Ligand Strain and Its Conformational Complexity Is a Major Factor in the Binding of Cyclic Dinucleotides to STING Protein
- PMID: 33616279
- PMCID: PMC8251555
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202016805
Ligand Strain and Its Conformational Complexity Is a Major Factor in the Binding of Cyclic Dinucleotides to STING Protein
Abstract
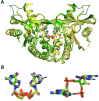
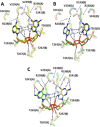
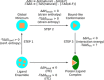
STING (stimulator of interferon genes) is a key regulator of innate immunity that has recently been recognized as a promising drug target. STING is activated by cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs) which eventually leads to expression of type I interferons and other cytokines. Factors underlying the affinity of various CDN analogues are poorly understood. Herein, we correlate structural biology, isothermal calorimetry (ITC) and computational modeling to elucidate factors contributing to binding of six CDNs-three pairs of natural (ribo) and fluorinated (2'-fluororibo) 3',3'-CDNs. X-ray structural analyses of six {STING:CDN} complexes did not offer any explanation for the different affinities of the studied ligands. ITC showed entropy/enthalpy compensation up to 25 kcal mol-1 for this set of similar ligands. The higher affinities of fluorinated analogues are explained with help of computational methods by smaller loss of entropy upon binding and by smaller strain (free) energy.
Keywords: conformational analysis; cyclic dinucleotides; entropy; quantum chemistry; strain energy.
© 2021 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
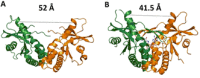


Similar articles
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biochemical and Biological Evaluation of Novel 7-Deazapurine Cyclic Dinucleotide Analogues as STING Receptor Agonists.J Med Chem. 2022 Oct 27;65(20):14082-14103. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01305. Epub 2022 Oct 6. J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36201304 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-Ligand Interactions in the STING Binding Site Probed by Rationally Designed Single-Point Mutations: Experiment and Theory.Biochemistry. 2021 Mar 2;60(8):607-620. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00949. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Biochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33586948
-
Crystal structures of porcine STINGCBD-CDN complexes reveal the mechanism of ligand recognition and discrimination of STING proteins.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jul 26;294(30):11420-11432. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007367. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31167783 Free PMC article.
-
2',3'-Cyclic GMP-AMP Dinucleotides for STING-Mediated Immune Modulation: Principles, Immunotherapeutic Potential, and Synthesis.ChemMedChem. 2022 Jan 19;17(2):e202100671. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100671. Epub 2021 Dec 4. ChemMedChem. 2022. PMID: 34807508 Review.
-
STING activation in cancer immunotherapy.Theranostics. 2019 Oct 15;9(25):7759-7771. doi: 10.7150/thno.37574. eCollection 2019. Theranostics. 2019. PMID: 31695799 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding automated multiconformer ligand modeling to macrocycles and fragments.Elife. 2025 Jun 30;14:RP103797. doi: 10.7554/eLife.103797. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40586518 Free PMC article.
-
The Many Ways to Deal with STING.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 20;24(10):9032. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109032. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carriers Multimerize STING Protein Fragments to Activate Type I Interferon Signaling in STING-Deficient Cancer Cells.Mol Pharm. 2025 Aug 4;22(8):4632-4650. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5c00226. Epub 2025 Jul 6. Mol Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40619768
-
PDE-stable 2'3'-cGAMP analogues, containing 5'-S-phosphorothioester linkage, as STING agonists.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Jan 9;15(5):1508-1514. doi: 10.1039/d3md00593c. eCollection 2024 May 22. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38784462 Free PMC article.
-
The Present and Future of Virology in the Czech Republic-A New Phoenix Made of Ashes?Viruses. 2022 Jun 14;14(6):1303. doi: 10.3390/v14061303. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35746773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ryde U., Soderhjelm P., Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 5520–5566. - PubMed
-
- “What Next for Quantum Mechanics in Structure-Based Drug Discovery?”: Bryce R. A. in Quantum Mechanics in Drug Discovery (Ed.: Heifetz A.), Springer US, New York, 2020, pp. 339–353. - PubMed
-
- Sandner A., Hufner-Wulsdorf T., Heine A., Steinmetzer T., Klebe G., J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 9753–9771. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Kim J., Hilty C., Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 5935–5943.RETURN TO ISSUEPREVARTICLENEXTRational Design of Novel Highly Potent and Selective Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase IIIβ (PI4KB) Inhibitors as Broad-Spectrum Antiviral Agents and Tools for Chemical Biology - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

