The perspectives of biomarker-based electrochemical immunosensors, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Medical Things toward COVID-19 diagnosis and management
- PMID: 33615086
- PMCID: PMC7877231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2021.100443
The perspectives of biomarker-based electrochemical immunosensors, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Medical Things toward COVID-19 diagnosis and management
Abstract
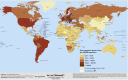
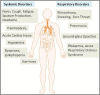
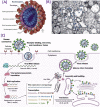
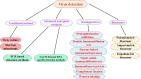
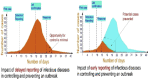
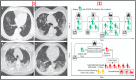
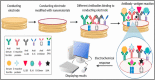
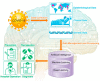
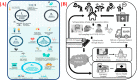
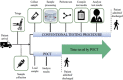
The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared the COVID-19 an international health emergency due to the severity of infection progression, which became more severe due to its continuous spread globally and the unavailability of appropriate therapy and diagnostics systems. Thus, there is a need for efficient devices to detect SARS-CoV-2 infection at an early stage. Nowadays, the reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technique is being applied for detecting this virus around the globe; however, factors such as stringent expertise, long diagnostic times, invasive and painful screening, and high costs have restricted the use of RT-PCR methods for rapid diagnostics. Therefore, the development of cost-effective, portable, sensitive, prompt and selective sensing systems to detect SARS-CoV-2 in biofluids at fM/pM/nM concentrations would be a breakthrough in diagnostics. Immunosensors that show increased specificity and sensitivity are considerably fast and do not imply costly reagents or instruments, reducing the cost for COVID-19 detection. The current developments in immunosensors perhaps signify the most significant opportunity for a rapid assay to detect COVID-19, without the need of highly skilled professionals and specialized tools to interpret results. Artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) can also be equipped with this immunosensing approach to investigate useful networking through database management, sharing, and analytics to prevent and manage COVID-19. Herein, we represent the collective concepts of biomarker-based immunosensors along with AI and IoMT as smart sensing strategies with bioinformatics approach to monitor non-invasive early stage SARS-CoV-2 development, with fast point-of-care (POC) diagnostics as the crucial goal. This approach should be implemented quickly and verified practicality for clinical samples before being set in the present times for mass-diagnostic research.
Keywords: Diagnostics; Electrochemical biosensors; Pandemic; Point-of-care; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Khan H. Letter to editor-impact of age factor in COVID-19 infectivity in population of nowshera KP, Pakistan. Middle East. J. Fam. Med. 2020;7(10):75.
-
- W. Coronavirus. WHO; 2020. https://covid19 int. Accessed.
-
- Paliwal P., Sargolzaei S., Bhardwaj S.K., Bhardwaj V., Dixit C., Kaushik A. Grand challenges in bio-nanotechnology to manage COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Nanotechnol. 2020;2:3.
-
- W. H. Organisation:. Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) situation report-48.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
