TGF-β2 Reduces the Cell-Mediated Immunogenicity of Equine MHC-Mismatched Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Without Altering Immunomodulatory Properties
- PMID: 33614658
- PMCID: PMC7889809
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.628382
TGF-β2 Reduces the Cell-Mediated Immunogenicity of Equine MHC-Mismatched Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Without Altering Immunomodulatory Properties
Abstract
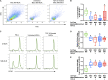
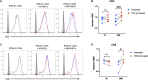
Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a promising cell therapy for treating numerous diseases, but major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-mismatched MSCs can be rejected by the recipient's immune system. Pre-treating MSCs with transforming growth factor-β2 (TGF-β2) to downregulate surface expression of MHC molecules may enhance the ability of allogeneic MSCs to evade immune responses. We used lymphocyte proliferation assays and ELISAs to analyze the immunomodulatory potential of TGF-β2-treated equine bone marrow-derived MSCs. T cell activation and cytotoxicity assays were then used to measure the in vitro cell-mediated immunogenicity. Similar to untreated MSCs, TGF-β2-treated MSCs inhibited T cell proliferation and did not stimulate MHC-mismatched T cells to proliferate. Additionally, similar quantities of prostaglandin E2 and TGF-β1 were detected in assays with untreated and TGF-β2-treated MSCs supporting that TGF-β2-treated MSCs retain their strong immunomodulatory properties in vitro. Compared to untreated MSCs, TGF-β2-treated MSCs induced less T cell activation and had reduced cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. These results indicate that treating MSCs with TGF-β2 is a promising strategy to reduce the cell-mediated immunogenicity of MHC-mismatched MSCs and facilitate allogeneic MSC therapy.
Keywords: TGF-β2; allogeneic; cytotoxicity; immunogenicity; major histocompatibility complex; mesenchymal stem cell.
Copyright © 2021 Berglund, Long, Robertson and Schnabel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Berglund A. K., Fisher M. B., Cameron K. A., Poole E. J., Schnabel L. V. (2017a). Transforming Growth Factor-β2 Downregulates Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) I and MHC II Surface Expression on Equine Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Without Altering Other Phenotypic Cell Surface Markers. Front. Vet. Sci. 4:84. 10.3389/fvets.2017.00084 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

