A New Family of Bacteriolytic Proteins in Dictyostelium discoideum
- PMID: 33614529
- PMCID: PMC7886984
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.617310
A New Family of Bacteriolytic Proteins in Dictyostelium discoideum
Abstract
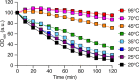
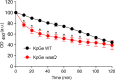
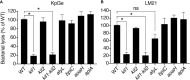
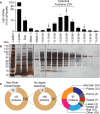
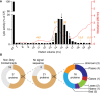
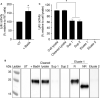
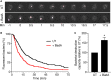
Phagocytic cells ingest and destroy bacteria efficiently and in doing so ensure the defense of the human body against infections. Phagocytic Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae represent a powerful model system to study the intracellular mechanisms ensuring destruction of ingested bacteria in phagosomes. Here, we discovered the presence of a bacteriolytic activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae in cellular extracts from D. discoideum. The bacteriolytic activity was detected only at a very acidic pH mimicking the conditions found in D. discoideum phagosomes. It was also strongly decreased in extracts of kil1 KO cells that were previously described to kill inefficiently internalized bacteria, suggesting that the activity observed in vitro is involved in killing of bacteria in phagosomes. We purified a fraction enriched in bacteriolytic activity where only 16 proteins were detected and focused on four proteins selectively enriched in this fraction. Three of them belong to a poorly characterized family of D. discoideum proteins exhibiting a DUF3430 domain of unknown function and were named BadA (Bacteriolytic D. discoideum A), BadB, and BadC. We overexpressed the BadA protein in cells, and the bacteriolytic activity increased concomitantly in cell extracts. Conversely, depletion of BadA from cell extracts decreased significantly their bacteriolytic activity. Finally, in cells overexpressing BadA, bacterial killing was faster than in parental cells. Together these results identify BadA as a D. discoideum protein required for cellular bactericidal activity. They also define a new strategy to identify and characterize bactericidal proteins in D. discoideum cells.
Keywords: Bacteriolytic D. discoideum A (BadA); Dictyostelium discoideum; Klebsiella pneumoniae; bacteriolytic proteins; intracellular killing; protein purification.
Copyright © 2021 Guilhen, Lima, Ifrid, Crespo-Yañez, Lamrabet and Cosson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antibacterial effectors in Dictyostelium discoideum: specific activity against different bacterial species.mSphere. 2024 Oct 29;9(10):e0047124. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00471-24. Epub 2024 Oct 8. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39377588 Free PMC article.
-
How Phagocytic Cells Kill Different Bacteria: a Quantitative Analysis Using Dictyostelium discoideum.mBio. 2021 Feb 16;12(1):e03169-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03169-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33593980 Free PMC article.
-
Compound K14 inhibits bacterial killing and protease activity in Dictyostelium discoideum phagosomes.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 26;19(8):e0309327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309327. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39186559 Free PMC article.
-
The multifarious lysozyme arsenal of Dictyostelium discoideum.Dev Comp Immunol. 2020 Jun;107:103645. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103645. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Dev Comp Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32061941 Review.
-
Eat, kill or die: when amoeba meets bacteria.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008 Jun;11(3):271-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.05.005. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18550419 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization of Ancient Prosaposin-like Proteins from the Protist Dictyostelium discoideum.Biochemistry. 2024 Nov 5;63(21):2768-2777. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00479. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 39421968 Free PMC article.
-
Production of functional recombinant antibodies in Dictyostelium discoideum.BMC Res Notes. 2025 Jun 4;18(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s13104-025-07314-z. BMC Res Notes. 2025. PMID: 40468350 Free PMC article.
-
Luminal Phospholipase D Attacks Bacterial Membranes in Dictyostelium discoideum Phagosomes.Mol Microbiol. 2025 Jul;124(1):54-65. doi: 10.1111/mmi.15367. Epub 2025 May 4. Mol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40320828 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial effectors in Dictyostelium discoideum: specific activity against different bacterial species.mSphere. 2024 Oct 29;9(10):e0047124. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00471-24. Epub 2024 Oct 8. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39377588 Free PMC article.
-
5-ethyl-2'-deoxyuridine fragilizes Klebsiella pneumoniae outer wall and facilitates intracellular killing by phagocytic cells.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 31;17(10):e0269093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269093. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36315510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balestrino D., Ghigo J.-M., Charbonnel N., Haagensen J. A. J., Forestier C. (2008). The characterization of functions involved in the establishment and maturation of Klebsiella pneumoniae in vitro biofilm reveals dual roles for surface exopolysaccharides. Environ. Microbiol. 10, 685–701. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01491.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

