Using computational modelling to reveal mechanisms of epigenetic Polycomb control
- PMID: 33616630
- PMCID: PMC7925002
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20190955
Using computational modelling to reveal mechanisms of epigenetic Polycomb control
Abstract
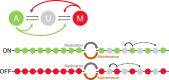
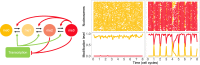
The Polycomb system is essential for stable gene silencing in many organisms. This regulation is achieved in part through addition of the histone modifications H3K27me2/me3 by Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2). These modifications are believed to be the causative epigenetic memory elements of PRC2-mediated silencing. As these marks are stored locally in the chromatin, PRC2-based memory is a cis-acting system. A key feature of stable epigenetic memory in cis is PRC2-mediated, self-reinforcing feedback from K27-methylated histones onto nearby histones in a read-write paradigm. However, it was not clear under what conditions such feedback can lead to stable memory, able, for example, to survive the perturbation of histone dilution at DNA replication. In this context, computational modelling has allowed a rigorous exploration of possible underlying memory mechanisms and has also greatly accelerated our understanding of switching between active and silenced states. Specifically, modelling has predicted that switching and memory at Polycomb loci is digital, with a locus being either active or inactive, rather than possessing intermediate, smoothly varying levels of activation. Here, we review recent advances in models of Polycomb control, focusing on models of epigenetic switching through nucleation and spreading of H3K27me2/me3. We also examine models that incorporate transcriptional feedback antagonism and those including bivalent chromatin states. With more quantitative experimental data on histone modification kinetics, as well as single-cell resolution data on transcription and protein levels for PRC2 targets, we anticipate an expanded need for modelling to help dissect increasingly interconnected and complex memory mechanisms.
Keywords: computational models; epigenetics; mathematical modelling; polycomb repressive complex 2.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

