The incidence of asymptomatic thrombosis related to peripherally inserted central catheter in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis People's
- PMID: 33617142
- PMCID: PMC8363368
- DOI: 10.1002/nop2.811
The incidence of asymptomatic thrombosis related to peripherally inserted central catheter in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis People's
Abstract
Aim: To examine the incidence and risk factors for asymptomatic peripherally inserted central catheter-related thrombosis (PICC-RT).
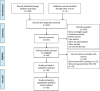
Design: We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis following the PRISMA guidelines.
Methods: The review was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42020186732). A systematic search of EMBASE, CINAHL, PubMed, Web of Science and Cochrane was performed from inception to 4 June 2020. Meta-analysis was performed to determine the pooled incidence of asymptomatic PICC-RT.
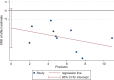
Results: Ten studies comprising 1591 participants with 1592 PICCs were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled incidence of asymptomatic PICC-RT in adults was 22% (95% CI, 0.17-0.29). The pooled incidence of PICC-RT in cancer patients was 19% (95% CI, 0.13-0.26). Asymptomatic PICC-RT mainly occurred in superficial veins. Most asymptomatic thrombosis occurred 3-12 days after the PICC insertion. A higher Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group score (ECOG), slower blood flow velocity and left basilic vein were independent risk factors of asymptomatic thrombosis.
Keywords: asymptomatic; incidence; peripherally inserted central catheter; thrombosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Nursing Open published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Risk of VTE associated with PORTs and PICCs in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Thromb Res. 2022 May;213:34-42. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2022.02.024. Epub 2022 Mar 7. Thromb Res. 2022. PMID: 35279504
-
Symptomatic Deep Vein Thrombosis Associated With Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters of Different Diameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023 Jan-Dec;29:10760296221144041. doi: 10.1177/10760296221144041. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023. PMID: 37366542 Free PMC article.
-
Different diagnostic strategies using D-dimer for peripherally inserted central catheter-related upper extremity deep vein thrombosis.J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2023 May;11(3):565-572. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2022.07.018. Epub 2023 Jan 18. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 2023. PMID: 36681296 Free PMC article.
-
Central venous catheter-related thrombosis in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.J Vasc Access. 2025 Jul;26(4):1180-1186. doi: 10.1177/11297298241262821. Epub 2024 Aug 1. J Vasc Access. 2025. PMID: 39091098
-
Continuous heparin infusion to prevent thrombosis and catheter occlusion in neonates with peripherally placed percutaneous central venous catheters.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD002772. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002772.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Apr 16;(2):CD002772. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002772.pub3. PMID: 16034876 Updated.
Cited by
-
Investigative study of hemodilution ratio: 4Vs for vein diameter, valve, velocity, and volumetric blood flow as factors for optimal forearm vein selection for intravenous infusion.J Vasc Access. 2024 Jan;25(1):140-148. doi: 10.1177/11297298221095287. Epub 2022 May 7. J Vasc Access. 2024. PMID: 35531766 Free PMC article.
-
D-dimer level for ruling out peripherally inserted central catheter-associated upper extremity deep vein thrombosis and superficial vein thrombosis.Nurs Open. 2022 Nov;9(6):2899-2907. doi: 10.1002/nop2.998. Epub 2021 Aug 16. Nurs Open. 2022. PMID: 34399039 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of PICC-related thrombosis in patients with hematological malignancies: a systematic review.Support Care Cancer. 2024 Jun 26;32(7):462. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08636-7. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38922487
-
Experience of a vascular ultrasound-guided program: from the ICU to the hospital.Ultrasound J. 2024 Sep 19;16(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13089-024-00393-2. Ultrasound J. 2024. PMID: 39297921 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the complexities of catheter-related thrombosis: risk factors, preventive strategies, and management.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025 Mar;58(3):443-457. doi: 10.1007/s11239-025-03073-7. Epub 2025 Mar 5. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2025. PMID: 40042718 Review.
References
-
- Ardon, M. S., Selles, R. W., Hovius, S. E., Stam, H. J., Murawska, M., Roebroeck, M. E., & Janssen, W. G. (2014). Stronger relation between impairment and manual capacity in the non‐dominant hand than the dominant hand in congenital hand differences; implications for surgical and therapeutic interventions. Journal of Hand Therapy 27(3), 201–208, quiz 208. 10.1016/j.jht.2013.11.002 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

