Cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19: a major mechanism of morbidity and mortality
- PMID: 33616462
- PMCID: PMC7919105
- DOI: 10.1080/08830185.2021.1884248
Cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19: a major mechanism of morbidity and mortality
Abstract
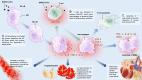
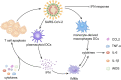
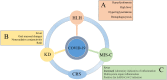
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) triggered by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) erupted in Hubei Province of China in December 2019 and has become a pandemic. Severe COVID-19 patients who suffer from acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and multi-organ dysfunction have high mortality. Several studies have shown that this is closely related to the cytokine release syndrome (CRS), often loosely referred to as cytokine storm. IL-6 is one of the key factors and its level is positively correlated with the severity of the disease. The molecular mechanisms for CRS in COVID-19 are related to the effects of the S-protein and N-protein of the virus and its ability to trigger NF-κB activation by disabling the inhibitory component IκB. This leads to activation of immune cells and the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α. Other mechanisms related to IL-6 include its interaction with GM-CSF and interferon responses. The pivotal role of IL-6 makes it a target for therapeutic agents and studies on tocilizumab are already ongoing. Other possible targets of treating CRS in COVID-19 include IL-1β and TNF-α. Recently, reports of a CRS like illness called multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in children have surfaced, with a variable presentation which in some cases resembles Kawasaki disease. It is likely that the immunological derangement and cytokine release occurring in COVID-19 cases is variable, or on a spectrum, that can potentially be governed by genetic factors. Currently, there are no approved biological modulators for the treatment of COVID-19, but the urgency of the pandemic has led to numerous clinical trials worldwide. Ultimately, there is great promise that an anti-inflammatory modulator targeting a cytokine storm effect may prove to be very beneficial in reducing morbidity and mortality in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6; Kawasaki disease; NF-κB; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine release syndrome; hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH); multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Ferrara JL, Abhyankar S, Gilliland DG.. Cytokine storm of graft-versus-host disease: a critical effector role for interleukin-1. Transplant Proc. 1993; 25(1 Pt 2):1216–1217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
