PTEN Reduces BMP9-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation Through Inhibiting Wnt10b in Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 33614622
- PMCID: PMC7889951
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.608544
PTEN Reduces BMP9-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation Through Inhibiting Wnt10b in Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
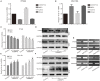
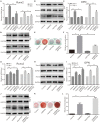
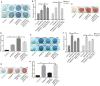
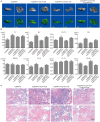
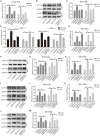
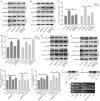
Bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) is one of the most efficacious osteogenic cytokines. PTEN and Wnt10b are both implicated in regulating the osteogenic potential of BMP9, but the potential relationship between them is unknown. In this study, we determined whether PTEN could reduce the expression of Wnt10b during the osteogenic process initialized by BMP9 in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and the possible molecular mechanism. We find that PTEN is inhibited by BMP9 in MSCs, but Wnt10b is increased simultaneously. The BMP9-induced osteogenic markers are reduced by PTEN but increased by silencing PTEN. The effects of knockdown PTEN on elevating BMP9-induced osteogenic markers are almost abolished by knockdown of Wnt10b. On the contrary, the BMP9-increased ALP activities and mineralization are both inhibited by PTEN but almost reversed by the combination of Wnt10b. Bone masses induced by BMP9 are enhanced by knockdown of PTEN, which is reduced by knockdown of Wnt10b. The BMP9-increased Wnt10b is decreased by PTEN but enhanced by knockdown of PTEN. Meanwhile, the BMP9-induced Wnt10b is also reduced by a PI3K-specific inhibitor (Ly294002) or rapamycin, respectively. The BMP9-induced phosphorylation of CREB or Smad1/5/9 is also reduced by PTEN, but enhanced by PTEN knockdown. In addition, p-CREB interacts with p-Smad1/5/9 in MSCs, and p-CREB or p-Smad1/5/9 are both enriched at the promoter region of Wnt10b. Our findings indicate that inhibitory effects of PTEN on BMP9's osteogenic potential may be partially mediated through decreasing the expression of Wnt10b via the disturbance of interaction between CREB and BMP/Smad signaling.
Keywords: BMP9; WNT10B; mesenchymal stem cell; osteogenic differentiation; phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Li, Li, Deng, Hu and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CREB/Wnt10b mediates the effect of COX-2 on promoting BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation via reducing adipogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Jun;120(6):9572-9587. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28234. Epub 2018 Dec 7. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30525243
-
COX-2 promotes the osteogenic potential of BMP9 through TGF-β1/p38 signaling in mesenchymal stem cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 4;13(8):11336-11351. doi: 10.18632/aging.202825. Epub 2021 Apr 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33833129 Free PMC article.
-
BMP9 and COX-2 form an important regulatory loop in BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Bone. 2013 Nov;57(1):311-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.08.015. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Bone. 2013. PMID: 23981660
-
The wonders of BMP9: From mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, angiogenesis, neurogenesis, tumorigenesis, and metabolism to regenerative medicine.Genes Dis. 2019 Jul 24;6(3):201-223. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2019.07.003. eCollection 2019 Sep. Genes Dis. 2019. PMID: 32042861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential regulatory role of BMP9 in inflammatory responses.Genes Dis. 2021 Sep 21;9(6):1566-1578. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2021.08.010. eCollection 2022 Nov. Genes Dis. 2021. PMID: 36157503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SDF-1 induces directional chemotaxis of BMSCs at the intervertebral fusion site and promotes osteogenic differentiation by regulating Wnt/β-catenin in the bone marrow chimera spinal intervertebral fusion mouse model.Turk J Biol. 2022 Dec 21;47(1):14-28. doi: 10.55730/1300-0152.2638. eCollection 2023. Turk J Biol. 2022. PMID: 37529111 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt/β-Catenin Promotes the Osteoblastic Potential of BMP9 Through Down-Regulating Cyp26b1 in Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023 Aug;20(5):705-723. doi: 10.1007/s13770-023-00526-z. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 37010733 Free PMC article.
-
Lysyl oxidase inhibits BMP9-induced osteoblastic differentiation through reducing Wnt/β-catenin via HIF-1a repression in 3T3-L1 cells.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Nov 29;18(1):911. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04251-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 38031108 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 6 promotes BMP9-induced osteoblastic differentiation through Stat3/mTORC1 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Feb 1;15(3):718-733. doi: 10.18632/aging.204504. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 36750182 Free PMC article.
-
M2 Microglia-Derived Exosomal miR-144-5p Attenuates White Matter Injury in Preterm Infants by Regulating the PTEN/AKT Pathway Through KLF12.Mol Biotechnol. 2025 Jan 22. doi: 10.1007/s12033-025-01364-1. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39841378
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

