetrating Peptides for Treating Intracellular Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 33614528
- PMCID: PMC7892433
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.612931
Antimicrobial Peptides and Cell-Penetrating Peptides for Treating Intracellular Bacterial Infections
Abstract
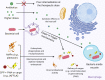
Bacterial infections caused by intracellular pathogens are difficult to control. Conventional antibiotic therapies are often ineffective, as high doses are needed to increase the number of antibiotics that will cross the host cell membrane to act on the intracellular bacterium. Moreover, higher doses of antibiotics may lead to elevated severe toxic effects against host cells. In this context, antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) and cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs) have shown great potential to treat such infections by acting directly on the intracellular pathogenic bacterium or performing the delivery of cargos with antibacterial activities. Therefore, in this mini-review, we cover the main AMPs and CPPs described to date, aiming at intracellular bacterial infection treatment. Moreover, we discuss some of the proposed mechanisms of action for these peptide classes and their conjugation with other antimicrobials.
Keywords: AMPs; CPPs; antimicrobial peptides; cell-penetrating peptides; intracellular bacteria.
Copyright © 2021 Buccini, Cardoso and Franco.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abu-Humaidan A. H., Elvén M., Sonesson A., Garred P., Sørensen O. E. (2018). Persistent intracellular Staphylococcus aureus in keratinocytes lead to activation of the complement system with subsequent reduction in the intracellular bacterial load. Front. Immunol. 9 (396), 1–14. 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00396 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai H., You Y., Yan H., Meng J., Xue X., Hou Z., et al. (2012). Antisense inhibition of gene expression and growth in gram-negative bacteria by cell-penetrating peptide conjugates of peptide nucleic acids targeted to rpoD gene. Biomaterials 33 (2), 659–667. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.09.075 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

