Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of miR-192 in Different Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33614788
- PMCID: PMC7878092
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8851035
Diagnostic and Prognostic Role of miR-192 in Different Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: It has been shown that miR-192 is abnormally expressed in a variety of cancer types and participates in different kinds of signaling pathways. The role of miR-192 in the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer has not been verified. This article is aimed at exploring the diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-192 through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
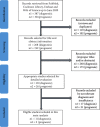
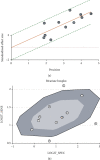
Methods: A systematic search was performed through PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library databases up to June 16, 2020. A total of 16 studies were enrolled in the meta-analyses, of which 11 articles were used for diagnostic meta-analysis and 5 articles were used for prognostic meta-analysis. The values of sensitivity and specificity using miR-192 expression as a diagnostic tool were pooled in the diagnostic meta-analysis. The hazard ratios (HRs) of overall survival (OS) with 95 confidence intervals (CIs) were extracted from the studies, and pooled HRs were evaluated in the prognostic meta-analysis. Eleven studies including 667 cancer patients and 514 controls met the eligibility criteria for the diagnostic meta-analysis. Five studies including 166 patients with high miR-192 expression and 236 patients with low miR-192 expression met the eligibility criteria for the prognostic meta-analysis.
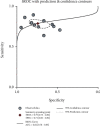
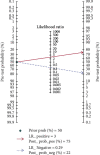
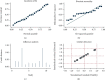
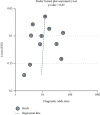
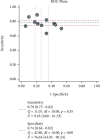
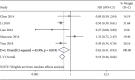
Results: The overall diagnostic accuracy was as follows: sensitivity 0.79 (95%CI = 0.75-0.82), specificity 0.74 (95%CI = 0.64-0.82), positive likelihood ratio 3.03 (95%CI = 2.11-4.34), negative likelihood ratio 0.29 (95%CI = 0.23-0.37), diagnostic odds ratio 10.50 (95%CI = 5.89-18.73), and area under the curve ratio (AUC) 0.82 (95%CI = 0.78-0.85). The overall prognostic analysis showed that high expression of miR-192 in patients was associated with positive survival (HR = 0.62, 95%CI : 0.41-0.93, p = 0.020).
Conclusion: Our results revealed that miR-192 was a potential biomarker with good sensitivity and specificity in cancers. Moreover, highly expressed miR-192 predicted a good prognosis for patients.
Copyright © 2021 Lili Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of miRNAs in Hepatoblastoma: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221087830. doi: 10.1177/15330338221087830. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 35532186 Free PMC article.
-
The value of miR-155 as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 14;19(1):1103. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6297-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31727002 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of diagnostic and prognostic value of miR-126 in non-small cell lung cancer.Biosci Rep. 2020 May 29;40(5):BSR20200349. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200349. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32329507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of microRNA-628 for cancers.J Cancer. 2018 Apr 12;9(9):1623-1634. doi: 10.7150/jca.24193. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29760801 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic role of miR-27a in cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Jul;247:154544. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154544. Epub 2023 May 22. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37235911 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-Coding RNA as a Biomarker in Lung Cancer.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Sep 30;10(5):50. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10050050. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 39452836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA Profiles of Canine Intestinal Carcinomas, Lymphomas and Enteritis Analysed by Digital Droplet PCR from FFPE Material.Vet Sci. 2023 Feb 6;10(2):125. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10020125. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36851429 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of the Immune System and Molecular Cell Signaling Pathways in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 12;24(2):1506. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021506. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological Findings in Gastrointestinal Neoplasms and Polyps in 860 Cats and a Pilot Study on miRNA Analyses.Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 3;9(9):477. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9090477. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36136693 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

