DNA Nanostructures in the Fight Against Infectious Diseases
- PMID: 33615315
- PMCID: PMC7883073
- DOI: 10.1002/anbr.202000049
DNA Nanostructures in the Fight Against Infectious Diseases
Abstract
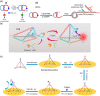
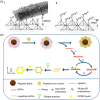
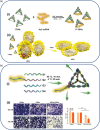
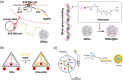
Throughout history, humanity has been threatened by countless epidemic and pandemic outbreaks of infectious diseases, from the Justinianic Plague to the Spanish flu to COVID-19. While numerous antimicrobial and antiviral drugs have been developed over the last 200 years to face these threats, the globalized and highly connected world of the 21st century demands for an ever-increasing efficiency in the detection and treatment of infectious diseases. Consequently, the rapidly evolving field of nanomedicine has taken up the challenge and developed a plethora of strategies to fight infectious diseases with the help of various nanomaterials such as noble metal nanoparticles, liposomes, nanogels, and virus capsids. DNA nanotechnology represents a comparatively recent addition to the nanomedicine arsenal, which, over the past decade, has made great progress in the area of cancer diagnostics and therapy. However, the past few years have seen also an increasing number of DNA nanotechnology-related studies that particularly focus on the detection and inhibition of microbial and viral pathogens. Herein, a brief overview of this rather young research field is provided, successful concepts as well as potential challenges are identified, and promising directions for future research are highlighted.
Keywords: DNA nanotechnologies; detection; infectious diseases; inhibitions; nanomedicine; pathogens.
© 2021 The Authors. Advanced NanoBiomed Research published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
