Nonlinear response characteristics of neural networks and single neurons undergoing optogenetic excitation
- PMID: 33615093
- PMCID: PMC7888483
- DOI: 10.1162/netn_a_00154
Nonlinear response characteristics of neural networks and single neurons undergoing optogenetic excitation
Abstract
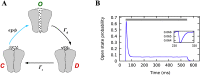
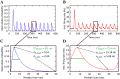
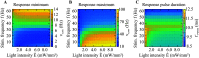
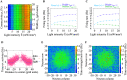
Optogenetic stimulation has become the method of choice for investigating neural computation in populations of neurons. Optogenetic experiments often aim to elicit a network response by stimulating specific groups of neurons. However, this is complicated by the fact that optogenetic stimulation is nonlinear, more light does not always equal to more spikes, and neurons that are not directly but indirectly stimulated could have a major impact on how networks respond to optogenetic stimulation. To clarify how optogenetic excitation of some neurons alters the network dynamics, we studied the temporal and spatial response of individual neurons and recurrent neural networks. In individual neurons, we find that neurons show a monotonic, saturating rate response to increasing light intensity and a nonmonotonic rate response to increasing pulse frequency. At the network level, we find that Gaussian light beams elicit spatial firing rate responses that are substantially broader than the stimulus profile. In summary, our analysis and our network simulation code allow us to predict the outcome of an optogenetic experiment and to assess whether the observed effects can be attributed to direct or indirect stimulation of neurons.
Keywords: Channelrhodopsin; Neural networks; Nonlinear response characteristics; Optogenetics.
© 2020 Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increasing the expression level of ChR2 enhances the optogenetic excitability of cochlear neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Nov 1;122(5):1962-1974. doi: 10.1152/jn.00828.2018. Epub 2019 Sep 18. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31533018 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the Effect of Temperature on Membrane Response of Light Stimulation in Optogenetically-Targeted Neurons.Front Comput Neurosci. 2020 Feb 4;14:5. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2020.00005. eCollection 2020. Front Comput Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32116619 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Neural Activity Predicts Sensory Acuity Under Optogenetic Manipulation.J Neurosci. 2018 Feb 21;38(8):2094-2105. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2457-17.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 24. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29367406 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress of Development of Optogenetic Implantable Neural Probes.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 11;18(8):1751. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081751. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28800085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optogenetic excitation of neurons with channelrhodopsins: light instrumentation, expression systems, and channelrhodopsin variants.Prog Brain Res. 2012;196:29-47. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-59426-6.00002-1. Prog Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22341319 Review.
Cited by
-
Optogenetic Stimulation Recruits Cortical Neurons in a Morphology-Dependent Manner.J Neurosci. 2024 Dec 4;44(49):e1215242024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1215-24.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39424369 Free PMC article.
-
Optogenetic stimulation of cell bodies versus axonal terminals generate comparable activity and functional connectivity patterns in the brain.Brain Stimul. 2025 May-Jun;18(3):822-828. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2025.03.006. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Brain Stimul. 2025. PMID: 40090667 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review to Compare Electrical, Magnetic, and Optogenetic Stimulation for Peripheral Nerve Repair.J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2024 Jun 29;6(5):722-739. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsg.2024.03.005. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Hand Surg Glob Online. 2024. PMID: 39381397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose-response relationship between the variables of unilateral optogenetic stimulation and transcallosal evoked responses in rat motor cortex.Front Neurosci. 2022 Sep 23;16:968839. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.968839. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36213739 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed interfacing by nanoscale photodiodes enables single-neuron light activation and sensory enhancement in 3D spinal explants.Sci Adv. 2022 Aug 12;8(32):eabp9257. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abp9257. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35960795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyden, E. S., Zhang, F., Bamberg, E., Nagel, G., & Deisseroth, K. (2005). Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nature Neuroscience, 8(9), 1263–1268. - PubMed
-
- Braitenberg, V., & Schüz, A. (1998). Cortex: statistics and geometry of neuronal connectivity (2nd ed.). Berlin, Germany: Springer.
-
- Brunel, N., Chance, F. S., Fourcaud, N., & Abbott, L. (2001). Effects of synaptic noise and filtering on the frequency response of spiking neurons. Physical Review Letters, 86(10), 2186. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
