Hypochloremia Secondary to Diuretics in Preterm Infants: Should Clinicians Pay Close Attention?
- PMID: 33614850
- PMCID: PMC7868482
- DOI: 10.1177/2333794X21991014
Hypochloremia Secondary to Diuretics in Preterm Infants: Should Clinicians Pay Close Attention?
Abstract
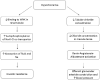
Diuretic therapy, commonly used in the newborn intensive care unit, is associated with a variety of electrolyte abnormalities such as hyponatremia, hypokalemia, and hypochloremia. Hypochloremia, often ignored, is associated with significant morbidities and increased mortality in infants and adults. Clinicians respond in a reflex manner to hyponatremia than to hypochloremia. Hypochloremia is associated with nephrocalcinosis, hypochloremic alkalosis, and poor growth. Besides, the diuretic resistance associated with hypochloremia makes maintaining chloride levels in the physiological range even more logical. Since sodium supplementation counters the renal absorption of calcium and lack of evidence for spironolactone role in diuretic therapy for bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), alternate chloride supplements such as potassium or arginine chloride may need to be considered in the management of hypochloremia due to diuretic therapy. In this review, we have summarized the current literature on hypochloremia secondary to diuretics and suggested a pragmatic approach to hypochloremia in preterm infants.
Keywords: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; diuretics; hypochloremia; metabolic alkalosis; preterm infants.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diuretic complications.Am J Med Sci. 2000 Jan;319(1):10-24. Am J Med Sci. 2000. PMID: 10653441 Review.
-
The Basic Metabolic Profile in Heart Failure-Marker and Modifier.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2017 Aug;14(4):311-320. doi: 10.1007/s11897-017-0344-x. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2017. PMID: 28674911 Review.
-
Hypochloremia, Diuretic Resistance, and Outcome in Patients With Acute Heart Failure.Circ Heart Fail. 2016 Aug;9(8):e003109. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.116.003109. Circ Heart Fail. 2016. PMID: 27507112 Clinical Trial.
-
Hypochloremia and Diuretic Resistance in Heart Failure: Mechanistic Insights.Circ Heart Fail. 2016 Aug;9(8):10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.116.003180 e003180. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.116.003180. Circ Heart Fail. 2016. PMID: 27507113 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Hypochloremia in cats - prevalence and associated diseases.Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere. 2016 Aug 17;44(4):237-44. doi: 10.15654/TPK-150647. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Kleintiere Heimtiere. 2016. PMID: 27074163
Cited by
-
Nomogram Prediction Model of Serum Chloride and Sodium Ions on the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury in Critically Ill Patients.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Aug 24;15:4785-4798. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S376168. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36045875 Free PMC article.
-
Cumulative Doses Predict the Risk of Furosemide-Induced Electrolyte Abnormalities in Critically Ill Neonates.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022 Jun 9;18:633-641. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S369737. eCollection 2022. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 35707182 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Hypochloremia Is Associated with Adverse Prognosis in Patients Repeatedly Hospitalized for Heart Failure.J Clin Med. 2023 Feb 5;12(4):1257. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041257. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36835793 Free PMC article.
-
Fluid and electrolyte management in the neonate and what can go wrong.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2024 Apr 1;36(2):198-203. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000001308. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 37962361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk factors and machine learning prediction models for bronchopulmonary dysplasia severity in the Chinese population.World J Pediatr. 2023 Jun;19(6):568-576. doi: 10.1007/s12519-022-00635-0. Epub 2022 Nov 10. World J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36357648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kao LC, Warburton D, Cheng MH, Cedeño C, Platzker AC, Keens TG. Effect of oral diuretics on pulmonary mechanics in infants with chronic bronchopulmonary dysplasia: results of a double-blind crossover sequential trial. Pediatrics. 1984;74:37-44. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical