Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells Induce Infiltration and Formation of CD163+ Macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 Pathway
- PMID: 33614685
- PMCID: PMC7893116
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.627927
Activated Hepatic Stellate Cells Induce Infiltration and Formation of CD163+ Macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 Pathway
Abstract
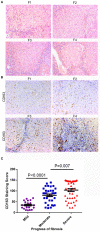
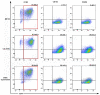
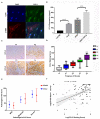
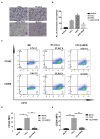
Background: Activated hepatic stellate cells (aHSCs) regulate the function of immune cells during liver fibrosis. As major innate cells in the liver, macrophages have inducible plasticity. Nevertheless, the mechanisms through which aHSCs regulate macrophages' phenotype and function during liver fibrosis and cirrhosis remain unclear. In this study, we examined the immunoregulatory function of aHSCs during liver fibrosis and explored their role in regulating macrophage phenotype and function. Methods: A total of 96 patients with different stages of chronic hepatitis B-related liver fibrosis were recruited in the study. Metavir score system was used to evaluate the degree of fibrosis. The expression of hepatic CCL2 and M2 phenotype macrophage marker CD163 were detected by immunohistochemistry, and the relationship among hepatic CD163, CCL2, and fibrosis scores were also explored. In the in vitro model, the aHSCs isolated from human liver tissues and THP-1-derived M0-type macrophages (M0MΦ) were co-cultured to observe whether and how aHSCs regulate the phenotype and function of macrophages. To explore whether CCL2/CCR2 axis has a crucial role in macrophage phenotypic changes during liver fibrosis, we treated the M0MΦ with recombinant human CCL2 or its specific receptor antagonist INCB-3284. Furthermore, we used LX2 and TGF-β-activated LX2 to mimic the different activation statuses of aHSCs to further confirm our results. Results: In patients, the infiltration of M2 macrophages increased during the progression of liver fibrosis. Intriguingly, as a key molecule for aHSC chemotactic macrophage aggregation, CCL2 markedly up-regulated the expression of CD163 and CD206 on the macrophages, which was further confirmed by adding the CCR2 antagonist (INCB 3284) into the cell culture system. In addition, the TGF-β stimulated LX2 further confirmed that aHSCs up-regulate the expression of CD163 and CD206 on macrophages. LX2 stimulated with TGF-β could produce more CCL2 and up-regulate other M2 phenotype macrophage-specific markers, including IL-10, ARG-1, and CCR2 besides CD163 and CD206 at the gene level, indicating that the different activation status of aHSCs might affect the final phenotype and function of macrophages. Conclusions: The expression of the M2 macrophage marker increases during liver fibrosis progression and is associated with fibrosis severity. AHSCs can recruit macrophages through the CCL2/CCR2 pathway and induce M2 phenotypic transformation.
Keywords: CCL2; M2 macrophage; activated hepatic stellate cells; hepatitis B; liver fibrosis.
Copyright © 2021 Xi, Zheng, Li, Jiang, Wu, Gong, Jie, Li, Cao, Sha, Zhang and Chong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

