Xpert Ultra versus Xpert MTB/RIF for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults with presumptive pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 33616229
- PMCID: PMC12045032
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub5
Xpert Ultra versus Xpert MTB/RIF for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults with presumptive pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
Background: Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra (Xpert Ultra) are World Health Organization (WHO)-recommended rapid tests that simultaneously detect tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in people with signs and symptoms of tuberculosis. This review builds on our recent extensive Cochrane Review of Xpert MTB/RIF accuracy.
Objectives: To compare the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF for the detection of pulmonary tuberculosis and detection of rifampicin resistance in adults with presumptive pulmonary tuberculosis. For pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance, we also investigated potential sources of heterogeneity. We also summarized the frequency of Xpert Ultra trace-positive results, and estimated the accuracy of Xpert Ultra after repeat testing in those with trace-positive results.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Infectious Diseases Group Specialized Register, MEDLINE, Embase, Science Citation Index, Web of Science, LILACS, Scopus, the WHO ICTRP, the ISRCTN registry, and ProQuest to 28 January 2020 with no language restriction.
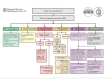
Selection criteria: We included diagnostic accuracy studies using respiratory specimens in adults with presumptive pulmonary tuberculosis that directly compared the index tests. For pulmonary tuberculosis detection, the reference standards were culture and a composite reference standard. For rifampicin resistance, the reference standards were culture-based drug susceptibility testing and line probe assays.
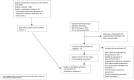
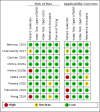
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted data using a standardized form, including data by smear and HIV status. We assessed risk of bias using QUADAS-2 and QUADAS-C. We performed meta-analyses comparing pooled sensitivities and specificities, separately for pulmonary tuberculosis detection and rifampicin resistance detection, and separately by reference standard. Most analyses used a bivariate random-effects model. For tuberculosis detection, we estimated accuracy in studies in participants who were not selected based on prior microscopy testing or history of tuberculosis. We performed subgroup analyses by smear status, HIV status, and history of tuberculosis. We summarized Xpert Ultra trace results.
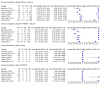
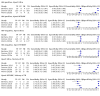
Main results: We identified nine studies (3500 participants): seven had unselected participants (2834 participants). All compared Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF for pulmonary tuberculosis detection; seven studies used a paired comparative accuracy design, and two studies used a randomized design. Five studies compared Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF for rifampicin resistance detection; four studies used a paired design, and one study used a randomized design. Of the nine included studies, seven (78%) were mainly or exclusively in high tuberculosis burden countries. For pulmonary tuberculosis detection, most studies had low risk of bias in all domains. Pulmonary tuberculosis detection Xpert Ultra pooled sensitivity and specificity (95% credible interval) against culture were 90.9% (86.2 to 94.7) and 95.6% (93.0 to 97.4) (7 studies, 2834 participants; high-certainty evidence) versus Xpert MTB/RIF pooled sensitivity and specificity of 84.7% (78.6 to 89.9) and 98.4% (97.0 to 99.3) (7 studies, 2835 participants; high-certainty evidence). The difference in the accuracy of Xpert Ultra minus Xpert MTB/RIF was estimated at 6.3% (0.1 to 12.8) for sensitivity and -2.7% (-5.7 to -0.5) for specificity. If the point estimates for Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF are applied to a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients, where 10% of those presenting with symptoms have pulmonary tuberculosis, Xpert Ultra will miss 9 cases, and Xpert MTB/RIF will miss 15 cases. The number of people wrongly diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis would be 40 with Xpert Ultra and 14 with Xpert MTB/RIF. In smear-negative, culture-positive participants, pooled sensitivity was 77.5% (67.6 to 85.6) for Xpert Ultra versus 60.6% (48.4 to 71.7) for Xpert MTB/RIF; pooled specificity was 95.8% (92.9 to 97.7) for Xpert Ultra versus 98.8% (97.7 to 99.5) for Xpert MTB/RIF (6 studies). In people living with HIV, pooled sensitivity was 87.6% (75.4 to 94.1) for Xpert Ultra versus 74.9% (58.7 to 86.2) for Xpert MTB/RIF; pooled specificity was 92.8% (82.3 to 97.0) for Xpert Ultra versus 99.7% (98.6 to 100.0) for Xpert MTB/RIF (3 studies). In participants with a history of tuberculosis, pooled sensitivity was 84.2% (72.5 to 91.7) for Xpert Ultra versus 81.8% (68.7 to 90.0) for Xpert MTB/RIF; pooled specificity was 88.2% (70.5 to 96.6) for Xpert Ultra versus 97.4% (91.7 to 99.5) for Xpert MTB/RIF (4 studies). The proportion of Ultra trace-positive results ranged from 3.0% to 30.4%. Data were insufficient to estimate the accuracy of Xpert Ultra repeat testing in individuals with initial trace-positive results. Rifampicin resistance detection Pooled sensitivity and specificity were 94.9% (88.9 to 97.9) and 99.1% (97.7 to 99.8) (5 studies, 921 participants; high-certainty evidence) for Xpert Ultra versus 95.3% (90.0 to 98.1) and 98.8% (97.2 to 99.6) (5 studies, 930 participants; high-certainty evidence) for Xpert MTB/RIF. The difference in the accuracy of Xpert Ultra minus Xpert MTB/RIF was estimated at -0.3% (-6.9 to 5.7) for sensitivity and 0.3% (-1.2 to 2.0) for specificity. If the point estimates for Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF are applied to a hypothetical cohort of 1000 patients, where 10% of those presenting with symptoms have rifampicin resistance, Xpert Ultra will miss 5 cases, and Xpert MTB/RIF will miss 5 cases. The number of people wrongly diagnosed with rifampicin resistance would be 8 with Xpert Ultra and 11 with Xpert MTB/RIF. We identified a higher number of rifampicin resistance indeterminate results with Xpert Ultra, pooled proportion 7.6% (2.4 to 21.0) compared to Xpert MTB/RIF pooled proportion 0.8% (0.2 to 2.4). The estimated difference in the pooled proportion of indeterminate rifampicin resistance results for Xpert Ultra versus Xpert MTB/RIF was 6.7% (1.4 to 20.1).
Authors' conclusions: Xpert Ultra has higher sensitivity and lower specificity than Xpert MTB/RIF for pulmonary tuberculosis, especially in smear-negative participants and people living with HIV. Xpert Ultra specificity was lower than that of Xpert MTB/RIF in participants with a history of tuberculosis. The sensitivity and specificity trade-off would be expected to vary by setting. For detection of rifampicin resistance, Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF had similar sensitivity and specificity. Ultra trace-positive results were common. Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF provide accurate results and can allow rapid initiation of treatment for rifampicin-resistant and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03154320 NCT03187964 NCT03356925 NCT03497195 NCT03712709 NCT04074369 NCT04122404 NCT02758236.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. on behalf of The Cochrane Collaboration.
Conflict of interest statement
JSZ received funding from USAID, administered by the World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland.
JSK has no known conflicts of interest.
IS received funding from USAID, administered by the World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland.
MK has received funding from USAID, administered by the World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland, for related systematic reviews.
ND has no known conflicts of interest.
SGS is employed by the Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND). FIND has conducted studies and published on Xpert MTB/RIF as part of a collaborative project between FIND, a Swiss nonprofit; Cepheid, a US company; and academic partners. The product developed through this partnership was developed under a contract that obligated FIND to pay for development costs and trial costs and Cepheid to make the test available at specified preferential pricing to the public sector in low‐ and middle‐income countries. In addition, FIND conducted studies for the Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assay, which have also been published.
EAO received funding from USAID, administered by the World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland.
FH received funding from USAID, administered by the World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland.
AAZ received funding from USAID, administered by the World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland.
MP serves on the Scientific Advisory Committee of Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND), Geneva. FIND is a nonprofit agency that works on global health diagnostics.
KRS received funding from USAID, administered by the World Health Organization (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland. In addition, she has received financial support from Cochrane Infectious Diseases, UK; McGill University, Canada; and the World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland, for the preparation of related systematic reviews and educational materials; consultancy fees from Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND), Switzerland (for the preparation of systematic reviews and GRADE tables), honoraria, and travel support to attend WHO guideline meetings.
DJH received funding from USAID, administered by the World Health Organization Global Tuberculosis Programme, Switzerland.
The authors have no financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in this review apart from those disclosed.
Figures






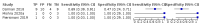





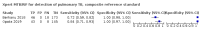

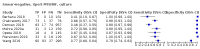
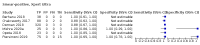


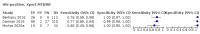
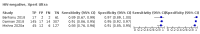
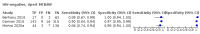
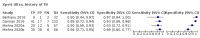
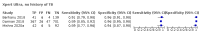

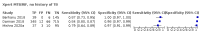


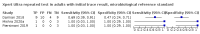
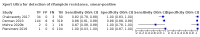



Update of
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 7;6(6):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 22;2:CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub5. PMID: 31173647 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Berhanu 2018 {published data only}
Chakravorty 2017 {published data only}
-
- Chakravorty S, Simmons AM, Rowneki M, Parmar H, Cao Y, Ryan J, et al. The new Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra: improving detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and resistance to rifampin in an assay suitable for point-of-care testing. Molecular Biology 2017;8(4):e00812-17. [DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00812-17] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Dorman 2018 {published data only}
Mishra 2020a {published data only}
-
- Mishra H, Reeve R, Palmer Z, Caldwell J, Dolby T, Naidoo C, et al. Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF for tuberculosis diagnosis in an HIV-endemic setting with a high burden of previous tuberculosis: a two cohort diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2020;8(4):368-82. - PubMed
Mishra 2020b {published data only}
-
- Mishra H, Reeve R, Palmer Z, Caldwell J, Dolby T, Naidoo C, et al. Xpert Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF for tuberculosis diagnosis in an HIV-endemic setting with a high burden of previous tuberculosis: a two cohort diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2020;8(4):368-82. - PubMed
Opota 2019 {published data only}
Pereira 2020 {published data only}
-
- Pereira GR, Barbosa MS, Dias NJD, Dos Santos FF, Rauber KA, Silva DR. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra performance for pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis in a city with high TB incidence in Brazil. Respiratory Medicine 2020;162:105876. - PubMed
Piersimoni 2019 {published data only}
-
- Piersimoni C, Gherardi G, Gracciotti N, Pocognoli A. Comparative evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF and the new Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra with respiratory and extra-pulmonary specimens for tuberculosis case detection in a low incidence setting. Journal of Clinical Tuberculosis and Other Mycobacterial Diseases 2019;15:100094. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2019.100094] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Wang 2019 {published data only}
-
- Wang G, Wang S, Jiang G, Yang X, Huang M, Huo F, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra improved the diagnosis of paucibacillary tuberculosis: a prospective cohort study. Journal of Infection 2019;78(4):311-6. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abong 2019 {published data only}
Acuna‐Villaorduna 2017 {published data only}
-
- Acuna-Villaorduna C, Orikiriza P, Nyehangane D, White LF, Mwanga-Amumpaire J, Kim S, et al. Effect of previous treatment and sputum quality on diagnostic accuracy of Xpert® MTB/RIF. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2017;21(4):389-97. - PubMed
Ade 2016 {published data only}
Adelman 2014 {published data only}
-
- Adelman MW, Tsegaye M, Kempker R, Abeje T, Tesfaye A, Aseffa A, et al. Enhanced active TB case finding among people living with HIV: impact of a rapid molecular test (XPERT MTB/RIF). Journal of Investigative Medicine 2014;62(2):570.
Afshan 2019 {published data only}
-
- Afshan G, Hussain M, Shafiq M. Sensitivity and specificity of Xpert MTB/RIF for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis, detection of RIF resistance and its concordance with gene sequencing for RIF Resistance. International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences 2019;8(10):59-66.
Agizew 2017 {published data only}
-
- Agizew T, Basotli J, Alexander H, Boyd R, Letsibogo G, Auld A, et al. Higher-than-expected prevalence of non-tuberculous mycobacteria in HIV setting in Botswana: implications for diagnostic algorithms using Xpert MTB/RIF assay. PLOS ONE 2017;12(12):e0189981. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0189981] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Agizew 2019 {published data only}
-
- Agizew T, Chihota V, Nyirenda S, Tedla Z, Auld AF, Mathebula U, et al. Tuberculosis treatment outcomes among people living with HIV diagnosed using Xpert MTB/RIF versus sputum-smear microscopy in Botswana: a stepped-wedge cluster randomised trial. BMC Infectious Diseases 2019;19(1):1058. - PMC - PubMed
Agrawal 2016 {published data only}
Agustina 2019 {published data only}
-
- Agustina B, Kartasasmita C, Hilmanto D. Comparison of GeneXpert MTB to Mycobacterium tuberculosis culture in children with tuberculosis. Paediatrica Indonesiana 2019;59(3):113-8.
Ai 2019 {published data only}
Akhter 2019 {published data only}
Alame‐Emane 2017 {published data only}
Al‐Ateah 2012 {published data only}
-
- Al-Ateah SM, Al-Dowaidi MM, El-Khizzi NA. Evaluation of direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in respiratory and non-respiratory clinical specimens using the Cepheid Gene Xpert® system. Saudi Medical Journal 2012;33(10):1100-5. - PubMed
Albay 2016 {published data only}
-
- Albay A, Guney M, Tekin K, Kisa O, Sig AK. Evaluation of the GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay for early diagnosis of tuberculosis and detection of rifampicin resistance in pulmonary and extrapulmonary specimens. Cukurova Medical Journal 2016;41(3):548-53.
Al‐Darraji 2016 {published data only}
-
- Al-Darraji HA, Altice FL, Kamarulzaman A. Undiagnosed pulmonary tuberculosis among prisoners in Malaysia: an overlooked risk for tuberculosis in the community. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2016;21(8):1049-58. - PubMed
Allahyartorkaman 2019 {published data only}
Alland 2015 {published data only}
-
- Alland D, Rowneki M, Smith L, Ryan J, Chancellor M, Marie Simmons A, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra: a new near-patient TB test with sensitivity equal to culture. Topics in Antiviral Medicine 2015;23(E-1):37.
Alnimr 2014 {published data only}
-
- Alnimr AM, Hassan MI. Potential of two nucleic acid amplification assays for quantifying mycobacterial load in respiratory and non-respiratory specimens: a prospective study. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2014;78(3):237-41. - PubMed
Alvarez 2015 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez GG, Dyk DD, Desjardlns M, Yasseen AS 3rd, Aaron SD, Cameron DW, et al. The feasibility, accuracy, and impact of Xpert MTB/RIF testing in a remote aboriginal community in Canada. Chest 2015;148(3):767-73. - PubMed
Alvarez‐Uria 2012 {published data only}
-
- Alvarez-Uria G, Azcona JM, Midde M, Naik PK, Reddy S, Reddy R. Rapid diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients. Comparison of LED fluorescent microscopy and the GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay in a district hospital in India. Tuberculosis Research and Treatment 2012;2012:932862. [DOI: 10.1155/2012/932862] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Alvis‐Zakzuk 2017 {published data only}
-
- Alvis-Zakzuk NJ, Carrasquilla ML, Gomez VJ, Robledo J, Alvis-Guzman NR, Hernandez JM. Diagnostic accuracy of three technologies for the diagnosis of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis [Precisión diagnóstica de tres pruebas moleculares para detectar la tuberculosis multirresistente]. Biomedica 2017;37(3):397-407. - PubMed
Andriani 2016 {published data only}
-
- Andriani R, Burhan E, Isbaniah F, Atas Asri SD. Preliminary study of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for mycobacterium tuberculosis detection in new presumptive tuberculosis patients with negative sputum acid-fast bacilli. Respirology 2016;21 Suppl 3:197.
Antonenka 2013 {published data only}
-
- Antonenka U, Hofmann-Thiel S, Turaev L, Esenalieva A, Abdulloeva M, Sahalchyk E, et al. Comparison of Xpert MTB/RIF with ProbeTec ET DTB and COBAS TaqMan MTB for direct detection of M. tuberculosis complex in respiratory specimens. BMC Infectious Diseases 2013;13:280. [DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-280] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ardizzoni 2019 {published data only}
Aricha 2019 {published data only}
-
- Aricha SA, Kingwara L, Mwirigi NW, Chaba L, Kiptai T, Wahogo J, et al. Comparison of GeneXpert and line probe assay for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampicin-mono resistance at the National Tuberculosis Reference Laboratory, Kenya. BMC Infectious Diseases 2019;19(1):852. - PMC - PubMed
Armand 2011 {published data only}
Asencio 2013 {published data only}
-
- Asencio Egea MA, Vaquero MH, Carranza Gonzalez R, Castellanos Monedero J, Franco Huerta M, Bravo Nieto JM, et al. Economic impact of the introduction of a technique for early detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex in clinical samples in a Spanish hospital. Revista Española de Salud Pública 2013;87(4):419-25. - PubMed
Aston 2016 {published data only}
-
- Aston SJ, Ho A, Jary H, Everett D, Mwandumba H, Heyderman RS, et al. Aetiology and outcome of community-acquired pneumonia in HIV-infected Malawian adults. Topics in Antiviral Medicine 2016;24(E-1):322.
Atashi 2017 {published data only}
Atehortua 2015 {published data only}
-
- Atehortua S, Ramirez F, Echeverri LM, Penata A, Ospina S. Xpert MTB/RIF test performance assay in respiratory samples at real work settings in a developing country. Biomedica 2015;35(1):125-30. - PubMed
Atuhumuza 2016 {published data only}
-
- Atuhumuza E, Yoon C, Katende J, Asege L, Mwebe S, Andama A, et al. Intensified tuberculosis case-finding among people living with HIV: diagnostic yield of Xpert MTB/RIF, urine lipoarabinomannan and liquid culture. Journal of the International AIDS Society 2016;19:WEAB0202.
Atwine 2015 {published data only}
-
- Atwine D, Nansumba M, Orikiriza P, Riera M, Nackers F, Kamara N, et al. Intra-gastric string test: an effective tool for diagnosing tuberculosis in adults unable to produce sputum. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2015;19(5):558-64. - PubMed
Auld 2016 {published data only}
Aurin 2014 {published data only}
Avashia 2016 {published data only}
-
- Avashia S, Choubey S, Mishra S, Kharate A. To study the usefulness of CBNAAT (cartridge based nuclear acid amplification test) in BAL (bronchoalveolar lavage) samples in the diagnosis of smear-negative/non sputum producing patients with suspected tuberculosis. JEMDS: Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2016;5(1):55-9.
Ayala 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ayala G, Garay J, Aragon M, Decroo T, Zachariah R. Trends in tuberculosis notification and treatment outcomes in prisons: a country-wide assessment in El Salvador from 2009-2014. Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública 2016;39(1):38-43. - PubMed
Aydemir 2019 {published data only}
-
- Aydemir O, Karakece E, Koroglu M, Altindis M, Terzi HA. Comparison of the GeneXpert MTB/RIF test and conventional methods in the diagnosis of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clinical Laboratory 2019;65(1-2):1-6. - PubMed
Bablishvili 2015 {published data only}
Badal‐Faesen 2017 {published data only}
-
- Badal-Faesen S, Firnhaber C, Kendall MA, Wu X, Grinsztejn B, Escada RO, et al. Impact of larger sputum volume on Xpert® MTB/RIF assay detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in smear-negative individuals with suspected tuberculosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017;6(8):e78. [DOI: 10.3390/jcm6080078] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Baikunje 2019 {published data only}
-
- Baikunje N, Behera D, Rajwanshi A, Sharma M, Sharma A, Sharma K. Comparative evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay, GeneXpert MTB/Rif and multiplex PCR for the diagnosis of tubercular lymphadenitis in HIV-infected patients of North India. Molecular and Cellular Probes 2019;48:101459. - PubMed
Bajrami 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bajrami R, Mulliqi G, Kurti A, Lila G, Raka L. Comparison of GeneXpert MTB/RIF and conventional methods for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in Kosovo. Journal of Infection in Developing Countries 2016;10(4):418-22. - PubMed
Balcha 2014 {published data only}
-
- Balcha TT, Winqvist N, Sturegard E, Skogmar S, Reepalu A, Jemal ZH, et al. Detection of lipoarabinomannan in urine for identification of active tuberculosis among HIV-positive adults in Ethiopian health centres. Tropical Medicine & International Health 2014;19(6):734-42. - PubMed
Banu 2014 {published data only}
Barcellini 2019 {published data only}
-
- Barcellini L, Borroni E, Cimaglia C, Girardi E, Matteelli A, Marchese V, et al. App-based symptoms screening with Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assay used for active tuberculosis detection in migrants at point of arrivals in Italy: the E-DETECT TB intervention analysis. PLOS ONE 2019;14(7):e0218039. - PMC - PubMed
Barkham 2016 {published data only}
-
- Barkham T, Tang WY. GeneXpert - a state of the art commercial PCR assay, misses a fifth of tuberculosis cases. Annals of the Academy of Medicine Singapore 2016;45 (9 Suppl 1):S53.
Barnard 2012 {published data only}
Bates 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bates M, O'Grady J, Maeurer M, Tembo J, Chilukutu L, Chabala C, et al. Assessment of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay for diagnosis of tuberculosis with gastric lavage aspirates in children in sub-Saharan Africa: a prospective descriptive study. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2013;13(1):36-42. - PubMed
Benjamin 2019 {published data only}
Bhardwaj 2019 {published data only}
-
- Bhardwaj A, Khan S, Kumar A, George L, Mehta A, Radhakrishnan K. Assessing the utility of GeneXpert MTB/Rif assay in a tertiary care centre in Southern India with established microscopy and liquid culture facilities. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 2019;67(8):31-4. - PubMed
Biadglegne 2014 {published data only}
Bilgin 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bilgin K, Yanik K, Karadag A, Odabasi H, Tas H, Gunaydin M. Comparison of a real-time polymerase chain reaction-based system and Erlich-Ziehl-Neelsen method with culture in the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2016;46(1):203-6. - PubMed
Bimba 2019 {published data only}
Bisognin 2018 {published data only}
Bjerrum 2015 {published data only}
Boakye‐Appiah 2016 {published data only}
-
- Boakye-Appiah JK, Steinmetz AR, Pupulampu P, Ofori-Yirenkyi S, Tetteh I, Frimpong M, et al. High prevalence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among patients with rifampicin resistance using GeneXpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampicin in Ghana. International Journal of Mycobacteriology 2016;5(2):226-30. - PubMed
Bojang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Bojang AL, Mendy FS, Tientcheu LD, Otu J, Antonio M, Kampmann B, et al. Comparison of TB-LAMP, GeneXpert MTB/RIF and culture for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in The Gambia. Journal of Infection 2016;72(3):332-7. - PubMed
Bonnet 2017 {published data only}
Borodulina 2019 {published data only}
-
- Borodulina EA, Borodulin BE, In'kova AT, Vdoushkina ES, Povalyayeva LV. New possibilities to diagnose pulmonary tuberculosis at a pulmonology inpatient department. Pulmonologiya 2019;29(3):321-6.
Boum 2016 {published data only}
Bowles 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bowles EC, Freyée B, Van Ingen J, Mulder B, Boeree MJ, Van Soolingen D. Xpert MTB/RIF®, a novel automated polymerase chain reaction-based tool for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2011;15(7):988-9. - PubMed
Bunsow 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bunsow E, Ruiz-Serrano MJ, Lopez Roa P, Kestler M, Viedma DG, Bouza E. Evaluation of GeneXpert MTB/RIF for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and resistance to rifampin in clinical specimens. Journal of Infection 2014;68(4):338-43. - PubMed
Byashalira 2019 {published data only}
-
- Byashalira K, Mbelele P, Semvua H, Chilongola J, Semvua S, Liyoyo A, et al. Clinical outcomes of new algorithm for diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis sepsis in HIV patients. International Journal of Mycobacteriology 2019;8(4):313-9. - PubMed
Capocci 2016 {published data only}
-
- Capocci S, Sewell J, Smith C, Cropley I, Bhagani S, Morris S, et al. Testing for TB in a contemporary UK HIV clinic - is it really worth it? HIV Medicine 2016;17(Suppl 1):38-9.
Causse 2011 {published data only}
Cavanaugh 2016 {published data only}
Cayci 2017 {published data only}
Celik 2015 {published data only}
-
- Celik C, Gozel MG, Bakici MZ, Berk S, Ozsahin SL, Gulturk E. Applicability of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for routine diagnosis of tuberculosis: a four-year single-center experience. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2015;45(6):1329-34. - PubMed
Chakraborty 2019 {published data only}
-
- Chakraborty A, Ramaswamy S, Shivananjiah AJ, Puttaswamy RB, Chikkavenkatappa N. The role of GeneXpert in the diagnosis of tubercular pleural effusion in India. Advances in Respiratory Medicine 2019;87(5):276-80. - PubMed
Chhajed 2019 {published data only}
Chishty 2016 {published data only}
-
- Chishty S, Farooqi J, Shafqat Y, Shafiq S, Jabeen K, Hasan R. Performance of Xpert MTB/RIF assay from fluorescent acid fast stained slides. European Respiratory Journal. European Respiratory Society Annual Congress 2016;48(Suppl 60):PA2781.
Ciftçi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ciftçi IH, Aslan MH, Aşik G. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF results for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in clinical samples. Mikrobiyoloji bülteni 2011;45(1):43-7. - PubMed
Clouse 2012 {published data only}
-
- Clouse K, Page-Shipp L, Dansey H, Moatlhodi B, Scott L, Bassett J, et al. Implementation of Xpert MTB/RIF for routine point-of-care diagnosis of tuberculosis at the primary care level. South African Medical Journal 2012;102(10):805-7. - PubMed
Cross 2014 {published data only}
Cross 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cross LJ, Anscombe C, McHugh TD, Abubakar I, Shorten RJ, Thorne N, et al. A rapid and sensitive diagnostic screening assay for detection of mycobacteria including Mycobacterium tuberculosis directly from sputum without extraction. International Journal of Bacteriology 2015;2015:593745. - PMC - PubMed
Dagnra 2015 {published data only}
Dahale 2019 {published data only}
Daum 2015 {published data only}
-
- Daum LT, Peters RP, Fourie PB, Jonkman K, Worthy SA, Rodriguez JD, et al. Molecular detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from sputum transported in PrimeStore® from rural settings. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2015;19(5):552-7. - PubMed
Deggim 2013 {published data only}
Dierberg 2016 {published data only}
Dorjee 2012 {published data only}
-
- Dorjee K, Salvo F, Dierberg KL. Xpert® MTB/RIF diagnosed disseminated smear-negative MDR-TB in a sub-district hospital in India. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2012;16(11):1560-1. - PubMed
Dorman 2012 {published data only}
Dowdy 2011 {published data only}
Eldin 2019 {published data only}
-
- Eldin MT, Hamid HA, Elnady M. Evaluation of GeneXpert as a new diagnostic tool for detection of pulmonary tuberculosis. Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis 2019;68(3):270-3.
Elzein 2019 {published data only}
Fantahun 2019 {published data only}
Feasey 2013 {published data only}
-
- Feasey NA, Banada PP, Howson W, Sloan DJ, Mdolo A, Boehme C, et al. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF for detection of tuberculosis from blood samples of HIV-infected adults confirms Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteremia as an indicator of poor prognosis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2013;51(7):2311-6. - PMC - PubMed
Fernandez 2017 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez Sanchez M, Lasso JI, Canas A, Morantes Ariza C, Cortes G, Sanchez Duran L, et al. Evaluation of the operating characteristics of GeneXpert MTB/RIF at a national reference center: Hospital Universitario San Ignacio, Bogota, Colombia. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. American Thoracic Society International Conference 2017;195:A2084.
FIND 2011 {published data only}
-
- Foundation for Innovative Diagnostics. Performance of Xpert MTB/RIF Version G4 assay, Version and date: 1.0/30 Nov 2011, Project: 7210. www.stoptb.org/wg/gli/assets/documents/map/findg4cartridge.pdf (accessed 8 May 2019).
Fong 2017 {published data only}
-
- Fong A, Wei C, Chang AH, Kerndt PR, Shulman IA, Butler-Wu S. Evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the detection of tuberculosis in patients being evaluated for tuberculosis in a large public hospital in the United States. Laboratory Investigation 2017;97 Suppl 1:390A.
Friedrich 2011 {published data only}
Gama de Andrade 2017 {published data only}
-
- Gama de Andrade TL, Gouget Ferreira Silvano RG, Pombo March MF, Coelho Soares EC, Couto Sant'anna C, Baroni Aurilio R. The Xpert MTB-RIF to diagnose tuberculosis in adolescents from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Pediatric Pulmonology 2017;52(Suppl 46):S164-5.
Garcia‐Basteiro 2019 {published data only}
Gati 2018 {published data only}
Gelalcha 2017 {published data only}
Gounder 2014 {published data only}
Griesel 2016 {published data only}
-
- Griesel R, Stewart A, Van Der Plas H, Sikhondze W, Rangaka M, Maartens G, et al. A clinical prediction rule for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in seriously ill adults. Topics in Antiviral Medicine 2016;24 (E-1):309-10.
Griesel 2017 {published data only}
Guenaoui 2016 {published data only}
-
- Guenaoui K, Harir N, Ouardi A, Zeggai S, Sellam F, Bekri F, et al. Use of GeneXpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampicin for rapid detection of rifampicin resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains of clinically suspected multi-drug resistance tuberculosis cases. Annals of Translational Medicine 2016;4(9):168. - PMC - PubMed
Gupta 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gupta RK, Lawn SD, Booth H, Morris-Jones S. What is the role for Xpert® MTB/RIF in high-resource settings? Experience from a central London hospital. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2014;18(11):1323-6. - PubMed
Gurbanova 2016 {published data only}
-
- Gurbanova E, Mehdiyev R, Blondal K, Tahirli R, Mirzayev F, Hillemann D, et al. Interpretation of indeterminate RIF-susceptibility results obtained by rapid molecular diagnostics test. European Respiratory Journal. European Respiratory Society Annual Congress 2016;48(Suppl 60):PA1907.
Gurbanova 2017 {published data only}
-
- Gurbanova E, Mehdiyev R, Blondal K, Tahirli R, Mirzayev F, Hillemann D, et al. Mitigation of discordant rifampicin-susceptibility results obtained by Xpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/Rifampicin and Mycobacterium Growth Indicator Tube. Microbial Drug Resistance 2017;23(8):1045-52. - PubMed
Gursoy 2016 {published data only}
-
- Gursoy NC, Yakupogullari Y, Tekerekoglu MS, Otlu B. Evaluation of the diagnostic performance of Xpert MTB/RIF test for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampin resistance in clinical samples. Mikrobiyoloji bülteni 2016;50(2):196-204. - PubMed
Habeenzu 2017 {published data only}
-
- Habeenzu C, Nakajima C, Solo E, Bwalya P, Kajino K, Miller M, et al. Evaluation of in-house loop-mediated isothermal amplification for tuberculosis diagnosis compared with Xpert MTB/RIF. Journal of Infection in Developing Countries 2017;11(6):440-4. - PubMed
Hai 2019 {published data only}
-
- Hai HT, Vinh DN, Thu DDA, Hanh NT, Phu NH, Srinivasan V, et al. Comparison of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis molecular bacterial load assay, microscopy and GeneXpert versus liquid culture for viable bacterial load quantification before and after starting pulmonary tuberculosis treatment. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2019;119:101864. - PMC - PubMed
Hanifa 2016 {published data only}
Heidebrecht 2016 {published data only}
Hillemann 2011 {published data only}
Hiza 2017 {published data only}
Ho 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ho J, Nguyen PT, Nguyen TA, Tran KH, Nguyen S, Nguyen NV, et al. Reassessment of the positive predictive value and specificity of Xpert MTB/RIF: a diagnostic accuracy study in the context of community-wide screening for tuberculosis. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2016;16(9):1045-51. - PubMed
Hodille 2019 {published data only}
-
- Hodille E, Maisson A, Charlet L, Bauduin C, Genestet C, Fredenucci I, et al. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra performance for pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis on smear-negative respiratory samples in a French centre. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 2019;38(3):601-5. - PubMed
Horo 2017 {published data only}
-
- Horo K, N'Guessan R, Koffi MO, Kouame-N'Takpe N, Kone A, Samake K, et al. Use of the Xpert® MTB/RIF test in routine screening of new cases of pulmonary tuberculosis in an endemic area. Revue des Maladies Respiratoires 2017;34(7):749-57. - PubMed
Hu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hu P, Bai L, Liu F, Ou X, Zhang Z, Yi S, et al. Evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay for diagnosis of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance in county-level laboratories in Hunan province, China. Chinese Medical Journal 2014;127(21):3744-50. - PubMed
Huang 2018 {published data only}
Huerga 2017 {published data only}
-
- Huerga H, Ferlazzo G, Bevilacqua P, Kirubi B, Ardizzoni E, Wanjala S, et al. Incremental yield of including determine-TB LAM assay in diagnostic algorithms for hospitalized and ambulatory HIV-positive patients in Kenya. PLOS ONE 2017;12(1):e0170976. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170976] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ioannidis 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ioannidis P, Papaventsis D, Nikolaou S, Karabela S, Konstantinidou E, Marinou I, et al. Tuberculosis resistance detection rate to the two main anti-TB drugs, isoniazid and rifampicin, using molecular techniques: experience of the Hellenic National Reference Center for Mycobacteria. Acta Microbiologica Hellenica 2010;55:175-82.
Ioannidis 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ioannidis P, Papaventsis D, Karabela S, Nikolaou S, Panagi M, Raftopoulou E, et al. Cepheid GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis detection and rifampin resistance identification in patients with substantial clinical indications of tuberculosis and smear-negative microscopy results. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2011;49(8):3068-70. - PMC - PubMed
Iram 2015 {published data only}
Jafari 2013 {published data only}
-
- Jafari C, Ernst M, Kalsdorf B, Lange C. Comparison of molecular and immunological methods for the rapid diagnosis of smear-negative tuberculosis. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2013;17(11):1459-65. - PubMed
Jin 2019 {published data only}
-
- Jin Y, Wang HQ, Fan JG, Pang J, Zhang PY, Li T. Evaluation of GeneXpert MTB/RIF and BACTEC-MGIT 960 for the detection of tuberculosis among pneumoconiosis-associated tuberculosis patients. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 2019;37(9):690-3. - PubMed
Jing 2017 {published data only}
-
- Jing H, Lu ZM, Deng YF, Gao DC, Li L, Graviss EA, et al. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF in detection of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis cases in China. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology 2017;10(4):4847-51.
Jipa 2016 {published data only}
-
- Jipa R, Manea E, Cernat R, Iringo K, Vat AA, Arbune M, et al. Drug-resistant tuberculosis in HIV infected patients. BMC Infectious Diseases 2016;16(4):A107.
Jones‐Lopez 2014 {published data only}
Kang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Kang JY, Hyung Woo K, Sanghoon J, Jaeha L, Shinyoung K, Chan Kwon P, et al. Clinical features of discordant result between molecular and phenotypic susceptibility tests in tuberculosis patients. Respirology 2016;21(Suppl 3):200.
Kaur 2016 {published data only}
Kayigire 2013 {published data only}
Kazemian 2019 {published data only}
-
- Kazemian H, Kardan-Yamchi J, Bahador A, Khonsari S, Nasehi M, Hamzehloo G, et al. Efficacy of line probe assay in detection of drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis in comparison with GeneXpert and phenotypic methods in Iran and genetic analysis of isolates by MIRU-VNTR. Infection and Drug Resistance 2019;12:3585-93. - PMC - PubMed
Kelly‐Cirino 2017 {published data only}
Kendall 2019 {published data only}
Kerkhoff 2013 {published data only}
Kerkhoff 2014 {published data only}
Khadka 2019 {published data only}
Khalil 2015 {published data only}
-
- Khalil KF, Butt T. Diagnostic yield of bronchoalveolar lavage gene Xpert in smear-negative and sputum-scarce pulmonary tuberculosis. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan 2015;25(2):115-8. - PubMed
Khan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Khan SU, Rahman H, Ayaz S, Qasim M, Jabbar A, Khurshid M, et al. GeneXpert assay for rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in respiratory specimens from a high TB endemic area of Pakistan. Microbial Pathogenesis 2016;95:82-5. - PubMed
Kim 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kim SY, Kim H, Kim SY, Ra EK, Joo SI, Shin S, et al. The Xpert® MTB/RIF assay evaluation in South Korea, a country with an intermediate tuberculosis burden. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2012;16(11):1471-6. - PubMed
Kim CH 2014 {published data only}
Kim CH 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kim CH, Hyun IG, Hwang YI, Kim DG, Lee CY, Lee MG, et al. Identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampin resistance in clinical specimens using the XpertMTB/RIF assay. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science 2015;45(1):32-8. - PubMed
Kim MJ 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kim MJ, Nam YS, Cho SY, Park TS, Lee HJ. Comparison of the Xpert MTB/RIF Assay and real-time PCR for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science 2015;45(3):327-32. - PubMed
Kim YW 2015 {published data only}
-
- Kim YW, Seong MW, Kim TS, Yoo CG, Han SK, Yim JJ. Evaluation of Xpert® MTB/RIF assay: diagnosis and treatment outcomes in rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2015;19(10):1216-21. - PubMed
Kolia‐Diafouka 2019 {published data only}
-
- Kolia-Diafouka P, Carrere-Kremer S, Lounnas M, Bourdin A, Kremer L, Van de Perre P, et al. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in paucibacillary sputum: performances of the Xpert MTB/RIF ultra compared to the Xpert MTB/RIF, and IS6110 PCR. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2019;94(4):365-70. - PubMed
Lange 2017 {published data only}
-
- Lange B, Khan P, Kalmambetova G, Al-Darraji HA, Alland D, Antonenka U, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the Xpert® MTB/RIF cycle threshold level to predict smear positivity: a meta-analysis. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2017;21(5):493-502. - PubMed
Laskar 2017 {published data only}
-
- Laskar N, Hossain MA, Nasreen SA, Kamal SM, Roy S, Nahar F, et al. Comparative yielding of BACTEC MGIT 960 and GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay for rapid diagnosis of drug resistance tuberculosis from sputum specimen. Mymensingh Medical Journal 2017;26(4):885-91. - PubMed
Lawn 2012a {published data only}
Lawn 2012b {published data only}
Lawn 2012c {published data only}
-
- Lawn SD, Kerkhoff AD, Vogt M, Wood R. Clinical significance of lipoarabinomannan detection in urine using a low-cost point-of-care diagnostic assay for HIV-associated tuberculosis. AIDS 2012;26(13):1635-43. - PubMed
Lawn 2013 {published data only}
Lawn 2015 {published data only}
-
- Lawn SD, Kerkhoff AD, Burton R, Schutz C, Van Wyk G, Vogt M, et al. Rapid microbiological screening for tuberculosis in HIV-positive patients on the first day of acute hospital admission by systematic testing of urine samples using Xpert MTB/RIF: a prospective cohort in South Africa. BMC Medicine 2015;13:192. - PMC - PubMed
Lawn 2017 {published data only}
-
- Lawn SD, Kerkhoff AD, Burton R, Schutz C, Boulle A, Vogt M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy, incremental yield and prognostic value of Determine TB-LAM for routine diagnostic testing for tuberculosis in HIV-infected patients requiring acute hospital admission in South Africa: a prospective cohort. BMC Medicine 2017;15(1):67. - PMC - PubMed
Lebina 2016 {published data only}
Lessells 2017 {published data only}
Li 2016 {published data only}
-
- Li Q, Bao XD, Liu Y, Ou XC, Pang Y, Zhao YL. Comparison of two molecular assays for detecting smear negative pulmonary tuberculosis. Biomedical and Environmental Sciences 2016;29(4):248-53. - PubMed
Li 2017 {published data only}
Li 2020 {published data only}
-
- Li X, Du W, Wang Y, Liu Z, Li K, Chen H, et al. Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis meningitis by detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell-free DNA in cerebrospinal fluid. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 2020;153(1):126-30. - PubMed
Ligthelm 2011 {published data only}
Lombardi 2017 {published data only}
Luetkemeyer 2016 {published data only}
-
- Luetkemeyer AF, Firnhaber C, Kendall MA, Wu X, Mazurek GH, Benator DA, et al. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIFversus AFB smear and culture to identify pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with suspected tuberculosis from low and higher prevalence settings. Clinical InfectiousDiseases 2016;62(9):1081–8. - PMC - PubMed
Mafort 2017 {published data only}
-
- Mafort TT, Rodrigues LS, Santos A, Reis LVT, Faria LF, Brito GMX, et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage GeneXpert MTB/RIF performance in smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis - a tertiary care experience in Rio De Janeiro, Brazil. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. American Thoracic Society International Conference 2017;195:A2085.
Malbruny 2011 {published data only}
-
- Malbruny B, Le Marrec G, Courageux K, Leclercq R, Cattoir V. Rapid and efficient detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in respiratory and non-respiratory samples. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2011;15(4):553-5. - PubMed
Marlowe 2011 {published data only}
Matabane 2015 {published data only}
Mave 2017 {published data only}
Maynard‐Smith 2014 {published data only}
Mechal 2019 {published data only}
Miller 2011 {published data only}
Miotto 2012 {published data only}
-
- Miotto P, Bigoni S, Migliori GB, Matteelli A, Cirillo DM. Early tuberculosis treatment monitoring by Xpert(R) MTB/RIF. European Respiratory Journal 2012;39(5):1269-71. - PubMed
Mntonintshi 2017 {published data only}
Modi 2016 {published data only}
-
- Modi S, Cavanaugh JS, Shiraishi RW, Alexander HL, McCarthy KD, Burmen B, et al. Performance of clinical screening algorithms for tuberculosis intensified case finding among people living with HIV in Western Kenya. PLOS ONE 2016;11(12):e0167685. [DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167685] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Mokaddas 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mokaddas EM, Saadaldeen H, Ahmad S. Comparison of two molecular methods and an automated liquid culture system for the early detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from both pulmonary and extrapulmonary specimens in Kuwait. International Journal of Mycobacteriology 2016;5 Suppl 1:S74-5. - PubMed
More 2017 {published data only}
Morozova 2016 {published data only}
-
- Morozova TI, Salina T. The results of drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to rifampicin by Xpert MTB/RIF BACTEC MGIT 960 as compared with the method of seeding on solid nutrient media. European Respiratory Journal. European Respiratory Society Annual Congress 2016;48(Suppl 60):PA2783.
Moure 2012 {published data only}
Mukherjee 2017 {published data only}
-
- Mukherjee S, Biswas D, Begum S, Ghosh P, Paul A, Sarkar S. Evaluation of cartridge based nucleic acid amplification test in diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. JEMDS: Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2017;6(74):5281-6.
Mulder 2017 {published data only}
-
- Mulder C, Mgode GF, Ellis H, Valverde E, Beyene N, Cox C, et al. Accuracy of giant African pouched rats for diagnosing tuberculosis: comparison with culture and Xpert® MTB/RIF. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2017;21(11):1127-33. - PubMed
Muñoz 2013 {published data only}
-
- Muñoz L, Moure R, Porta N, Gonzalez L, Guerra R, Alcaide F, et al. GeneXpert® for smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis: does it play a role in low-burden countries? Diagnostic Microbiology Infectious Disease 2013;75(3):325-6. - PubMed
Myneedu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Myneedu VP, Behera D, Verma AK, Bhalla M, Singh N, Arora J, et al. Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for tuberculosis diagnosis: evaluation in an Indian setting. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2014;18(8):958-60. - PubMed
Naidoo 2016 {published data only}
Narasimooloo 2012 {published data only}
-
- Narasimooloo R, Ross A. Delay in commencing treatment for MDR TB at a specialised TB treatment centre in KwaZulu-Natal. South African Medical Journal 2012;102(6 Pt 2):360-2. - PubMed
Ng 2018 {published data only}
Nguyen 2018 {published data only}
-
- Nguyen VA, Nguyen HV, Dinh TV, Du HH, Do CN, Marks GB, et al. Evaluation of Loopamp™ MTBC detection kit for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis at a peripheral laboratory in a high burden setting. Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2017;90(3):190-5. - PubMed
Ngwira 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ngwira LG, Khundi M, Barnes GL, Nkhoma A, Murowa M, Cohn S, et al. Screening for tuberculosis with Xpert MTB/RIF versus fluorescent microscopy among people newly diagnosed with HIV in rural Malawi: a cluster-randomized trial. Journal of the International AIDS Society 2017;20:93-4.
Nhu 2013 {published data only}
Nicol 2011 {published data only}
Ninan 2016 {published data only}
Nosova 2013a {published data only}
-
- Nosova EY, Krasnova MA, Galkina KY, Makarova MV, Litvinov VI, Moroz AM. Comparing performance of "TB-BIOCHIP", "Xpert MTB/RIF" and "genotype MTBDRplus" assays for fast identification of mutations in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in sputum from TB patients. Molekuliarnaia Biologiia (Mosk) 2013;47(2):267-74. - PubMed
Nosova 2013b {published data only}
-
- Nosova EY, Krasnova MA, Galkina KY, Makarova MV, Litvinov VI, Moroz AM. Comparative analysis of TB Biochip, Xpert MTB/RIF, and GenoType MTBDRplus test systems for rapid determination of mutations responsible for drug resistance of M-tuberculosis complex (in sputum from patients in Moscow region). Molecular Biology (Moscow) 2013;47(2):236-41.
Ntinginya 2012 {published data only}
-
- Ntinginya EN, Squire SB, Millington KA, Mtafya B, Saathoff E, Heinrich N, et al. Performance of the Xpert® MTB/RIF assay in an active case-finding strategy: a pilot study from Tanzania. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2012;16(11):1468-70. - PubMed
O'Grady 2012 {published data only}
-
- O'Grady J, Bates M, Chilukutu L, Mzyece J, Cheelo B, Chilufya M, et al. Evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay at a tertiary care referral hospital in a setting where tuberculosis and HIV infection are highly endemic. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2012;55(9):1171-8. - PubMed
Oliveira 2019 {published data only}
-
- Oliveira MCB, Sant'Anna CC, Luiz RR, Soares ECC, Kritski AL. Contribution of Xpert MTB/RIF to clinical diagnosis in adolescents with tuberculosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2019;23(10):1115-21. - PubMed
Omar 2019 {published data only}
-
- Omar A, Elfadl AE, Ahmed Y, Hosny M. Genexpert test and tuberculous pleural effusion: a new diagnostic method for an old medical problem. Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis 2019;68(4):493-7.
Omrani 2014 {published data only}
Opota 2016 {published data only}
-
- Opota O, Senn L, Prod'hom G, Mazza-Stalder J, Tissot F, Greub G, et al. Added value of molecular assay Xpert MTB/RIF compared to sputum smear microscopy to assess the risk of tuberculosis transmission in a low-prevalence country. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2016;22(7):613-9. - PubMed
Osman 2014 {published data only}
Ou 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ou X, Xia H, Li Q, Pang Y, Wang S, Zhao B, et al. A feasibility study of the Xpert MTB/RIF test at the peripheral level laboratory in China. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2015;31:41-6. - PubMed
Ozkutuk 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ozkutuk N, Surucüoglu S. Evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF assay for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis in an intermediate-prevalence setting. Mikrobiyoloji Bulteni 2014;48(2):223-32. - PubMed
Pandey P 2017 {published data only}
Pandey S 2017 {published data only}
-
- Pandey S, Congdon J, McInnes B, Pop A, Coulter C. Evaluation of the GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay on extrapulmonary and respiratory samples other than sputum: a low burden country experience. Pathology 2017;49(1):70-4. - PubMed
Parcell 2017 {published data only}
-
- Parcell BJ, Jarchow-MacDonald AA, Seagar AL, Laurenson IF, Prescott GJ, Lockhart M. Three year evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF in a low prevalence tuberculosis setting: a Scottish perspective. Journal of Infection 2017;74(5):466-72. - PubMed
Patel 2020 {published data only}
-
- Patel J, Upadhyay M, Kundnani V, Merchant Z, Jain S, Kire N. Diagnostic efficacy, sensitivity, and specificity of Xpert MTB/RIF assay for spinal tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance. Spine 2020;45(3):163-9. - PubMed
Patil 2014 {published data only}
Patil 2017 {published data only}
Peter 2012 {published data only}
Peter 2013 {published data only}
Peter 2015 {published data only}
-
- Peter J, Theron G, Chanda D, Clowes P, Rachow A, Lesosky M, et al. Test characteristics and potential impact of the urine LAM lateral flow assay in HIV-infected outpatients under investigation for TB and able to self-expectorate sputum for diagnostic testing. BMC Infectious Diseases 2015;15:262. - PMC - PubMed
Qureshi 2019 {published data only}
-
- Qureshi S, Sohaila A, Hannan S, Amir Sheikh MD, Qamar FN. Comparison of Xpert MTB/RIF with AFB smear and AFB culture in suspected cases of paediatric tuberculosis in a tertiary care hospital, Karachi. Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2019;69(9):1273-8. - PubMed
Rachow 2012 {published data only}
-
- Rachow A, Clowes P, Saathoff E, Mtafya B, Michael E, Ntinginya EN, et al. Increased and expedited case detection by Xpert MTB/RIF assay in childhood tuberculosis: a prospective cohort study. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2012;54(10):1388-96. - PubMed
Rahman 2016 {published data only}
Raizada 2015 {published data only}
Ramamurthy 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ramamurthy K, Bhat S, Shenoy S, Rangnekar A. Xpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampicin assay: a boon in tuberculosis diagnostics. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research 2016;9(5):225-7.
Ramirez 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ramirez HL, Garcia-Clemente MM, Alvarez-Alvarez C, Palacio-Gutierrez JJ, Pando-Sandoval A, Gagatek S, et al. Impact of the Xpert® MTB/RIF molecular test on the late diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2014;18(4):435-7. - PubMed
Rasheed 2019 {published data only}
Rathish 2019 {published data only}
Rathour 2019 {published data only}
-
- Rathour JS, Mantan M, Khanna A, Hanif M. Evaluation of Gene Xpert assay in extrapulmonary tuberculosis in children. JEMDS: Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2019;8(1).
Reechaipichitkul 2016 {published data only}
-
- Reechaipichitkul W, Phetsuriyawong A, Chaimanee P, Ananta P. Diagnostic test of sputum GeneXpert MTB/RIF for smear negative pulmonary tuberculosis. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2016;47(3):457-66. - PubMed
Reechaipichitkul 2017 {published data only}
-
- Reechaipichitkul W, Suleesathira T, Chaimanee P. Comparison of GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay with conventional AFB smear for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in northeastern Thailand. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health 2017;48(2):313-21. - PubMed
Reed 2016 {published data only}
-
- Reed JL, Walker ZJ, Basu D, Allen V, Nicol MP, Kelso DM, et al. Highly sensitive sequence specific qPCR detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in respiratory specimens. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2016;101:114-24. - PubMed
Rees 2018 {published data only}
Reis 2019 {published data only}
-
- Reis AJ, Diniz J, Silva ABS, Silveira J, Basso R, Vieira R, et al. Laboratory tools for tuberculosis control in a setting with a high burden of HIV/AIDS. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2019;68(11):1622-8. - PubMed
Rivera 2019 {published data only}
Rossato 2018 {published data only}
-
- Rossato Silva D, Sotgiu G, D'Ambrosio L, Rodrigues Pereira G, Silva Barbosa M, Dutra Dias NJ, et al. Diagnostic performances of the Xpert MTB/RIF in Brazil. Respiratory Medicine 2018;134:12-5. - PubMed
Rufai 2014 {published data only}
Ruiz 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ruiz P, Causse M, Vaquero M, Gutierrez JB, Casal M. Evaluation of a new automated Abbott RealTime MTB RIF/INH assay for qualitative detection of rifampicin/isoniazid resistance in pulmonary and extra-pulmonary clinical samples of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infection and Drug Resistance 2017;10:463-7. - PMC - PubMed
Sachdeva 2015 {published data only}
Saeed 2017 {published data only}
-
- Saeed M, Iram S, Hussain S, Ahmed A, Akbar M, Aslam M. GeneXpert: a new tool for the rapid detection of rifampicin resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis. Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2017;67(2):270-4. - PubMed
Sanchez‐Padilla 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sanchez-Padilla E, Merker M, Beckert P, Jochims F, Dlamini T, Kahn P, et al. Detection of drug-resistant tuberculosis by Xpert MTB/RIF in Swaziland. New England Journal of Medicine 2015;372(12):1181-2. - PubMed
Sauzullo 2016 {published data only}
-
- Sauzullo I, Rodio DM, Facchinetti S, Puggioni G, De Angelis M, Goldoni P, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF versus smear microscopy in the early diagnosis tuberculosis in the real life of "Umberto I" Hospital Rome. New Microbiologica 2016;39(4):304-6. - PubMed
Schutz 2019 {published data only}
Set 2019 {published data only}
-
- Set R, Bankar S, Sharma D, Shah D, Shastri J. Performance of Xpert MTB/RIF for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in pus aspirates. Indian Journal of Tuberculosis 2019;66(4):433-6. - PubMed
Shah 2014 {published data only}
Shah 2020 {published data only}
-
- Shah M, Paradis S, Betz J, Beylis N, Bharadwaj R, Caceres T, et al. Multicenter study of the accuracy of the BD MAX MDR-TB assay for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Complex and mutations associated with resistance to rifampin and isoniazid. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2020;71(5):1161-7. [DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz932] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Sharma 2019 {published data only}
-
- Sharma K, Gupta A, Sharma M, Sharma A, Bansal R, Sharma SP, et al. The emerging challenge of diagnosing drug-resistant tubercular uveitis: experience of 110 eyes from North India. Ocular Immunology and Inflammation 2019;Oct 3:1-8. - PubMed
Shenai 2013 {published data only}
Shenoy 2019 {published data only}
-
- Shenoy VP, Kumar A, Chawla K. Diagnostic performance of Xpert MTB /RIF in comparison with LED fluorescence microscopy and culture in suspected cases of pulmonary tuberculosis. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology 2019;13(3):1461-5.
Shilpa 2017 {published data only}
-
- Shilpa, Nadagir SD, Jnaneshwara KB, Patil AB, Pendari AG, Chikkaraddi U. Detection of rifampicin resistance in HIV seropositive individuals with suspected pulmonary tuberculosis by using CBNAAT. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology 2017;11(1):387-92.
Simone 2019 {published data only}
-
- Simone A. Comparative analysis of the bacilloscopy technique in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis against GeneXpert in samples of patients in the city of Recife, Pernambuco [Análise comparativa da técnica de baciloscopia no diagnóstico da tuberculose pulmonar frente ao GeneXpert em amostras de pacientes da cidade de Recife, Pernambuco]. Revista Brasileira de Análises Clínicas 2019;51(1):65-9.
Singh 2019 {published data only}
-
- Singh M, Sethi GR, Mantan M, Khanna A, Hanif M. Respiratory specimens for the diagnosis of pediatric pulmonary tuberculosis: a Comparative Assessment. SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine 2019;1(12):1056-9.
Smith 2014 {published data only}
-
- Smith P, Van Esch A, Wallace M, Wood R, Bekker LG. GeneXpert TB 8: a point-of-care diagnostic pilot. South African Medical Journal 2014;104(8):524. - PubMed
Somashekar 2014 {published data only}
-
- Somashekar N, Chadha VK, Praseeja P, Sharada MA, Chandrakala GR, Srivastava R, et al. Role of pre-Xpert(R) screening using chest X-ray in early diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2014;18(10):1243-4. - PubMed
Somily 2016 {published data only}
-
- Somily AM, Barry MA, Habib HA, Alotaibi FE, Al-Zamil FA, Khan MA, et al. Evaluation of GeneXpert MTB/RIF for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and rpo B gene in respiratory and non-respiratory clinical specimens at a tertiary care teaching hospital in Saudi Arabia. Saudi Medical Journal 2016;37(12):1404-7. - PMC - PubMed
Strydom 2015 {published data only}
-
- Strydom K, Ismail F, Matabane MM, Onwuegbuna O, Omar SV, Ismail N. Comparison of three commercial molecular assays for detection of rifampin and isoniazid resistance among Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates in a high-HIV-prevalence setting. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2015;53(9):3032-4. - PMC - PubMed
Sumalani 2019 {published data only}
-
- Sumalani KK, Akhter N, Chawla D, Rizvi NA. Diagnostic yield of sputum induction in patients with pleural tuberculosis at a tertiary care hospital in Karachi. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2019;23(11):1213-6. - PubMed
Sumayya 2019 {published data only}
-
- Sumayya, Durga K, Nithyananda BS, Fatima S, Krishnaiah A. Study of CBNAAT and anti-MPT64 detection in cytological and histopathological material for early diagnosis of TB lymphadenitis. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2019;8(47):3540-4.
Sun 2019 {published data only}
-
- Sun L, Qi X, Liu F, Wu X, Yin Q, Guo Y, et al. A test for more accurate diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. Pediatrics 2019;144(5):e20190262. - PubMed
Sureshbabu 2016 {published data only}
-
- Sureshbabu R, Lakshmi Murali A, Palaniswamy M. Molecular diagnosis of drug resistance tuberculosis in the districts of Tamilnadu. International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences 2016;7(4):B42-6.
Tadesse 2016 {published data only}
-
- Tadesse M, Aragaw D, Dimah B, Efa F, Abebe G. Xpert MTB/RIF for rapid detection of rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis from pulmonary tuberculosis patients in southwest Ethiopia. International Journal of Mycobacteriology 2016;5 Suppl 1:S48-9. - PubMed
Tahseen 2016 {published data only}
-
- Tahseen S, Qadeer E, Khanzada FM, Rizvi AH, Dean A, Van Deun A, et al. Use of Xpert® MTB/RIF assay in the first national anti-tuberculosis drug resistance survey in Pakistan. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2016;20(4):448-55. - PubMed
Tahseen 2019 {published data only}
-
- Tahseen S, Ambreen A, Masood F, Qadir M, Hussain A, Jamil M, et al. Primary drug resistance in extra-pulmonary tuberculosis: a hospital-based prospective study from Pakistan. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2019;23(8):900-6. - PubMed
Talib 2019 {published data only}
Tan 2017 {published data only}
Taylor 2012 {published data only}
Teo 2011 {published data only}
-
- Teo J, Jureen R, Chiang D, Chan D, Lin R. Comparison of two nucleic acid amplification assays, the Xpert MTB/RIF and the amplified Mycobacterium tuberculosis Direct assay, for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in respiratory and non-respiratory specimens. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 2011;49(10):3659-62. - PMC - PubMed
Theron 2012 {published data only}
Theron 2014a {published data only}
Theron 2016 {published data only}
Theron 2018 {published data only}
Thibbadee 2016 {published data only}
-
- Thibbadee C. Evaluation of decentralised use of the Xpert MTB/RRIF test for diagnosis of tuberculosis and multidrug resistance in Rayong hospital, Thailand. Respirology 2016;21 (Suppl 3):198.
Thit 2017 {published data only}
To 2017 {published data only}
-
- To KW, Kam KM, Lee SS, Chan KP, Yip T, Lo R, et al. Clinical application of GeneXpert on BAL samples in management of TB in intermediate burden area. Chest 2017;152 (4 Suppl 1):A194.
Tortoli 2012 {published data only}
-
- Tortoli E, Russo C, Piersimoni C, Mazzola E, Dal Monte P, Pascarella M, et al. Clinical validation of Xpert MTB/RIF for the diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. European Respiratory Journal 2012;40(2):442-7. - PubMed
Uddin 2019 {published data only}
-
- Uddin MJ, Rahim MA, Hasan MN, Mazumder MK, Haq MM, Rahman MA, et al. Etiological evaluation of patients with lymphadenopathy by clinical, histopathological and microbiological assessment. Mymensingh Medical Journal 2019;28(4):854-61. - PubMed
Udgirkar 2019 {published data only}
-
- Udgirkar S, Jain S, Pawar S, Chandnani S, Contractor Q, Rathi P. Clinical profile, drug resistance pattern and treatment outcomes of abdominal tuberculosis patients in western India. Archives of Gastroenterology 2019;56(2):178-83. - PubMed
Ullah 2016 {published data only}
Ullah 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ullah I, Javaid A, Masud H, Ali M, Basit A, Ahmad W, et al. Rapid detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in extrapulmonary tuberculosis and sputum smear-negative pulmonary suspects using Xpert MTB/RIF. Journal of Medical Microbiology 2017;66(4):412-8. - PubMed
Vadwai 2011 {published data only}
Van Kampen 2015 {published data only}
Van Rie 2011 {published data only}
-
- Van Rie A. A single Xpert MTB/RIF test of sputum for diagnosis of tuberculosis and multidrug resistance shows high sensitivity and specificity and reduces diagnosis and treatment delays. BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine 2011;16(6):174-5. - PubMed
Walters 2012 {published data only}
-
- Walters E, Gie RP, Hesseling AC, Friedrich SO, Diacon AH. Rapid diagnosis of pediatric intrathoracic tuberculosis from stool samples using the Xpert MTB/RIF Assay: a pilot study. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 2012;31(12):1316. - PubMed
Walusimbi 2013 {published data only}
Wang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wang XW, Pappoe F, Huang Y, Cheng XW, Xu DF, Wang H, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in children: a meta-analysis. Clinical Laboratory 2015;61(11):1775-85. - PubMed
Wang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Wang SF, Ou XC, Li Q, Zheng HW, Wang YF, Zhao YL. The Abbott RealTime MTB assay and the Cepheid GeneXpert assay show comparable performance for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum specimens. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2016;45:78-80. - PubMed
Williamson 2012 {published data only}
-
- Williamson DA, Roberts SA, Bower JE, Vaughan R, Newton S, Lowe O, et al. Clinical failures associated with rpoB mutations in phenotypically occult multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2012;16(2):216-20. - PubMed
Wood 2012 {published data only}
Xie 2017 {published data only}
Yadav 2017 {published data only}
-
- Yadav R, Sharma N, Khaneja R, Agarwal P, Kanga A, Behera D, et al. Evaluation of the TB-LAMP assay for the rapid diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in northern India. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2017;21(10):1150-3. - PubMed
Yan 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yan L, Xiao H, Zhang Q. Systematic review: Comparison of Xpert MTB/RIF, LAMP and SAT methods for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2016;96:75-86. - PubMed
Yang X 2020 {published data only}
-
- Yang X, Che N, Duan H, Liu Z, Li K, Li H, et al. Cell-free Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA test in pleural effusion for tuberculous pleurisy: a diagnostic accuracy study. Clinical Microbiology and Infection 2020;26(8):1089.e1-1089.e6. - PubMed
Yeong 2019 {published data only}
-
- Yeong C, Byrne AL, Cho JG, Sintchenko V, Crighton T, Marais BJ. Use of GeneXpert MTB/RIF(R) on a single pooled sputum specimen to exclude pulmonary tuberculosis among hospital inpatients placed in respiratory isolation. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2019;92:175-80. - PubMed
Yu 2020 {published data only}
-
- Yu G, Shen Y, Ye B, Chen D, Xu K. Comparison of CapitalBio Mycobacterium nucleic acid detection test and Xpert MTB/RIF assay for rapid diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Journal of Microbiological Methods 2020;168:105780. - PubMed
Zar 2012 {published data only}
Zar 2019 {published data only}
Zemlyansky 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zemlyansky OA, Tyurina EB, Bashkirev AA, Kalyuzhnaya EV, Zemlyanskaya LO. Experience and efficiency of laboratory diagnosis of tuberculosis with PCR detector system GeneXpert in Belgorod region. International Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 2016;8(4):27072-9.
Zhou 2020 {published data only}
-
- Zhou Z, Zheng Y, Wang L. A comparative study on the value of Xpert MTB/RIF and T-SPOT.TB tests in the diagnosis of bone and joint tuberculosis. Clinica Chimica Acta 2020;500:115-9. - PubMed
Zimba 2019 {published data only}
Zurcher 2019 {published data only}
-
- Zurcher K, Ballif M, Kiertiburanakul S, Chenal H, Yotebieng M, Grinsztejn B, et al. Diagnosis and clinical outcomes of extrapulmonary tuberculosis in antiretroviral therapy programmes in low- and middle-income countries: a multicohort study. Journal of the International AIDS Society 2019;22(9):e25392. - PMC - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ChiCTR180001479 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR1800014792. Diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for tuberculous bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in HIV-infected adults: a prospective cohort study [Diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for tuberculous bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in HIV-infected adults: a prospective cohort study]. http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=25172 (first received 5 February 2018).
ChiCTR1800014792 {published data only}
-
- ChiCTR1800014792. Study on the accuracy of fecal Xpert_MTB/RIF_Ultra test in diagnosis of childhood tuberculosis [Diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for tuberculous bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in HIV-infected adults: a prospective cohort study]. http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=25233 (first received 12 February 2018).
ChiCTR1900026491 {unpublished data only}
-
- ChiCTR1900026491. The diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy combined with Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra in smear and culture negative pulmonary tuberculosis [The diagnostic value of medical thoracoscopy combined with Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra in smear and culture negative pulmonary tuberculosis]. http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=44194 (first received 12 October 2019).
ISRCTN77241966 {published data only}
-
- ISRCTN77241966. Evaluation of GeneXpert Ultra and digital chest radiography for diagnosing tuberculosis [Utility of the Xpert® MTB/RIF Ultra assay with the GeneXpert®Omni System and digital chest radiography for diagnosis of tuberculosis in high HIV prevalence settings: protocol for a randomised control trial]. www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN77241966 (first received 9 February 2019).
NCT03154320 {published data only}
-
- NCT03154320. A trial of same-day testing and treatment to improve outcomes among symptomatic patients newly diagnosed with HIV [A trial of same-day testing and treatment to improve outcomes among symptomatic patients newly diagnosed with HIV]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03154320 (first received 16 May 2017).
NCT03187964 {published data only}
-
- NCT03187964. Xpert Ultra and Xpert HIV-VL in people living with HIV (Ultra HIV) [Xpert Ultra and Xpert HIV-VL in people living with HIV (Ultra HIV)]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03187964 (first received 15 June 2017).
NCT03356925 {published data only}
-
- NCT03356925. Improving tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment through basic, applied and health systems research (BAR) [Improving tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment through basic, applied and health systems research (BAR)]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03356925 (first received 29 November 2017).
NCT03497195 {published data only}
-
- NCT03497195. Achieving tuberculosis (TB) control In Zambia (TB) [Comparison of 2 diagnostic tools (chest X-ray with computer-assisted diagnosis versus C-reactive protein) and Xpert Ultra for active community-based tuberculosis case detection]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03497195 (first received 13 April 2018).
NCT03712709 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT03712709. Clinical evaluation of the Truenat point-of-care tuberculosis diagnostic test [Clinical evaluation of the Truenat point-of-care tuberculosis diagnostic test]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03712709 (first received 19 October 2018).
NCT04074369 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT04074369. Evaluation of CRISPR-based test for the rapid identification of TB in pulmonary tuberculosis suspects [Evaluation of CRISPR-based test for the rapid identification of TB in pulmonary tuberculosis suspects]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04074369 (first received 30 August 2019).
NCT04122404 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT04122404. POC strategies to improve TB care in advanced HIV disease (TBPOC) [Point-of-care strategies to improve tuberculosis care among severely immunosuppressed HIV-infected patients]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04122404 (first received 10 October 2019). [NCT04122404]
NCT058236 {unpublished data only}
-
- NTC02758236. Tuberculosis research of INA-RESPOND on drug resistance (TRIPOD) [Tuberculosis research of INA-RESPOND on drug resistance]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02758236 (first received 2 May 2016).
Additional references
Altman 1995
American Thoracic Society 2000
-
- American Thoracic Society, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Infectious Disease Society of America. Diagnostic Standards and Classification of Tuberculosis in Adults and Children. This official statement of the American Thoracic Society and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention was adopted by the ATS Board of Directors, July 1999. This statement was endorsed by the Council of the Infectious Disease Society of America, September 1999. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2000;161(4 Pt 1):1376-95. - PubMed
Balshem 2011
-
- Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):401-6. - PubMed
Banada 2010
Beynon 2018
Bjerrum 2019
-
- Bjerrum S, Schiller I, Dendukuri N, Kohli M, Nathavitharana RR, Zwerling AA, et al. Lateral flow urine lipoarabinomannan assay for detecting active tuberculosis in people living with HIV. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019, Issue 10. Art. No: CD011420. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011420.pub3] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Blakemore 2010
Boehme 2010
Bossuyt 2015
Boyles 2014
-
- Boyles TH, Hughes J, Cox V, Burton R, Meintjes G, Mendelson M. False-positive Xpert® MTB/RIF assays in previously treated patients: need for caution in interpreting results. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2014;18(7):876-8. - PubMed
Branigan 2019
-
- Branigan D, Treatment Action Group. The tuberculosis diagnostics pipeline: new tests, same barriers. treatmentactiongroup.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/12/pipeline_tb_diagnoti... (accessed 9 April 2020).
Broger 2020
Buzoianu 2008
-
- Buzoianu M, Kadane JB. Adjusting for verification bias in diagnostic test evaluation: a Bayesian approach. Statistics in Medicine 2008;27(13):2453-73. - PubMed
Cazabon 2018
-
- Cazabon D, Pande T, Kik S, Van Gemert W, Sohn H, Denkinger C, et al. Market penetration of Xpert MTB/RIF in high tuberculosis burden countries: a trend analysis from 2014 - 2016 [version 2; referees: 4 approved]. Gates Open Research 2018;2:35. [DOI: 10.12688/gatesopenres.12842.1] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
CDC 2020
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Questions and answers about TB. www.cdc.gov/tb/publications/faqs/qa_introduction.htm (accessed 8 December 2020).
Cepheid 2018
-
- Cepheid. Brochure: Xpert® MTB/RIF Ultra. www.cepheid.com/en/tests/Critical-Infectious-Diseases/Xpert-MTB-RIF-Ultra (accessed 26 March 2020).
Cepheid 2019
-
- Cepheid. Xpert® MTB/RIF. Two-hour detection of MTB and rifampin resistance mutations. www.cepheid.com/Package%20Insert%20Files/Xpert-MTB-RIF-ENGLISH-Package-I... (accessed 29 March 2020).
Chang 2012
-
- Chang K, Lu W, Wang J, Zhang K, Jia S, Li F, et al. Rapid and effective diagnosis of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance with Xpert MTB/RIF assay: a meta-analysis. Journal of Infection 2012;64(6):580-8. - PubMed
Chu 2006
-
- Chu H, Cole SR. Bivariate meta-analysis of sensitivity and specificity with sparse data: a generalized linear mixed model approach. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(12):1331–2. - PubMed
Chu 2009
Covidence [Computer program]
-
- Veritas Health Innovation Covidence. Version accessed 27 January 2020. Melbourne, Australia: Veritas Health Innovation. Available at covidence.org.
Denamps 2020 [pers comm]
-
- Denamps S. Quick Xpert Ultra question, market penetration [personal communication]. Email to: S Denamps 18 May 2020.
Di Tanna 2019
Flores 2005
Friedrich 2013
-
- Friedrich SO, Rachow A, Saathoff E, Singh K, Mangu CD, Dawson R, et al Pan African Consortium for the Evaluation of Anti-tuberculosis Antibiotics (PanACEA). Assessment of the sensitivity and specificity of Xpert MTB/RIF assay as an early sputum biomarker of response to tuberculosis treatment. Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2013;1(6):462-70. - PubMed
Getahun 2007
-
- Getahun H, Harrington M, O'Brien R, Nunn P. Diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis in people with HIV infection or AIDS in resource-constrained settings: informing urgent policy changes. Lancet 2007;369(9578):2042-9. - PubMed
Getahun 2010
-
- Getahun H, Gunneberg C, Granich R, Nunn P. HIV infection-associated tuberculosis: the epidemiology and the response. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2010;50(Suppl 3):201-7. - PubMed
Global Laboratory Initiative 2017
-
- Global Laboratory Initiative. Planning for country transition to Xpert® MTB/RIF Ultra cartridges. www.stoptb.org/wg/gli/assets/documents/gli_ultra.pdf (accessed 26 March 2020).
Global Laboratory Initiative 2019
-
- Global Laboratory Initiative. Practical guide to implementing a quality assurance system for Xpert MTB/RIF testing. www.stoptb.org/wg/gli/assets/documents/Xpert-QA-guide-2019.pdf (accessed 7 January 2020).
Gopinath 2010
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
-
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime) GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed 29 October 2016. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime). Available at gradepro.org.
Greenland 2016
Gupta‐Wright 2018
-
- Gupta-Wright A, Corbett EL, Van Oosterhout JJ, Wilson D, Grint D, Alufandika-Moyo M, et al. Rapid urine-based screening for tuberculosis in HIV-positive patients admitted to hospital in Africa (STAMP): a pragmatic, multicentre, parallel-group, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018;392(10144):292-301. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Hadgu 2005
-
- Hadgu A, Dendukuri N, Hilden J. Evaluation of nucleic acid amplification tests in the absence of a perfect gold-standard test: a review of the statistical and epidemiologic issues. Epidemiology 2005;16(5):604–12. - PubMed
Haraka 2018
Hartmann 1967
-
- Hartmann G, Honikel KO, Knüsel F, Nüesch J. The specific inhibition of the DNA-directed RNA synthesis by rifamycin. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1967;145(3):843-4. - PubMed
Helb 2010
Jiang 2020
-
- Jiang J, Yang J, Shi Y, Jin Y, Tang S, Zhang N, et al. Head-to-head comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for tuberculosis: a meta-analysis. Infectious Diseases 2020;52(11):763-75. - PubMed
Kay 2020
-
- Kay AW, González Fernández L, Takwoingi Y, Eisenhut M, Vu RD, Steingart KR, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assays for active tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in children. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 8. Art. No: CD013359. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013359] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Kendall 2017
Kohli 2021
-
- Kohli M, Schiller I, Dendukuri N, Yao M, Dheda K, Denkinger CM, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra and Xpert MTB/RIF assays for extrapulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2021, Issue 1. Art. No: CD012768. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012768.pub3] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Leeflang 2013
Lewinsohn 2017
-
- Lewinsohn DM, Leonard MK, LoBue PA, Cohn DL, Daley CL, Desmond E, et al. Official American Thoracic Society/Infectious Diseases Society of America/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Clinical Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis of tuberculosis in adults and children. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2017;64(2):e1-33. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lunn 2009
-
- Lunn D, Spiegelhalter D, Thomas A, Best N. The BUGS project: evolution, critique, and future directions. Statistics in Medicine 2009;28(25):3049-67. - PubMed
Macaskill 2010
-
- Macaskill P, Gatsonis C, Deeks JJ, Harbord RM, Takwoingi Y. Chapter 10: Analysing and presenting results. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2010. Available from srdta.cochrane.org.
McInnes 2018
-
- McInnes MDF, Moher D, Thombs BD, McGrath TA, Bossuyt PM, PRISMA-DTA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies: the PRISMA-DTA statement [published correction appears in JAMA. 2019 Nov 26;322(20):2026]. JAMA 2018;319(4):388-96. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.19163] - DOI - PubMed
Moher 2009
Nathavitharana 2017
-
- Nathavitharana RR, Cudahy PG, Schumacher SG, Steingart KR, Pai M, Denkinger CM. Accuracy of line probe assays for the diagnosis of pulmonary and multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European Respiratory Journal 2017;49(1):1601075. [DOI: 10.1183/13993003.01075-2016] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ngabonziza 2020
Pai 2018
Perez‐Risco 2018
Perkins 2007
-
- Perkins MD, Cunningham J. Facing the crisis: improving the diagnosis of tuberculosis in the HIV era. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2007;196(Suppl 1):S15-27. - PubMed
Peter 2016
-
- Peter JG, Zijenah LS, Chanda D, Clowes P, Lesosky M, Gina P, et al. Effect on mortality of point-of-care, urine-based lipoarabinomannan testing to guide tuberculosis treatment initiation in HIV-positive hospital inpatients: a pragmatic, parallel-group, multicountry, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;387(10024):1187-97. [PMID: ] - PubMed
R Core Team 2019 [Computer program]
-
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing R Core Team (2019). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2019. Available at R-project.org.
Reitsma 2005
-
- Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten RJ, Bossuyt PM, Zwinderman AH. Bivariate analysis of sensitivity and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic reviews. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(10):982-90. - PubMed
Review Manager 2020 [Computer program]
-
- Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager 5 (RevMan 5). Version 5.4. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
Schumacher 2019
-
- Schumacher SG, Denkinger CM. The impact of Xpert MTB/RIF - do we have a final answer? Lancet Global Health 2019;7(2):e161-2. - PubMed
Schünemann 2008
Schünemann 2016
-
- Schünemann HJ, Mustafa R, Brozek J, Santesso N, Alonso-Coello P, Guyatt G, et al, GRADE Working Group. GRADE Guidelines: 16. GRADE evidence to decision frameworks for tests in clinical practice and public health. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016;76:89-98. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.01.032] - DOI - PubMed
Schünemann 2020a
-
- Schünemann HJ, Mustafa R, Brozek J, Steingart KR, Leeflang M, Murad MH, et al. GRADE Guidelines: 21 part 1. Study design, risk of bias and indirectness in rating the certainty across a body of evidence for test accuracy. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2020;122:129-41. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.12.020] - DOI - PubMed
Schünemann 2020b
-
- Schünemann HJ, Mustafa R, Brozek J, Steingart KR, Leeflang M, Murad MH, et al. GRADE Guidelines: 21 part 2. Inconsistency, imprecision, publication bias and other domains for rating the certainty of evidence for test accuracy and presenting it in evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2020;122:142-52. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2019.12.021] - DOI - PubMed
Shapiro 2020
-
- Shapiro AE, Ross JM, Schiller I, Kohli M, Dendukuri N, Steingart KR, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert Ultra assays for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults irrespective of signs or symptoms of pulmonary tuberculosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2020, Issue 7. Art. No: CD013694. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013694] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Small 2011
-
- Small PM, Pai M. Tuberculosis diagnosis - time for a game change. New England Journal of Medicine 2011;363(111):1070–1. - PubMed
Stata 2017 [Computer program]
-
- Stata. Version 15. College Station, TX, USA: StataCorp, 2017. Available at www.stata.com.
Steingart 2006a
-
- Steingart KR, Henry M, Ng V, Hopewell PC, Ramsay A, Cunningham J, et al. Fluorescence versus conventional sputum smear microscopy for tuberculosis: a systematic review. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2006;6(9):570-81. - PubMed
Steingart 2006b
-
- Steingart KR, Ng V, Henry M, Hopewell PC, Ramsay A, Cunningham J, et al. Sputum processing methods to improve the sensitivity of smear microscopy for tuberculosis: a systematic review. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2006;6(10):664-74. - PubMed
Steingart 2015
-
- Steingart KR, Schiller I, Dendukuri N, Lalli M, Houben R, Churchyard G, et al. In reply to ‘False-positive Xpert® MTB/RIF assays in previously treated patients'. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease 2015;19(3):366-7. - PubMed
Takwoingi 2013
-
- Takwoingi Y, Leeflang MM, Deeks JJ. Empirical evidence of the importance of comparative studies of diagnostic test accuracy. Annals of Internal Medicine 2013;158(7):544-54. - PubMed
Telenti 1993
-
- Telenti A, Imboden P, Marchesi F, Lowrie D, Cole S, Colston MJ, et al. Detection of rifampicin-resistance mutations in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Lancet 1993;341(8846):647-50. - PubMed
Theron 2014b
-
- Theron G, Zijenah L, Chanda D, Clowes P, Rachow A, Lesosky M, et al. Feasibility, accuracy, and clinical effect of point-of-care Xpert MTB/RIF testing for tuberculosis in primary-care settings in Africa: a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2014;383(9915):424-35. - PubMed
Unitaid 2017
-
- Boyle D. Tuberculosis Diagnostics Technology and Market Landscape. 5th edition. Vernier: World Health Organization Unitaid Secretariat, 2017.
Vonasek 2020
Walzl 2018
-
- Walzl G, McNerney R, Du Plessis N, Bates M, McHugh TD, Chegou NN, et al. Tuberculosis: advances and challenges in development of new diagnostics and biomarkers. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2018;18(7):e199-210. - PubMed
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, et al. QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155(8):529-36. - PubMed
WHO 2007
-
- World Health Organization. Definition of a new sputum smear-positive TB case, 2007. who.int/tb/laboratory/policy_sputum_smearpositive_tb_case/en/index.html (accessed 10 December 2020).
WHO 2011a
-
- World Health Organization. Rapid implementation of the Xpert MTB/RIF diagnostic test: technical and operational ‘how-to’; practical considerations; 2011. who.int/tb/publications/tb-amplificationtechnology-implementation/en/ (accessed 3 July 2020).
WHO 2011b
-
- World Health Organization. Policy statement: automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: Xpert MTB/RIF system; 2011. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK304235/ (accessed 3 July 2020). - PubMed
WHO 2013
-
- World Health Organization. Automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: Xpert MTB/RIF system for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extrapulmonary TB in adults and children: policy update; 2013. apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/112472 (accessed 3 July 2020). - PubMed
WHO 2015a
-
- World Health Organization. The END TB strategy; 2015. apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/331326/WHO-HTM-TB-2015.19-eng.pdf (accessed 29 March 2020).
WHO 2015b
-
- World Health Organization. Implementing tuberculosis diagnostics: a policy framework; 2015. who.int/tb/publications/implementing_TB_diagnostics/en/ (accessed 3 July 2020).
WHO 2017
-
- World Health Organization. WHO meeting report of a technical expert consultation: non-inferiority analysis of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra compared to Xpert MTB/RIF; 2017. who.int/tb/publications/2017/XpertUltra/en/ (accessed 3 July 2020).
WHO 2021
-
- World Health Organization. Technical report on critical concentrations for drug susceptibility testing of isoniazid and the rifamycins (rifampicin, rifabutin and rifapentine). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021. www.who.int/publications/i/item/technical-report-on-critical-concentrati... (accessed 13 February 2021).
WHO Consolidated Guidelines (Module 3) 2020
-
- World Health Organization. WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 3: diagnosis – rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis detection. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. who.int/publications/i/item/who-consolidated-guidelines-on-tuberculosis-... (accessed 1 July 2020). - PubMed
WHO Consolidated Guidelines (Module 4) 2020
-
- World Health Organization. WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 4: treatment - drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment; June 2020. who.int/publications/i/item/9789240007048 (accessed 1 July 2020).
WHO Global tuberculosis report 2020
-
- World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2020. who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/ (accessed 20 October 2020).
World Bank 2020
-
- World Bank. World Bank List of Economies. datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-coun... (accessed 30 March 2020).
Yang B 2020
-
- Yang B, Whiting P, Davenport C, Deeks J, Hyde C, Mallett S, et al. Development of QUADAS-C, a risk of bias tool for comparative diagnostic accuracy studies. Available from osf.io/hq8mf (accessed 11 June 2020).
Zhang 2019
-
- Zhang M, Xue M, He J. Diagnostic accuracy of the new Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for tuberculosis disease: a preliminary systematic review and meta-analysis. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2019;90:35-45. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Horne 2019
-
- Horne DJ, Kohli M, Zifodya JS, Schiller I, Dendukuri N, Tollefson D, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2019, Issue 6. Art. No: CD009593. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub4] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Sohn 2012
Steingart 2013
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

